
Describe the mechanism of Hatch and Slack pathway in $C_4$ plants?
Answer
547.8k+ views
Hint: HSK pathway is an important pathway for photosynthesis in \[C4\] plants. This pathway takes place in mesophyll cells which are present near the bundle sheath cells. Plants which are habituated in hot and dry climates adapt this type of pathway to save water loss. In this \[C4\] acid is broken to produce carbon dioxide and three carbon by-products.
Complete answer:
HSK pathway is adapted by the plants which belong to the tropical climate like sugarcane, sorghum. It occurs in the chloroplasts.
1)In this pathway, the primary acceptor of carbon dioxide is a three- carbon molecule called the phosphoenol pyruvate(PEP). This reaction converts ATP and Pi to AMP and PPi.
2)The fixation of carbon dioxide in \[C4\]plants is carried out by PEP carboxylase enzyme.
3)The PEP is converted to a 4-Carbon compound called the OxaloAcetic Acid in the mesophyll cells. This is not a stable product. It is converted into malic acid which is a 4-Carbon compound and is stable. It is transported to bundle sheath cells where it breaks into a 3-carbon compound and carbon dioxide.
5)The initial steps are carried out in the mesophyll cells whereas the cycle is completed in bundle sheath cells.
6)HSK pathway requires 30 ATP to synthesize one glucose molecule.
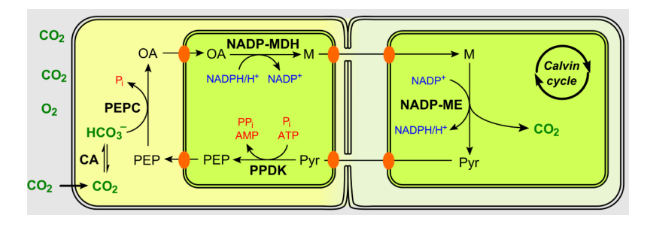
Note: HSK pathway takes place in the dark cycle of photosynthesis so as to prevent loss of water. It is an alternative to Calvin cycle. In the Calvin cycle the fixation of carbon dioxide takes place at one place whereas in HSK it happens at different places.
Complete answer:
HSK pathway is adapted by the plants which belong to the tropical climate like sugarcane, sorghum. It occurs in the chloroplasts.
1)In this pathway, the primary acceptor of carbon dioxide is a three- carbon molecule called the phosphoenol pyruvate(PEP). This reaction converts ATP and Pi to AMP and PPi.
2)The fixation of carbon dioxide in \[C4\]plants is carried out by PEP carboxylase enzyme.
3)The PEP is converted to a 4-Carbon compound called the OxaloAcetic Acid in the mesophyll cells. This is not a stable product. It is converted into malic acid which is a 4-Carbon compound and is stable. It is transported to bundle sheath cells where it breaks into a 3-carbon compound and carbon dioxide.
5)The initial steps are carried out in the mesophyll cells whereas the cycle is completed in bundle sheath cells.
6)HSK pathway requires 30 ATP to synthesize one glucose molecule.

Note: HSK pathway takes place in the dark cycle of photosynthesis so as to prevent loss of water. It is an alternative to Calvin cycle. In the Calvin cycle the fixation of carbon dioxide takes place at one place whereas in HSK it happens at different places.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




