
Describe different tropic movement in the plants with examples.
Answer
601.5k+ views
Hint: These are the biological phenomena that are indicating the growth or the turning movement of the organism or the par of an organism due to their surrounding.
Complete step-by-step answer:
When a plant shows some growth movement in response to a stimulus is known as tropism. Tropism is a direction, which is specific and depends on the direction of the stimulus.
Plants may either show a positive or negative movement as a response to a stimulus. If the movement is towards the direction, it is known as positive tropism, if the movement is away from the stimuli, it is known as negative stimuli.
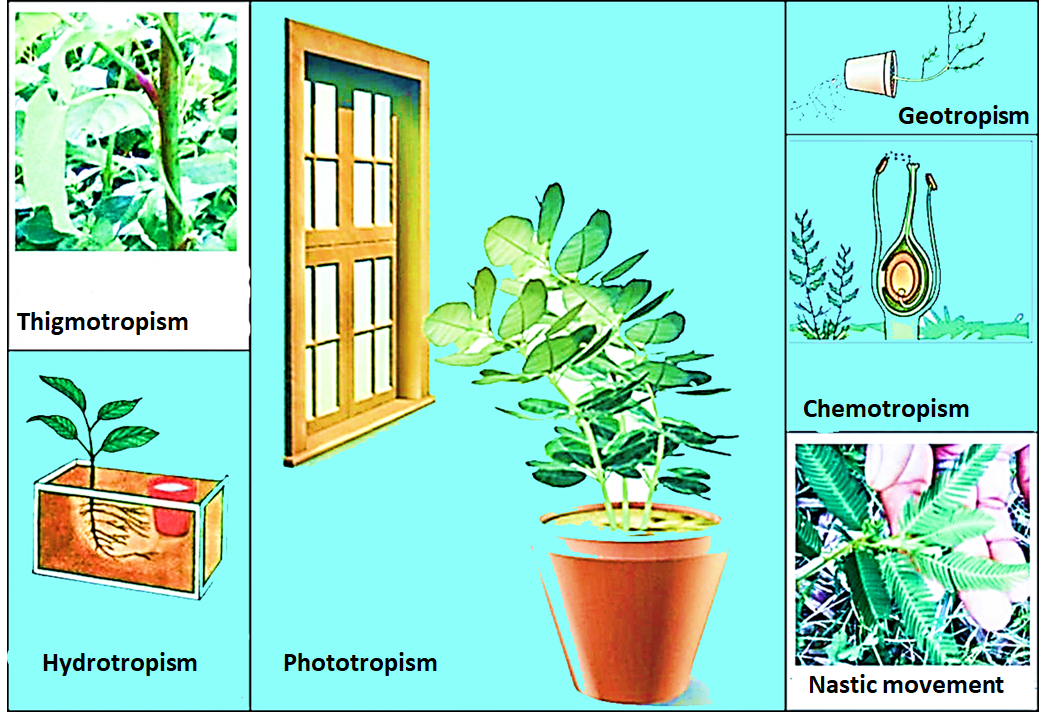
Different types of tropic movement in plants
Phototropism – the growth of plants towards or away from the light. This type of movement is in response to light. Generally, stems show positive phototropism while roots show negative phototropism.
Gravitropism – the movement and growth of plants are in response to gravity. Stems show negative geotropism while roots show positive geotropism.
Hydrotropism – the movement and growth of a plant in response to the water stimulus. Roots show positive hydrotropism as they grow and move towards the water.
Chemotropism – the movement of plants in response to certain chemicals. Few chemicals are responsible for the movement and growth of plant organs.
Thigmotropism – the growth and development of the plants in response to contact with a solid object. These types of movements are generally seen as tendrils and twiners.
Thermotropism – the growth and movement of a plant or it’s part in response to the changing atmospheric temperature.
Note: Charles Darwin and his son Francis in 1880 discovered that the phototrophic stimulus is detected at the tip of the plant. The term tropism was derived from the Greek word, meaning ‘a turning’. Tropism was first observed in 1927 by Cholodny and Went.
Complete step-by-step answer:
When a plant shows some growth movement in response to a stimulus is known as tropism. Tropism is a direction, which is specific and depends on the direction of the stimulus.
Plants may either show a positive or negative movement as a response to a stimulus. If the movement is towards the direction, it is known as positive tropism, if the movement is away from the stimuli, it is known as negative stimuli.
Different types of tropic movement in plants
Phototropism – the growth of plants towards or away from the light. This type of movement is in response to light. Generally, stems show positive phototropism while roots show negative phototropism.
Gravitropism – the movement and growth of plants are in response to gravity. Stems show negative geotropism while roots show positive geotropism.
Hydrotropism – the movement and growth of a plant in response to the water stimulus. Roots show positive hydrotropism as they grow and move towards the water.
Chemotropism – the movement of plants in response to certain chemicals. Few chemicals are responsible for the movement and growth of plant organs.
Thigmotropism – the growth and development of the plants in response to contact with a solid object. These types of movements are generally seen as tendrils and twiners.
Thermotropism – the growth and movement of a plant or it’s part in response to the changing atmospheric temperature.

Note: Charles Darwin and his son Francis in 1880 discovered that the phototrophic stimulus is detected at the tip of the plant. The term tropism was derived from the Greek word, meaning ‘a turning’. Tropism was first observed in 1927 by Cholodny and Went.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

A solution of a substance X is used for white washing class 11 chemistry CBSE




