
Describe the structure of the following with the help of labelled diagrams.
(i) Nucleus
(ii) Centrosome
Answer
568.5k+ views
Hint:Cell is usually defined as the basic structural and also functional unit of life. The cell is a basic structure that makes a living body and contains many organelles. Nucleus is a well-defined organelle that is present only in Eukaryotic cells.
Complete answer:
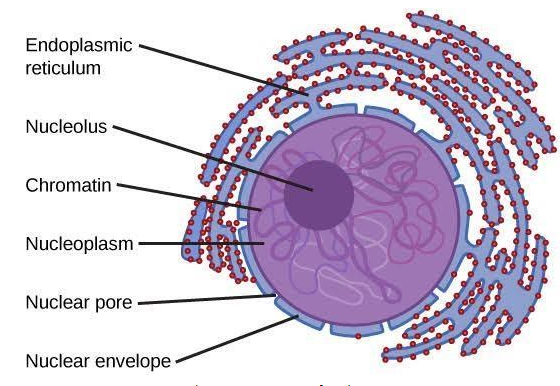
Nucleus
-Nucleus shows a membrane-bound organelle containing the hereditary information responsible for controlling both the growth and reproduction cycle of the cell.
-A nucleus is composed of a nuclear membrane, chromosomes, nucleoplasm, and nucleolus.
i) Nuclear Membrane: This is defined as a double membrane structure enclosing nuclear contents. The outer membrane layer gets connected with the endoplasmic reticulum; while the nuclear envelope forms a lipid bilayer compromising phospholipids.
ii) Nucleoplasm: The gelatinous substance that is present and enclosed within the nuclear envelope represents the nucleoplasm.
iii) Nucleolus: The nucleolus content of the nucleus is defined as dense and a membrane devoid structure consisting of RNA and proteins.
Centrosome
>Centrosome is defined as an organelle that acts as a microtubule-organizing centre of animal cells, and also a regulator of cell-cycle progression. The centrosome is thought to have evolved only within the metazoan lineage of eukaryotic cells. Fungi and plants do not possess centrosomes and thus use structures.
>Centrosomes are made up of two centrioles arranged at right-angles to each other. Each centriole is predicated on a nine-triplet microtubule that gets arranged in a cartwheel structure containing centrin, cenexin, and tektin.
Centrosomes' functions
i) It leads to Organizing changes to the form of the cytomembrane that allows the membrane to "pinch" in two during cellular division.
ii) It ensures that chromosomes are properly distributed to daughter cells by creating and shortening mitotic spindle fibres.

Note:Centrosome mainly occurred within cytoplasm near the nucleus. It is composed of two centrioles oriented at right angles, embedded during a mass of amorphous material containing proteins. It's duplicated during the S phase of the cell cycle.
Complete answer:
Nucleus
-Nucleus shows a membrane-bound organelle containing the hereditary information responsible for controlling both the growth and reproduction cycle of the cell.
-A nucleus is composed of a nuclear membrane, chromosomes, nucleoplasm, and nucleolus.
i) Nuclear Membrane: This is defined as a double membrane structure enclosing nuclear contents. The outer membrane layer gets connected with the endoplasmic reticulum; while the nuclear envelope forms a lipid bilayer compromising phospholipids.
ii) Nucleoplasm: The gelatinous substance that is present and enclosed within the nuclear envelope represents the nucleoplasm.
iii) Nucleolus: The nucleolus content of the nucleus is defined as dense and a membrane devoid structure consisting of RNA and proteins.

Centrosome
>Centrosome is defined as an organelle that acts as a microtubule-organizing centre of animal cells, and also a regulator of cell-cycle progression. The centrosome is thought to have evolved only within the metazoan lineage of eukaryotic cells. Fungi and plants do not possess centrosomes and thus use structures.
>Centrosomes are made up of two centrioles arranged at right-angles to each other. Each centriole is predicated on a nine-triplet microtubule that gets arranged in a cartwheel structure containing centrin, cenexin, and tektin.
Centrosomes' functions
i) It leads to Organizing changes to the form of the cytomembrane that allows the membrane to "pinch" in two during cellular division.
ii) It ensures that chromosomes are properly distributed to daughter cells by creating and shortening mitotic spindle fibres.

Note:Centrosome mainly occurred within cytoplasm near the nucleus. It is composed of two centrioles oriented at right angles, embedded during a mass of amorphous material containing proteins. It's duplicated during the S phase of the cell cycle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




