
Describe the structure of HIV with diagram
Answer
571.8k+ views
Hint: Human immunodeficiency virus or HIV is a virus that attacks the immune system of the body. If HIV is left untreated, it can lead to AIDS or acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. One can get HIV from contact with infected blood, vaginal fluids or semen.
Complete answer:
HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) has a spherical shape. It is composed of 15 types of viral proteins, two strands of RNA, and a few proteins from the last host cell it infected, all surrounded by a lipid bilayer membrane. This protein envelope has several spikes of the glycoprotein. The outer part of glycoprotein is called as gp120 and it is attached to the gp41 which is the inner part of the glycoprotein. The envelope of HIV also contains other proteins including some Human Leucocyte Antigen or HLA antigens. It has RNA binding protein called tat which is essential for replication. Two helices of RNA molecules in folded form are present in the genome of HIV. The enzymes reverse transcriptase, which is responsible for the conversion of the RNA to form the DNA. There is another enzyme called integrase, it helps the viral genome to incorporate in the host cell.
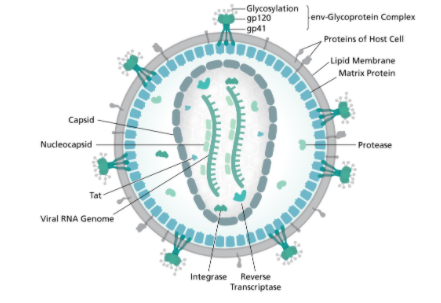
Together, these molecules allow the HIV to infect cells of a body’s immune system and new copies of the virus are created. Each molecule in the virus plays a major role in this process, from the first steps of viral attachment to the final process of budding.
Note: The researches on the structural biology of HIV have revealed the atomic details of its proteins. These structures are available in the Protein Data Bank (PDB) archive. Using this data, new treatments for HIV infection are designed, including effective drug regimens that reduce the growth of the virus. The structures provide us a hope for development of vaccine against HIV.
Complete answer:
HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) has a spherical shape. It is composed of 15 types of viral proteins, two strands of RNA, and a few proteins from the last host cell it infected, all surrounded by a lipid bilayer membrane. This protein envelope has several spikes of the glycoprotein. The outer part of glycoprotein is called as gp120 and it is attached to the gp41 which is the inner part of the glycoprotein. The envelope of HIV also contains other proteins including some Human Leucocyte Antigen or HLA antigens. It has RNA binding protein called tat which is essential for replication. Two helices of RNA molecules in folded form are present in the genome of HIV. The enzymes reverse transcriptase, which is responsible for the conversion of the RNA to form the DNA. There is another enzyme called integrase, it helps the viral genome to incorporate in the host cell.

Together, these molecules allow the HIV to infect cells of a body’s immune system and new copies of the virus are created. Each molecule in the virus plays a major role in this process, from the first steps of viral attachment to the final process of budding.
Note: The researches on the structural biology of HIV have revealed the atomic details of its proteins. These structures are available in the Protein Data Bank (PDB) archive. Using this data, new treatments for HIV infection are designed, including effective drug regimens that reduce the growth of the virus. The structures provide us a hope for development of vaccine against HIV.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




