
Describe the hierarchy of taxonomic categories.
Answer
594.9k+ views
Hint: Diverse kinds of organisms known to scientists are studied from the taxonomical aspect which led to the development of some definite categories. These definite categories or ranks in the classification of plants, animals, and other organisms are categorized into seven obligate categories.
Complete answer:
The process of classification of living organisms is not a single step process but it involves several steps i.e., a hierarchy of steps in which each step represents a rank or category. Since the category is a part of the overall taxonomic arrangement, it is called a Taxonomic Category.
The diverse kinds of organisms are classified into seven obligate categories in which all living organisms are classified in a descending sequence starting from kingdom to species or in ascending sequence starting from species to kingdom.
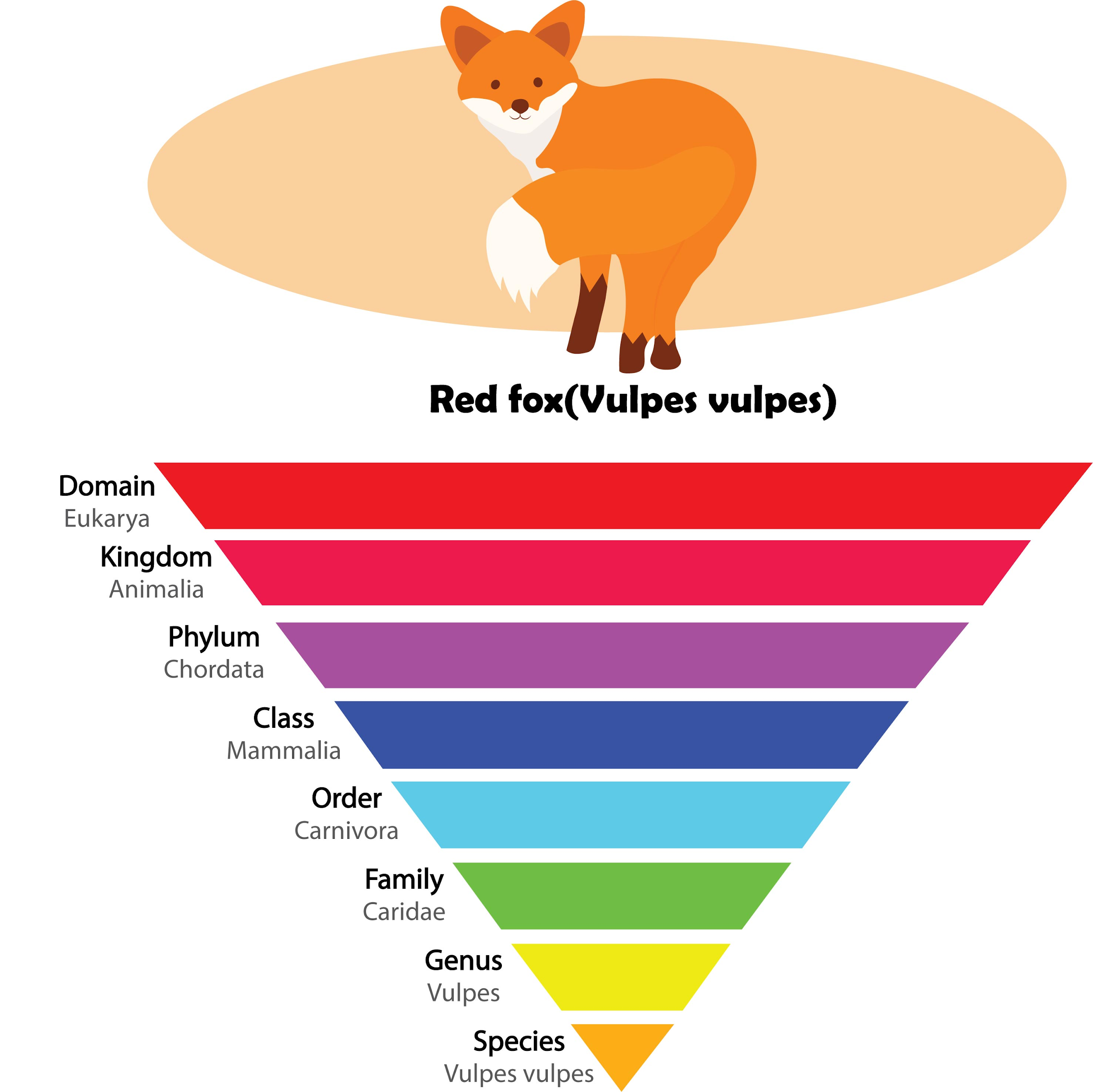
The hierarchical arrangement is as follows:
- Kingdom
-Phylum (for animals) or Division (for plants)
- Class
- Order
- Family
- Genus
- Species
Additional Information
-Kingdom: It is the highest category in the taxonomic hierarchy. It is a group of phyla or divisions, which have certain basic common characteristics.
-Phylum/ Division: It is a category higher than class. The term “Phylum” is used for animals whereas the term “division” is used for plants. Different classes, comprising animals like fishes, amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals together constitute the phylum Chordata in kingdom Animalia.
-Class: A class is a group of one or more related orders. Class is an assemblage of order with similar characteristics. For example, the order Rodentia, Primata, and Carnivora are all placed together under the class Mammalia as they have milk-producing glands and hair on their skin.
-Order: It is a group of families that means related families are kept in the same order. For example, the family Felidae and family Canidae are placed under the order Carnivora.
-Family: The next category after genus is family. It includes various groups of related genera, which share less number of similarities as compared to that of genus and species. For example, genus Felis of cats and the genus Panthera including lion, tiger and leopard are placed under the family Felidae.
-Genus: It is a group of related species, which has more characters in common in comparison to species of other genera. For example, genus Panthera involves species like leo, tigris, and pardus.
-Species: A species is a group of actually or potentially interbreeding populations that are reproductively isolated from other such groups. All the species represent the different organisms which are kept in the same genus due to some similarities in their morphological features.
Note:
- Taxonomists have also developed some sub-categories like sub-phylum or sub-division etc. in this hierarchy to make the arrangement more transparent and scientifically useful. - Each category is referred to as a unit of classification. It also represents rank in the taxonomic category. - A taxon represents any level of grouping of organisms based on certain easily observable common characteristics, - Specificity decreases when we go from species to kingdom i.e., the higher the category, the lesser will be the number of similar characteristics of the organisms belonging to that category.
You can use the following pneumonic to remember the hierarchy.
Kids – Kingdom Prefer – Phylum Cheese – Class Over – Order Fried – Family Green – Genus Spinach – Species
Complete answer:
The process of classification of living organisms is not a single step process but it involves several steps i.e., a hierarchy of steps in which each step represents a rank or category. Since the category is a part of the overall taxonomic arrangement, it is called a Taxonomic Category.
The diverse kinds of organisms are classified into seven obligate categories in which all living organisms are classified in a descending sequence starting from kingdom to species or in ascending sequence starting from species to kingdom.
The hierarchical arrangement is as follows:
- Kingdom
-Phylum (for animals) or Division (for plants)
- Class
- Order
- Family
- Genus
- Species
Additional Information
-Kingdom: It is the highest category in the taxonomic hierarchy. It is a group of phyla or divisions, which have certain basic common characteristics.
-Phylum/ Division: It is a category higher than class. The term “Phylum” is used for animals whereas the term “division” is used for plants. Different classes, comprising animals like fishes, amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals together constitute the phylum Chordata in kingdom Animalia.
-Class: A class is a group of one or more related orders. Class is an assemblage of order with similar characteristics. For example, the order Rodentia, Primata, and Carnivora are all placed together under the class Mammalia as they have milk-producing glands and hair on their skin.
-Order: It is a group of families that means related families are kept in the same order. For example, the family Felidae and family Canidae are placed under the order Carnivora.
-Family: The next category after genus is family. It includes various groups of related genera, which share less number of similarities as compared to that of genus and species. For example, genus Felis of cats and the genus Panthera including lion, tiger and leopard are placed under the family Felidae.
-Genus: It is a group of related species, which has more characters in common in comparison to species of other genera. For example, genus Panthera involves species like leo, tigris, and pardus.
-Species: A species is a group of actually or potentially interbreeding populations that are reproductively isolated from other such groups. All the species represent the different organisms which are kept in the same genus due to some similarities in their morphological features.
Note:
- Taxonomists have also developed some sub-categories like sub-phylum or sub-division etc. in this hierarchy to make the arrangement more transparent and scientifically useful. - Each category is referred to as a unit of classification. It also represents rank in the taxonomic category. - A taxon represents any level of grouping of organisms based on certain easily observable common characteristics, - Specificity decreases when we go from species to kingdom i.e., the higher the category, the lesser will be the number of similar characteristics of the organisms belonging to that category.
You can use the following pneumonic to remember the hierarchy.
Kids – Kingdom Prefer – Phylum Cheese – Class Over – Order Fried – Family Green – Genus Spinach – Species

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

A solution of a substance X is used for white washing class 11 chemistry CBSE




