
Deoxygenated blood is found in
A. Right ventricle
B. Pulmonary vein
C. Pulmonary artery
D. A and B only
E. A and C only
Answer
602.4k+ views
Hint: They carry the deoxygenated (blood from which oxygen is removed) blood from the heart to the lungs to take up the oxygen.
Complete answer
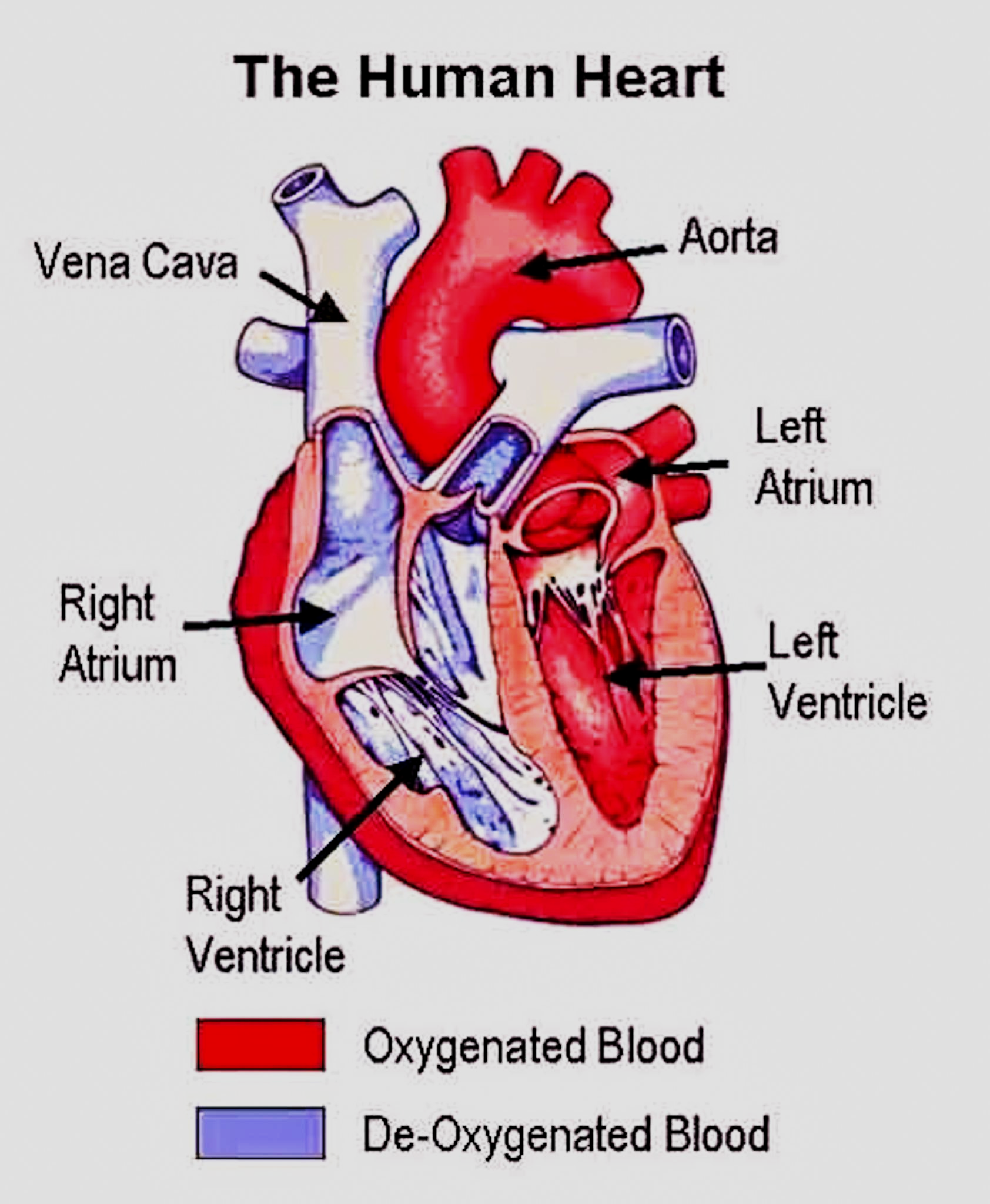
Deoxygenated blood is the blood that has lower oxygen content when compared to the blood leaving the lungs. The deoxygenated blood is also known as the venous blood. The deoxygenated blood is carried from the right ventricle of the heart to the lungs through the pulmonary artery.
Additional information
- In mammals, the heart is four-chambered, consisting of two ventricles (left and right) and two atria (left and right).
- The blood flows in a unidirectional way from the heart due to the presence of heart valves which prevent the backflow of the blood.
- The epicardium, myocardium, and endocardium are the three layers of which the heart is made up of.
- The heart is surrounded by a protective layer called the pericardium.
- The heart consists of two types of circulation: systemic circulation and pulmonary circulation.
- The right heart collects deoxygenated blood from the two large veins, superior and inferior vena cavae.
- This deoxygenated blood is carried from the heart to the lungs via the pulmonary artery.
- In the left heart, the oxygenated blood is returned from the lungs via pulmonary veins.
So, the correct answer is ‘A and C only’.
Note: In fishes, the heart is two-chambered, having an atrium and a ventricle while the reptiles have three-chambered heart, consisting of two atria and one partially divided ventricle except crocodile, which has a four-chambered heart. The amphibians also consist of a three-chambered heart while the birds have a four-chambered heart.
Complete answer
Deoxygenated blood is the blood that has lower oxygen content when compared to the blood leaving the lungs. The deoxygenated blood is also known as the venous blood. The deoxygenated blood is carried from the right ventricle of the heart to the lungs through the pulmonary artery.
Additional information
- In mammals, the heart is four-chambered, consisting of two ventricles (left and right) and two atria (left and right).
- The blood flows in a unidirectional way from the heart due to the presence of heart valves which prevent the backflow of the blood.
- The epicardium, myocardium, and endocardium are the three layers of which the heart is made up of.
- The heart is surrounded by a protective layer called the pericardium.
- The heart consists of two types of circulation: systemic circulation and pulmonary circulation.
- The right heart collects deoxygenated blood from the two large veins, superior and inferior vena cavae.
- This deoxygenated blood is carried from the heart to the lungs via the pulmonary artery.
- In the left heart, the oxygenated blood is returned from the lungs via pulmonary veins.
So, the correct answer is ‘A and C only’.

Note: In fishes, the heart is two-chambered, having an atrium and a ventricle while the reptiles have three-chambered heart, consisting of two atria and one partially divided ventricle except crocodile, which has a four-chambered heart. The amphibians also consist of a three-chambered heart while the birds have a four-chambered heart.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




