
Define vernalization and write its two advantages.
Answer
590.7k+ views
Hint:After Vernalization the plants have acquired the ability to flower, but they may require additional seasonal cues or weeks of growth before they will flower. This technique is very profitable for growing a two year crop in one year.
Complete answer:
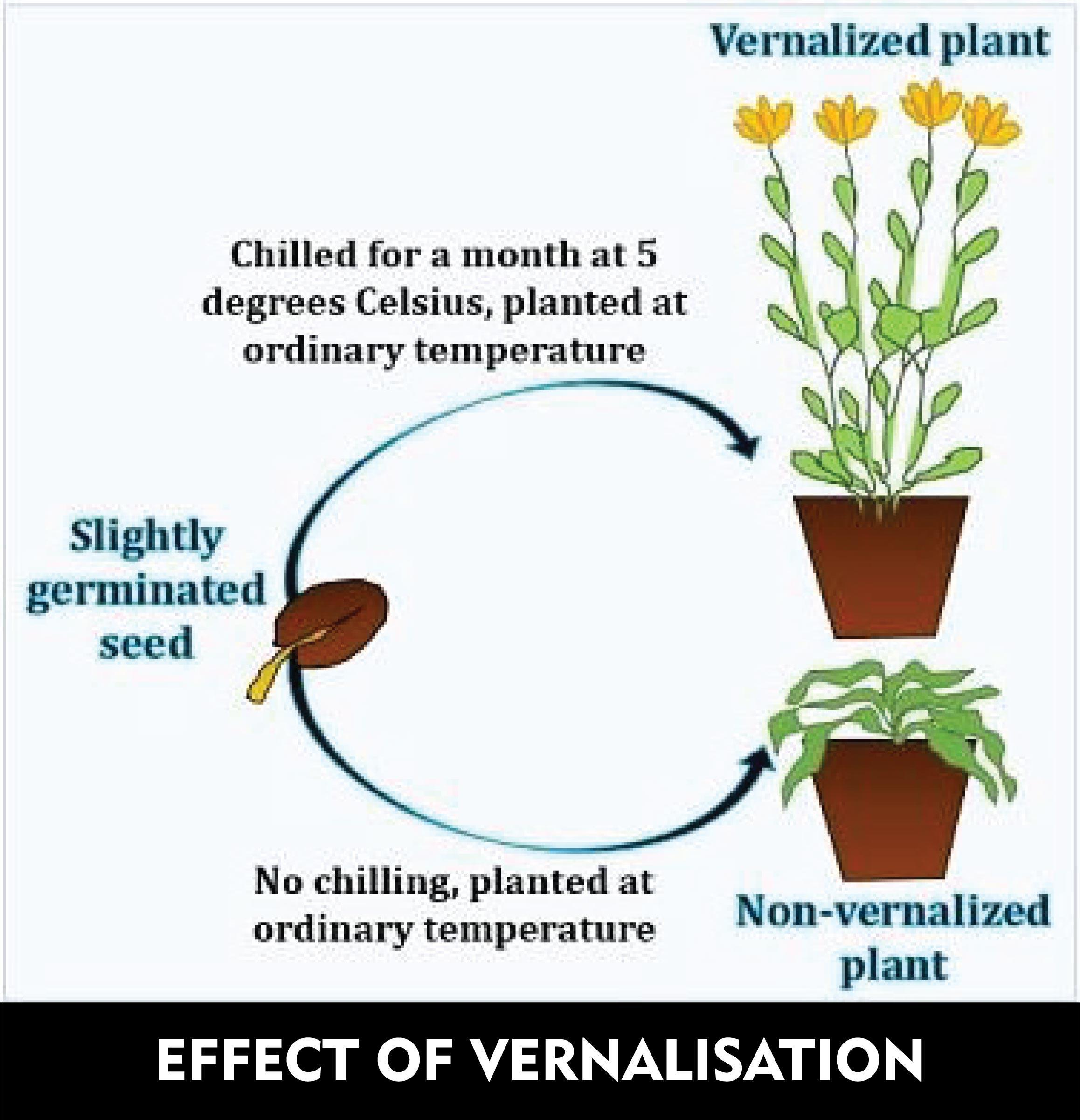
Vernalization is the artificial exposure of plants or seeds to low temperatures to stimulate flowering or to enhance seed production. By satisfying the cold requirement of many temperate zone (found in colder areas) plants, flowering can be induced to occur earlier than normal or in warm climates lacking the required seasonal chilling.
- Requirements for vernalization:
1. A low temperature between 2°C and 12°C with a 50- day treatment is required.
2. In the case of water- plants, the plants need proper hydration (moisture) to receive the stimulus from cold temperatures.
3. The seeds need to be moist before exposure to low temperature because it does not work on dry seeds.
4. An aerobic environment is needed for vernalization.
5. Essential nutrients are also required.
- Site of vernalization:
The site where cold treatment is given could be the apical meristem in the shoots, the germinating seed, or the vegetative parts such as leaves. It can be different in different plants.
The two advantages of vernalization are:
1. It increases the plant yield.
2. It provides resistance to cold and diseases to the plant.
Additional Information:
- Vernalization allows the plants to grow in regions where they normally do not grow.
- Vernalization enables biennial plants to behave like annual plants.
Note: Vernalization is both, qualitative or quantitative dependence of the plants on exposure to a low temperature to flowers. Devernalization (reversing vernalization) can be brought about by exposing previously vernalized plants or seeds to high temperatures. It causes a reversion to the original non- flowering condition.
Complete answer:
Vernalization is the artificial exposure of plants or seeds to low temperatures to stimulate flowering or to enhance seed production. By satisfying the cold requirement of many temperate zone (found in colder areas) plants, flowering can be induced to occur earlier than normal or in warm climates lacking the required seasonal chilling.
- Requirements for vernalization:
1. A low temperature between 2°C and 12°C with a 50- day treatment is required.
2. In the case of water- plants, the plants need proper hydration (moisture) to receive the stimulus from cold temperatures.
3. The seeds need to be moist before exposure to low temperature because it does not work on dry seeds.
4. An aerobic environment is needed for vernalization.
5. Essential nutrients are also required.
- Site of vernalization:
The site where cold treatment is given could be the apical meristem in the shoots, the germinating seed, or the vegetative parts such as leaves. It can be different in different plants.
The two advantages of vernalization are:
1. It increases the plant yield.
2. It provides resistance to cold and diseases to the plant.

Additional Information:
- Vernalization allows the plants to grow in regions where they normally do not grow.
- Vernalization enables biennial plants to behave like annual plants.
Note: Vernalization is both, qualitative or quantitative dependence of the plants on exposure to a low temperature to flowers. Devernalization (reversing vernalization) can be brought about by exposing previously vernalized plants or seeds to high temperatures. It causes a reversion to the original non- flowering condition.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




