
Derive $ R = 2f $ for a spherical mirror, where the symbols have their usual meaning.
Answer
512.4k+ views
Hint :First law of reflection states that the incident ray, reflected ray and normal, all lie in the same plane. Second law of reflection states that the angle of reflection is always equal to the angle of incidence. The angles are measured relative to the perpendicular to the surface at the point where the ray strikes the surface.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Let $ OA $ be the incident ray and $ CA $ be the line normal to the surface at the point $ A $ where the ray $ \left( {OA} \right) $ strikes the surface of a spherical mirror. Let $ f $ and $ R $ be the focal length and radius of curvature. Also let $ i $ and $ r $ be the angle of incidence and the angle of reflection. Then we can draw the figure as follows
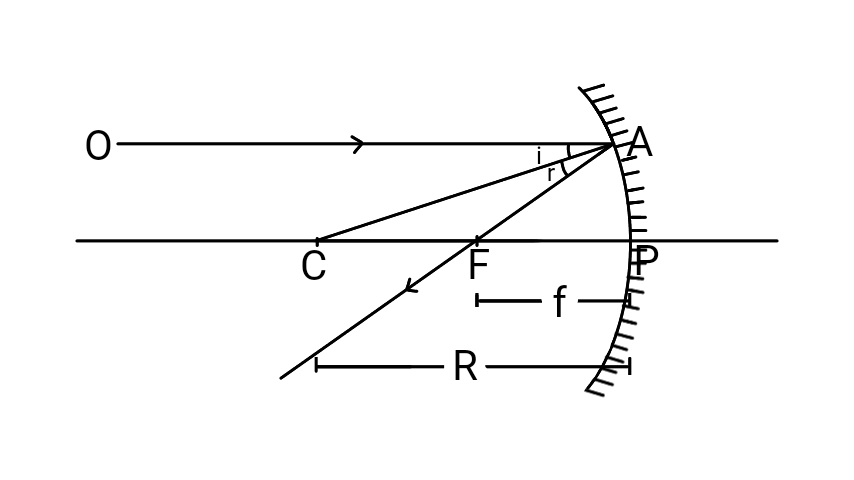
Hence $ FP = f $ and $ CP = R $ .
Also $ C $ is the centre of the circle and $ R $ is also the radius of the sphere.
According to second law of reflection
$ i = r $ ----(1)
Since $ OA $ is parallel to $ CP $ we get $ \left| \!{\underline {\,
{ACP} \,}} \right. = \left| \!{\underline {\,
{OAC} \,}} \right. = i $ ---(2)
From the equation (1), the equation (2) becomes
$ \left| \!{\underline {\,
{ACP} \,}} \right. = i = r = \left| \!{\underline {\,
{CAF} \,}} \right. $
Then $ \Delta ACF $ is an isosceles triangle. Therefore $ CF = FA $ ---(3)
For mirror of small aperture we get $ FA \approx FP $ ---(4)
From the equation (3) and (4), we get
$ CF = FP $ ---(5)
then $ CP = CF + FP = FP + FP = 2\;FP $
$ \Rightarrow R = 2f $ .
Hence the proof.
Note :
Myopia(near-sightedness) is corrected by using a Concave Lens of suitable power. Hypermetropia(farsightedness) is corrected by using a convex lens of suitable power. A spherical mirror is a mirror which has the shape of a piece cut out of a spherical surface. There are two types of spherical mirrors: concave, and convex.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Let $ OA $ be the incident ray and $ CA $ be the line normal to the surface at the point $ A $ where the ray $ \left( {OA} \right) $ strikes the surface of a spherical mirror. Let $ f $ and $ R $ be the focal length and radius of curvature. Also let $ i $ and $ r $ be the angle of incidence and the angle of reflection. Then we can draw the figure as follows

Hence $ FP = f $ and $ CP = R $ .
Also $ C $ is the centre of the circle and $ R $ is also the radius of the sphere.
According to second law of reflection
$ i = r $ ----(1)
Since $ OA $ is parallel to $ CP $ we get $ \left| \!{\underline {\,
{ACP} \,}} \right. = \left| \!{\underline {\,
{OAC} \,}} \right. = i $ ---(2)
From the equation (1), the equation (2) becomes
$ \left| \!{\underline {\,
{ACP} \,}} \right. = i = r = \left| \!{\underline {\,
{CAF} \,}} \right. $
Then $ \Delta ACF $ is an isosceles triangle. Therefore $ CF = FA $ ---(3)
For mirror of small aperture we get $ FA \approx FP $ ---(4)
From the equation (3) and (4), we get
$ CF = FP $ ---(5)
then $ CP = CF + FP = FP + FP = 2\;FP $
$ \Rightarrow R = 2f $ .
Hence the proof.
Note :
Myopia(near-sightedness) is corrected by using a Concave Lens of suitable power. Hypermetropia(farsightedness) is corrected by using a convex lens of suitable power. A spherical mirror is a mirror which has the shape of a piece cut out of a spherical surface. There are two types of spherical mirrors: concave, and convex.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




