
Define the terms: identification, nomenclature, systematics, taxonomy.
Answer
596.1k+ views
Hint: Classification determines methods for organizing the range of life on Earth. Since life first appeared on Earth 3.5 billion years ago, many new sorts of organisms have evolved. Many of those organisms became extinct, while some have developed into this flora and fauna of the planet.
Complete answer:
Identification: Identification is "the practical side of taxonomy, the method of determining that a specific (organism) belongs to a recognized taxon." Or the method of nomenclature or naming is merely possible when the organism is described correctly and that we are known to what organism the name is attached to.
Nomenclature: The term nomenclature means the scientific naming of organisms consistent with a long time system. The naming of plants on a scientific basis is named botanical or plant nomenclature. In earlier days common names were in use which generally changes with different languages. After observing the problem with different common names one common internationally accepted name was used for a species, scientific names (Technical names) are introduced in sort of polynomial, binomial and trinomial systems of nomenclature.
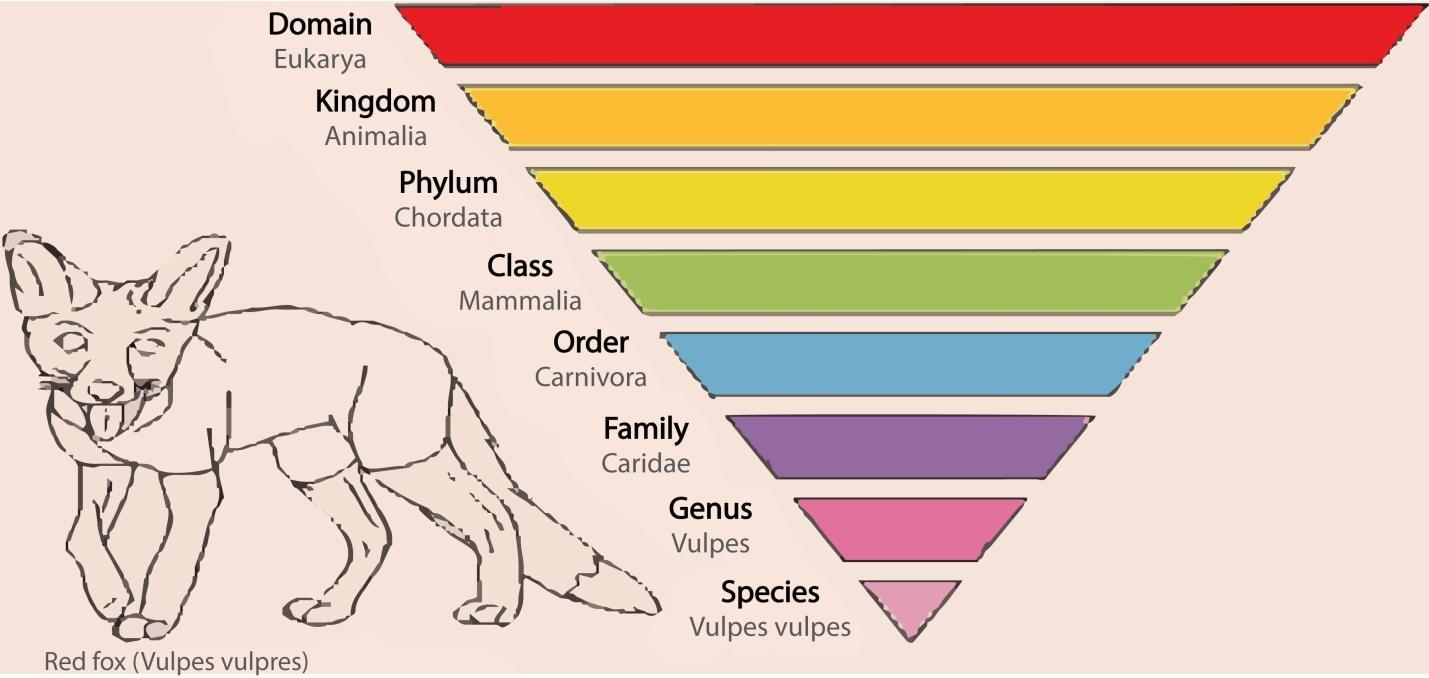
Systematics: It deals with the classification of organisms that supported their diversities and relationships among them. The term was proposed by Linnaeus who wrote 'Systema Naturae'. Systematics may be a discipline of biology that explicitly examines the natural variation and relationships of organisms, and which incorporates the sector of taxonomy. It also deals with the relationships of various groups of organisms, reflecting evolutionary relationships.
Taxonomy: Taxonomy is that field of biology which deals with the nomenclature, identification, and classification of organisms. There are over a million known species on Earth and doubtless, several million more not yet identified. Taxonomists are liable for identifying, naming, and classifying these different species.
Types of taxonomy:
Morphotaxonomy, cytotaxonomy, chemotaxonomy, karyotaxonomy, numerical taxonomy
Note: The organisms are classified due to the following reasons:
- Classification makes identification and the study of a wide variety of organisms simpler.
- It reveals interrelationships among different groups of organisms to perform evolutionary studies.
- It provides information about the organisms and fossils of other localities too.
Complete answer:
Identification: Identification is "the practical side of taxonomy, the method of determining that a specific (organism) belongs to a recognized taxon." Or the method of nomenclature or naming is merely possible when the organism is described correctly and that we are known to what organism the name is attached to.
Nomenclature: The term nomenclature means the scientific naming of organisms consistent with a long time system. The naming of plants on a scientific basis is named botanical or plant nomenclature. In earlier days common names were in use which generally changes with different languages. After observing the problem with different common names one common internationally accepted name was used for a species, scientific names (Technical names) are introduced in sort of polynomial, binomial and trinomial systems of nomenclature.

Systematics: It deals with the classification of organisms that supported their diversities and relationships among them. The term was proposed by Linnaeus who wrote 'Systema Naturae'. Systematics may be a discipline of biology that explicitly examines the natural variation and relationships of organisms, and which incorporates the sector of taxonomy. It also deals with the relationships of various groups of organisms, reflecting evolutionary relationships.
Taxonomy: Taxonomy is that field of biology which deals with the nomenclature, identification, and classification of organisms. There are over a million known species on Earth and doubtless, several million more not yet identified. Taxonomists are liable for identifying, naming, and classifying these different species.
Types of taxonomy:
Morphotaxonomy, cytotaxonomy, chemotaxonomy, karyotaxonomy, numerical taxonomy
Note: The organisms are classified due to the following reasons:
- Classification makes identification and the study of a wide variety of organisms simpler.
- It reveals interrelationships among different groups of organisms to perform evolutionary studies.
- It provides information about the organisms and fossils of other localities too.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

Actinoid contraction is more than lanthanoid contraction class 11 chemistry CBSE

The transition element that has lowest enthalpy of class 11 chemistry CBSE

Can anyone list 10 advantages and disadvantages of friction

State the laws of reflection of light




