
Describe the structure of a flower.
Answer
564.9k+ views
Hint: Plants bearing flowers are known as angiosperms. The flower is the reproductive structure of plants. The typical flower consists of the vegetative part which includes petals and calyx and reproductive part includes stamen and pistil.
Complete answer: The flower is considered to be a modified shoot. A typical flower consists of 4 main parts: calyx, corolla, androecium and gynoecium.
a) Calyx: It is the outermost whorl of the flower. A single unit of the calyx is called as sepals i.e. many sepals together form the calyx. Sepals are green with a slightly leafy structure. The function of the calyx is protection in inner floral whorls when in bud condition.
b) Corolla: Flowers are the beautiful and attractive cause of petals. Many petals unite to form a corolla i.e. a single unit of the corolla is called petal. Anthocyanin pigment determines the colour of petals. The main function of the petal is to help in pollination by attracting insects. Bright colours attract the insect.
c) Androecium: Male reproductive whorl of the flower is called androecium. A single unit of androecium is known as the stamen. A Stamen is made up of anther, connective and filament. The anther is the fertile part that produces microspore or pollen grains. Process of formation of microspore is called microsporogenesis.
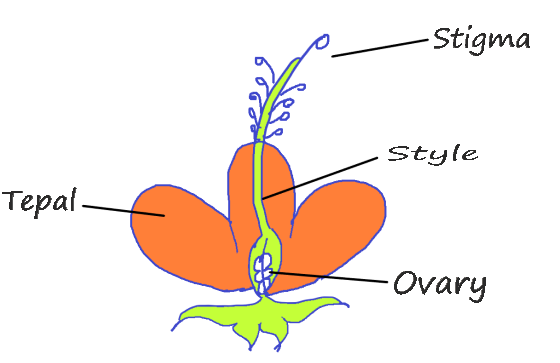
d) Gynoecium: Gynoecium or carpel is the female reproductive part of the flower. The gynoecium is sometimes referred to as pistil. It consists of three parts namely stigma, style and ovary. The ovary produces ovules or eggs. The ovary is the basal swollen portion of the carpel. Ovules are also called megasporangia.
Note: Calyx and corolla are accessory whorls of the flower. Stamen and carpel are necessary whorls or are essential whorls of the flower. Ovary matures into fruit and ovules mature into seeds.
Complete answer: The flower is considered to be a modified shoot. A typical flower consists of 4 main parts: calyx, corolla, androecium and gynoecium.
a) Calyx: It is the outermost whorl of the flower. A single unit of the calyx is called as sepals i.e. many sepals together form the calyx. Sepals are green with a slightly leafy structure. The function of the calyx is protection in inner floral whorls when in bud condition.
b) Corolla: Flowers are the beautiful and attractive cause of petals. Many petals unite to form a corolla i.e. a single unit of the corolla is called petal. Anthocyanin pigment determines the colour of petals. The main function of the petal is to help in pollination by attracting insects. Bright colours attract the insect.

c) Androecium: Male reproductive whorl of the flower is called androecium. A single unit of androecium is known as the stamen. A Stamen is made up of anther, connective and filament. The anther is the fertile part that produces microspore or pollen grains. Process of formation of microspore is called microsporogenesis.
d) Gynoecium: Gynoecium or carpel is the female reproductive part of the flower. The gynoecium is sometimes referred to as pistil. It consists of three parts namely stigma, style and ovary. The ovary produces ovules or eggs. The ovary is the basal swollen portion of the carpel. Ovules are also called megasporangia.
Note: Calyx and corolla are accessory whorls of the flower. Stamen and carpel are necessary whorls or are essential whorls of the flower. Ovary matures into fruit and ovules mature into seeds.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




