
Describe an activity to show that the incident ray, the reflected ray, and the normal at the point of incidence lie in the same plane.
Answer
517.2k+ views
Hint: The main factor while choosing the activity is to prove that incident ray, reflected ray, and normal lie on the same plane. A clear understanding of the incident ray reflected ray and the properties of reflection will enable one to deduce an activity for this rule. When light is incident on a mirror or a reflective surface the light will bounce or reflect into the same medium.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Apparatus: Drawing board, Sheet of paper, laser light, plane mirror.
Procedure:
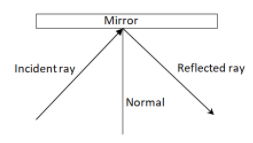
Place a sheet of paper on the drawing board. Place a plane mirror on the piece of paper and draw an outline of the mirror. Also, draw a normal to the mirror.
Now shine the laser light at an angle to the mirror such that it falls on the normal at the bottom of the mirror. If shined normal to the mirror, no incidence or reflected ray will be observed as the angle of incidence, in this case, is zero, thereby the angle of reflection is also zero.
When the laser light is incident on the mirror, it gets reflected at an angle to the normal.
We can easily observe that the incident ray, the reflected ray, and the normal at the point of incidence all lie in the same plane.
From this activity, it is observed that the normal, the line of incidence, and the reflected ray all lie on the same plane.
Note: This activity can also be used to determine that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. Care must be taken while handling laser light. Do not point the laser source to your eyes as it can cause permanent damage. In the case of reflection another imperative property is that the angle of incidence is always equal to the angle of reflection.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Apparatus: Drawing board, Sheet of paper, laser light, plane mirror.
Procedure:
Place a sheet of paper on the drawing board. Place a plane mirror on the piece of paper and draw an outline of the mirror. Also, draw a normal to the mirror.
Now shine the laser light at an angle to the mirror such that it falls on the normal at the bottom of the mirror. If shined normal to the mirror, no incidence or reflected ray will be observed as the angle of incidence, in this case, is zero, thereby the angle of reflection is also zero.
When the laser light is incident on the mirror, it gets reflected at an angle to the normal.
We can easily observe that the incident ray, the reflected ray, and the normal at the point of incidence all lie in the same plane.
From this activity, it is observed that the normal, the line of incidence, and the reflected ray all lie on the same plane.

Note: This activity can also be used to determine that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. Care must be taken while handling laser light. Do not point the laser source to your eyes as it can cause permanent damage. In the case of reflection another imperative property is that the angle of incidence is always equal to the angle of reflection.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

Full form of STD, ISD and PCO

Advantages and disadvantages of science

Right to vote is a AFundamental Right BFundamental class 8 social science CBSE

What are the 12 elements of nature class 8 chemistry CBSE




