
Describe the structure of the multipolar neuron.
Answer
577.5k+ views
Hint: Multipolar neuron is a functional unit of nervous tissue.
Multipolar neurons are the types of neurons found in the CNS (central nervous system). They together form the autonomic ganglia.
Complete answer:
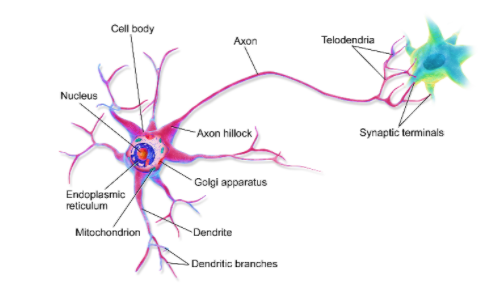
Multipolar neurons consist of the majority of neurons in the central nervous system. They include motor neurons and interneurons or relaying neurons, and can mostly be found in the cortex of the brain and the spinal cord. Tangentially, the multipolar neurons are found in the autonomic ganglia.
The multipolar neurons have a single axon and many dendrites, followed by dendritic branches.
It possesses a nerve cell body or the perikaryon, from which, (as stated above), one axonal extension along with a number of dendritic extensions originate. The axon is responsible for transferring the impulses from cell to cell whereas the dendrites function as zones to receive those impulses.
1) Cell body is the centrally located nucleus, which is observed in the body of these nerve cells. It is bright, euchromatic, and the nucleolus stands out about its size and degree of coloration. In the cytoplasm, which is stained basophilically, it can be observed that the groupings are intensely stained by the base dyes. These groupings are known as the Nissl bodies or the Nissl material.
2) Number of dendritic branches originate from the cell body. On these dendritic branches, there are numerous discharges that are known as dendritic thorns.
3) The axonal extension (originating from the perikaryon) may possibly be externally encased by the myelin sheath. This myelin sheath never spreads continuously along the axons, but in certain places. This means that it is discontinuous.
4) At times, at these gaps, axons may be separated crosswise, at right angles (90 degrees) by branches labelled as collateral. Each of the branches can come in contact with the dendrite or the cell body of the other neuron as well as of the same neuron.
Note:
Neurofilaments are types of the intermediate filaments, found solely in the nerve cells. Microtubules, actin filaments and neurofilaments are present in the perikaryon.
Multipolar neurons are the types of neurons found in the CNS (central nervous system). They together form the autonomic ganglia.
Complete answer:

Multipolar neurons consist of the majority of neurons in the central nervous system. They include motor neurons and interneurons or relaying neurons, and can mostly be found in the cortex of the brain and the spinal cord. Tangentially, the multipolar neurons are found in the autonomic ganglia.
The multipolar neurons have a single axon and many dendrites, followed by dendritic branches.
It possesses a nerve cell body or the perikaryon, from which, (as stated above), one axonal extension along with a number of dendritic extensions originate. The axon is responsible for transferring the impulses from cell to cell whereas the dendrites function as zones to receive those impulses.
1) Cell body is the centrally located nucleus, which is observed in the body of these nerve cells. It is bright, euchromatic, and the nucleolus stands out about its size and degree of coloration. In the cytoplasm, which is stained basophilically, it can be observed that the groupings are intensely stained by the base dyes. These groupings are known as the Nissl bodies or the Nissl material.
2) Number of dendritic branches originate from the cell body. On these dendritic branches, there are numerous discharges that are known as dendritic thorns.
3) The axonal extension (originating from the perikaryon) may possibly be externally encased by the myelin sheath. This myelin sheath never spreads continuously along the axons, but in certain places. This means that it is discontinuous.
4) At times, at these gaps, axons may be separated crosswise, at right angles (90 degrees) by branches labelled as collateral. Each of the branches can come in contact with the dendrite or the cell body of the other neuron as well as of the same neuron.
Note:
Neurofilaments are types of the intermediate filaments, found solely in the nerve cells. Microtubules, actin filaments and neurofilaments are present in the perikaryon.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




