
Describe the structure and function of peroxisomes.
Answer
590.7k+ views
Hint: Peroxisome is a membrane bound organelle present in a eukaryotic organism. Its main function is oxidation of biomolecules.
Complete Answer:
Peroxisomes are found in the cytoplasm of all eukaryotic cells. It was formerly known as microbodies. They play an important role in the oxidation of long chain fatty acids.
The oxidation reaction produces hydrogen peroxide on which is the name peroxisome based on.
Structure: Peroxisomes are spherical bodies found in both plants and animals. It is found in proximity with endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria and chloroplast. They are variable in size and shape according to the cell. It consists of a single membrane which is lipoproteins in nature. The membrane encloses granular matrix. The matrix contains crystal which contain enzymes like catalase, oxidases etc.
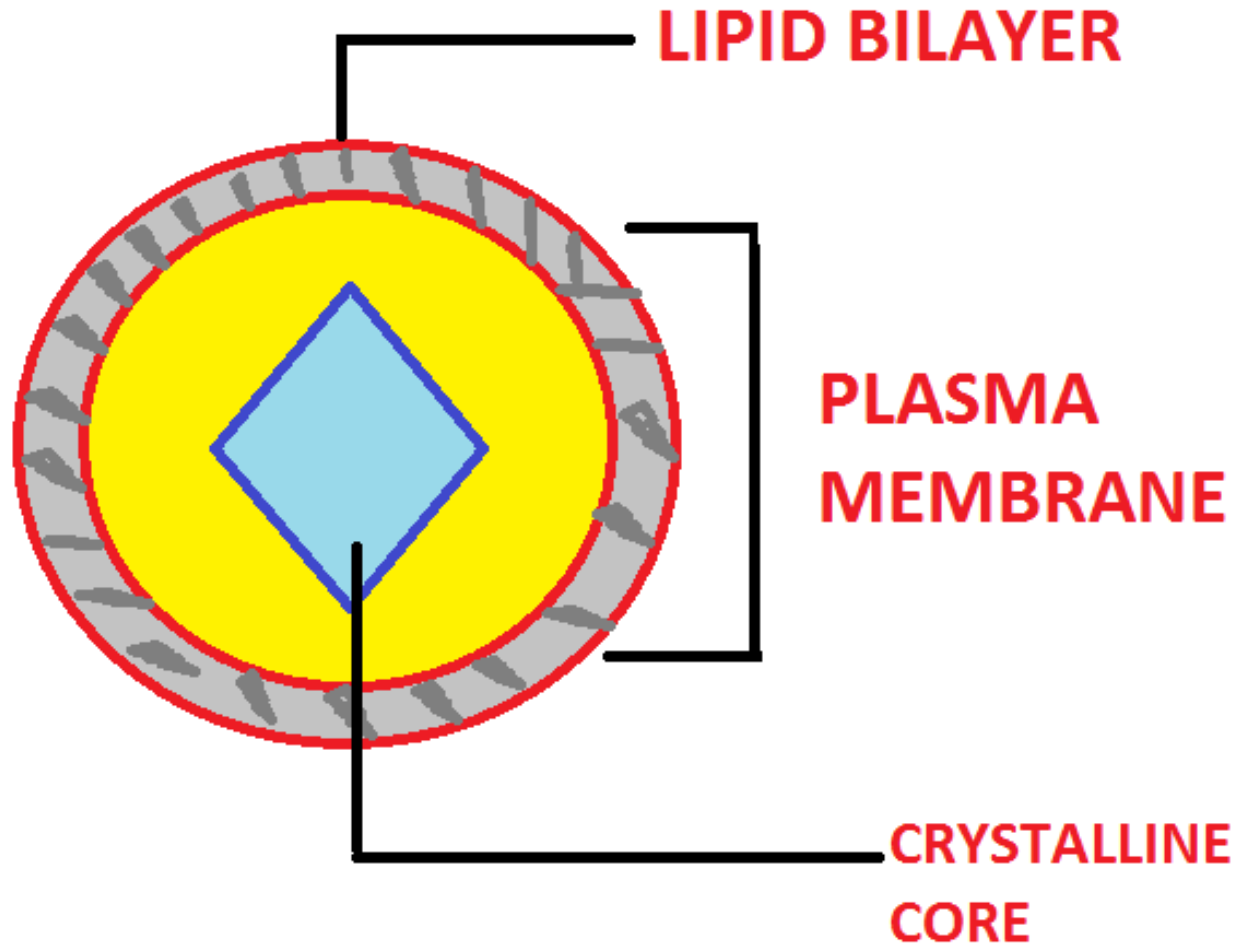
Fig: Structure of peroxisomes
Function:
- It involves oxidation of biomolecules by production of hydrogen peroxide. The peroxide is toxic for the cells. Peroxisomes have certain enzymes called the catalase which convert hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen and thus neutralises toxicity.
- They synthesise plasmalogens which is a membrane lipid.
- In plants, it helps in recycling of carbon from phosphoglycolate during photorespiration.
Some peroxisomes present in the plants are known as glycosomes. They oxidise fatty acids to carbohydrates.
Additional Information:
Bioluminescence in fireflies is due the enzyme luciferase which is present in the peroxisomes.
Note: Peroxisomes are present eukaryotic cells. It is found free floating in the cytoplasm. It is responsible for the oxidation of specific complex fatty acid, lipids etc.
Complete Answer:
Peroxisomes are found in the cytoplasm of all eukaryotic cells. It was formerly known as microbodies. They play an important role in the oxidation of long chain fatty acids.
The oxidation reaction produces hydrogen peroxide on which is the name peroxisome based on.
Structure: Peroxisomes are spherical bodies found in both plants and animals. It is found in proximity with endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria and chloroplast. They are variable in size and shape according to the cell. It consists of a single membrane which is lipoproteins in nature. The membrane encloses granular matrix. The matrix contains crystal which contain enzymes like catalase, oxidases etc.

Fig: Structure of peroxisomes
Function:
- It involves oxidation of biomolecules by production of hydrogen peroxide. The peroxide is toxic for the cells. Peroxisomes have certain enzymes called the catalase which convert hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen and thus neutralises toxicity.
- They synthesise plasmalogens which is a membrane lipid.
- In plants, it helps in recycling of carbon from phosphoglycolate during photorespiration.
Some peroxisomes present in the plants are known as glycosomes. They oxidise fatty acids to carbohydrates.
Additional Information:
Bioluminescence in fireflies is due the enzyme luciferase which is present in the peroxisomes.
Note: Peroxisomes are present eukaryotic cells. It is found free floating in the cytoplasm. It is responsible for the oxidation of specific complex fatty acid, lipids etc.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




