
Define the term hyperconjugation.
Answer
570.9k+ views
Hint: We know that in organic chemistry, electron displacement plays a vital role for chemical and physical properties of the molecule. Inductive effect, electromeric effect and hyperconjugation are important electron displacement effects in organic molecules. Some of these effects show permanent and temporary effects in molecules.
Complete step by step answer:
We have to remember that in organic molecules most of them are formed by covalent bonds. These covalent bond are classified as two types
There are
1.Sigma bond
2.Pi bond
We need to know that the mutual sharing two electrons in between two atoms, overlapping \[p\]orbitals to form sigma $\left( \sigma \right)$ and pi $\left( \pi \right)$ bond. Sigma bond means overlapping in head to head overlap in orbitals. Pi bond means overlapping occurs side wise in orbitals.
We need to know that hyperconjugation is one of the displacements of the electron in organic chemistry. The delocalisation of the sigma electron in bond is known as hyperconjugation. This hyperconjugation gives the special stability of the molecule, because one sigma electron delocalisation to form bonding or antibonding pi bond in conjugated carbon atom. This hyperconjugation is also called “no bond resonance”.
For example, propene having three canonical forms due to hyperconjugation. An electron in $C - H$ sigma bond is changed to form a pi bond ($C = C$) in conjugated carbon atoms. In this hyperconjugation three resonance structures arise to increase the stability of propene.
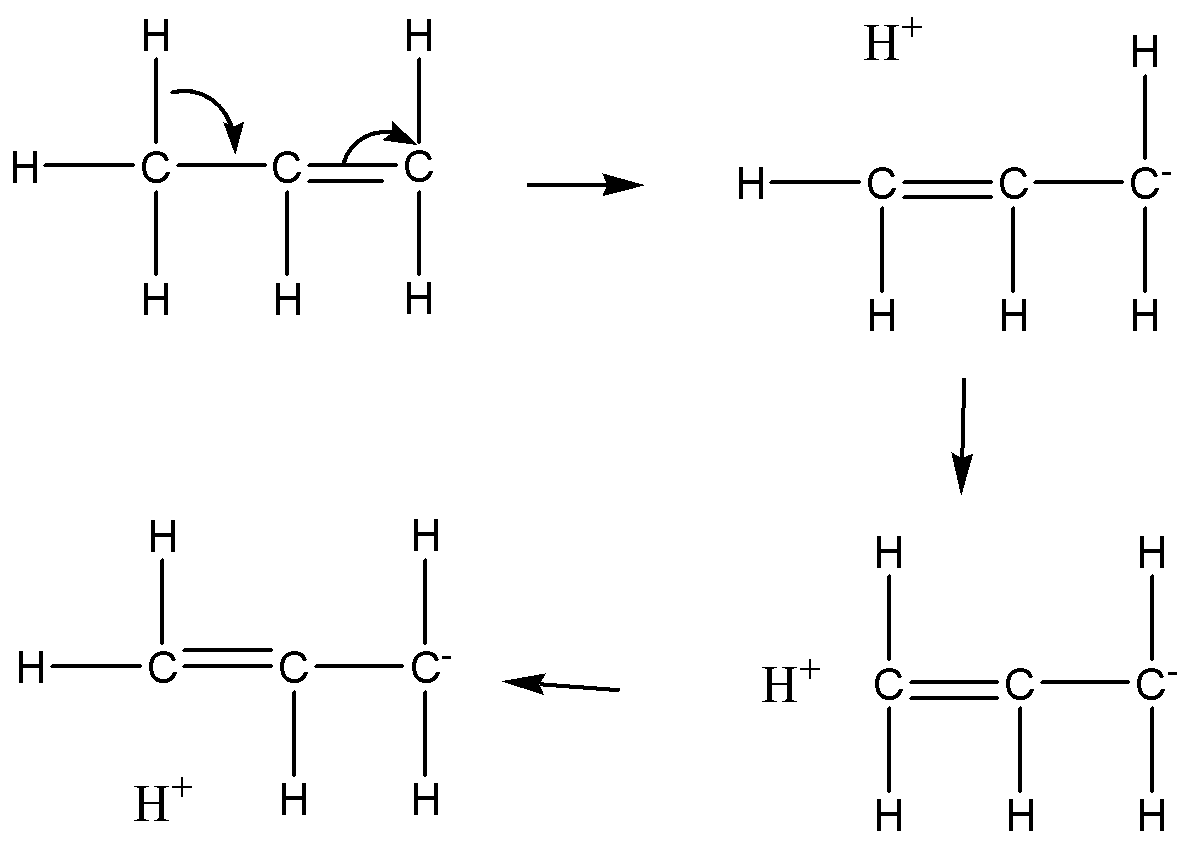
Note: We need to know that the stability of the carbocation is dependent on the hyperconjugation. The tertiary carbocation is more stable than secondary and primary carbocation. The hyperconjugation to produce the various resonance structures of the one molecule. The more resonance structure possible in one molecule means that molecule is more stable. This stability is used to identify by the substitution reaction in the molecules. Hyperconjugation is a permanent effect in the molecule. In some reactions, hyperconjugation is known as the “Baker-Nathan effect”.
Complete step by step answer:
We have to remember that in organic molecules most of them are formed by covalent bonds. These covalent bond are classified as two types
There are
1.Sigma bond
2.Pi bond
We need to know that the mutual sharing two electrons in between two atoms, overlapping \[p\]orbitals to form sigma $\left( \sigma \right)$ and pi $\left( \pi \right)$ bond. Sigma bond means overlapping in head to head overlap in orbitals. Pi bond means overlapping occurs side wise in orbitals.
We need to know that hyperconjugation is one of the displacements of the electron in organic chemistry. The delocalisation of the sigma electron in bond is known as hyperconjugation. This hyperconjugation gives the special stability of the molecule, because one sigma electron delocalisation to form bonding or antibonding pi bond in conjugated carbon atom. This hyperconjugation is also called “no bond resonance”.
For example, propene having three canonical forms due to hyperconjugation. An electron in $C - H$ sigma bond is changed to form a pi bond ($C = C$) in conjugated carbon atoms. In this hyperconjugation three resonance structures arise to increase the stability of propene.

Note: We need to know that the stability of the carbocation is dependent on the hyperconjugation. The tertiary carbocation is more stable than secondary and primary carbocation. The hyperconjugation to produce the various resonance structures of the one molecule. The more resonance structure possible in one molecule means that molecule is more stable. This stability is used to identify by the substitution reaction in the molecules. Hyperconjugation is a permanent effect in the molecule. In some reactions, hyperconjugation is known as the “Baker-Nathan effect”.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




