
Describe the structure of an antibody.
Answer
585k+ views
Hint: Antibodies are unique, Y-shaped proteins that form a lock- and- key structure with the antigens or the pathogens that enter the body. The pathogens can be viruses, bacteria, fungi, or other parasitic worms.
Complete step by step answer:
Antibodies are 'Y' shaped pretentious structures, which are made up of four polypeptide chains. Two heavy polypeptide chains and two light chains constitute the antibody and help in performing various functions. Different functions of antibodies are done by different parts, such as the binding with antigen is done by Fab fragment and the other part is the Fc region.
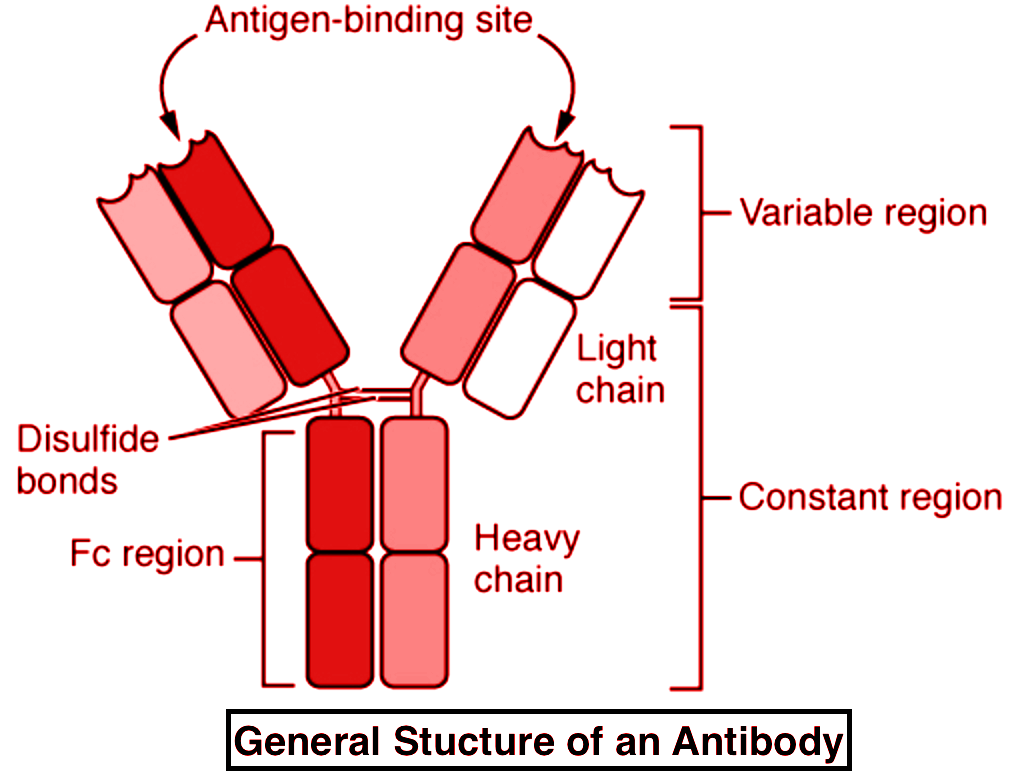
- Fab fragment(fragment antigen- binding) is the area of an antibody that binds with the antigens. Fab fragments contain one constant region and a variable region consisting of the heavy chain and the light chain. These regions also construct the paratope which is the site where antigen binds preciously.
- Fc region (fragment crystallizable region) is the tail portion of the antibody that comes in contact with the surface receptors of cells known as the Fc receptors along with several complement system proteins. Antibodies activate the immune system using these features. N-glycosylation sites which are highly conserved regions, present in the Fc regions.
Note:
- Depending on the type of the heavy chain present, they are divided into five immunoglobulin classes, which are Immunoglobulin G (IgG), Immunoglobulin M (IgM), Immunoglobulin A (IgA), Immunoglobulin E (IgE), and Immunoglobulin D(IgD). They are commonly found in the blood serum.
- Immunoglobulin G antibodies have a molecular weight of 150 kDa and constituted by chains of the peptide. They are globular proteins with two similar heavy chains (gamma) of molecular weight 50 kDa and light chains of molecular weight 25 kDa.
- Immunoglobulin E antibodies are only present in mammals, produced by the plasma cells.
Immunoglobulin E is known for binding with mast cells and basophils as an immunogenic response.
Complete step by step answer:
Antibodies are 'Y' shaped pretentious structures, which are made up of four polypeptide chains. Two heavy polypeptide chains and two light chains constitute the antibody and help in performing various functions. Different functions of antibodies are done by different parts, such as the binding with antigen is done by Fab fragment and the other part is the Fc region.

- Fab fragment(fragment antigen- binding) is the area of an antibody that binds with the antigens. Fab fragments contain one constant region and a variable region consisting of the heavy chain and the light chain. These regions also construct the paratope which is the site where antigen binds preciously.
- Fc region (fragment crystallizable region) is the tail portion of the antibody that comes in contact with the surface receptors of cells known as the Fc receptors along with several complement system proteins. Antibodies activate the immune system using these features. N-glycosylation sites which are highly conserved regions, present in the Fc regions.
Note:
- Depending on the type of the heavy chain present, they are divided into five immunoglobulin classes, which are Immunoglobulin G (IgG), Immunoglobulin M (IgM), Immunoglobulin A (IgA), Immunoglobulin E (IgE), and Immunoglobulin D(IgD). They are commonly found in the blood serum.
- Immunoglobulin G antibodies have a molecular weight of 150 kDa and constituted by chains of the peptide. They are globular proteins with two similar heavy chains (gamma) of molecular weight 50 kDa and light chains of molecular weight 25 kDa.
- Immunoglobulin E antibodies are only present in mammals, produced by the plasma cells.
Immunoglobulin E is known for binding with mast cells and basophils as an immunogenic response.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




