
Describe symbiotic nitrogen fixation with the help of a diagram.
Answer
593.1k+ views
Hint: When the nitrogen-fixing bacteria live in symbiotic relationships with the host then it is called symbiotic nitrogen fixation. It is used by plants such as legumes for fixing atmospheric nitrogen gas to ammonia. It is established broadly in nature and has very low economic and environmental costs.
Complete answer:
The biological nitrogen fixation process that converts atmospheric nitrogen into the nitrogenous compounds of living organisms is called symbiotic nitrogen fixation. For example – Rhizobium, Frankia, etc. Most of the microorganisms partner themselves with host plants to fix nitrogen symbiotically. By the process of photosynthesis, plants provide sugars that are utilized by nitrogen-fixing microorganisms for producing energy that is necessary for nitrogen fixation.
The common example of symbiotic nitrogen fixation is Azolla’s symbiosis with a cyanobacterium Anabaena azollae. In this process, specialized cells are called heterocyst formed by the particular amount of nitrogen that is fixed by cyanobacteria. In wetlands of Southeast Asia, this type of symbiosis has been used for the last 1000 years as a biofertilizer.
The most crucial symbiotic relationship takes place between legumes and Rhizobium and Bradyrhizobium bacteria. This symbiotic association is common in the worldwide ecology. Some examples of legumes that are used in symbiotic nitrogen fixation are alfalfa, beans, clover, lupines, peanuts, etc.
In the symbiotic relationship, the supply of nitrogen by bacteria directly takes place in the legume and it indirectly provides nitrogen to the adjacent grass plants.
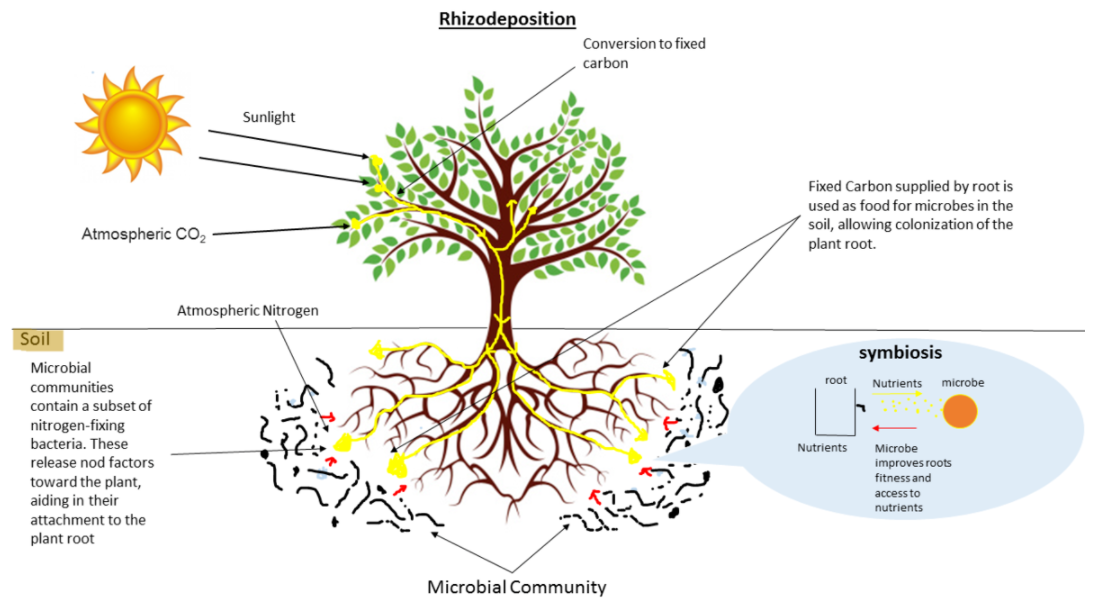
Note: Prokaryotes can fix nitrogen very easily and efficiently by the process of symbiotic nitrogen fixation. Thus, most plants are there that provide nutrients to one another by making a symbiotic relationship. In this way nutrient requirements of every plant complete. The plants will get the benefit and prevent them from getting dead.
Complete answer:
The biological nitrogen fixation process that converts atmospheric nitrogen into the nitrogenous compounds of living organisms is called symbiotic nitrogen fixation. For example – Rhizobium, Frankia, etc. Most of the microorganisms partner themselves with host plants to fix nitrogen symbiotically. By the process of photosynthesis, plants provide sugars that are utilized by nitrogen-fixing microorganisms for producing energy that is necessary for nitrogen fixation.
The common example of symbiotic nitrogen fixation is Azolla’s symbiosis with a cyanobacterium Anabaena azollae. In this process, specialized cells are called heterocyst formed by the particular amount of nitrogen that is fixed by cyanobacteria. In wetlands of Southeast Asia, this type of symbiosis has been used for the last 1000 years as a biofertilizer.
The most crucial symbiotic relationship takes place between legumes and Rhizobium and Bradyrhizobium bacteria. This symbiotic association is common in the worldwide ecology. Some examples of legumes that are used in symbiotic nitrogen fixation are alfalfa, beans, clover, lupines, peanuts, etc.
In the symbiotic relationship, the supply of nitrogen by bacteria directly takes place in the legume and it indirectly provides nitrogen to the adjacent grass plants.

Note: Prokaryotes can fix nitrogen very easily and efficiently by the process of symbiotic nitrogen fixation. Thus, most plants are there that provide nutrients to one another by making a symbiotic relationship. In this way nutrient requirements of every plant complete. The plants will get the benefit and prevent them from getting dead.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




