
Define the structure of an artery and a vein. Explain how their structure helps in their functioning?
Answer
559.2k+ views
Hint: Blood vessels are tubes that are widely spread in our body. And it transports blood from the heart to the different parts of the body. There are a total of three types of blood vessels:- Arteries, veins, and capillaries. All the blood vessels have a function to transport blood or bring blood to the heart.
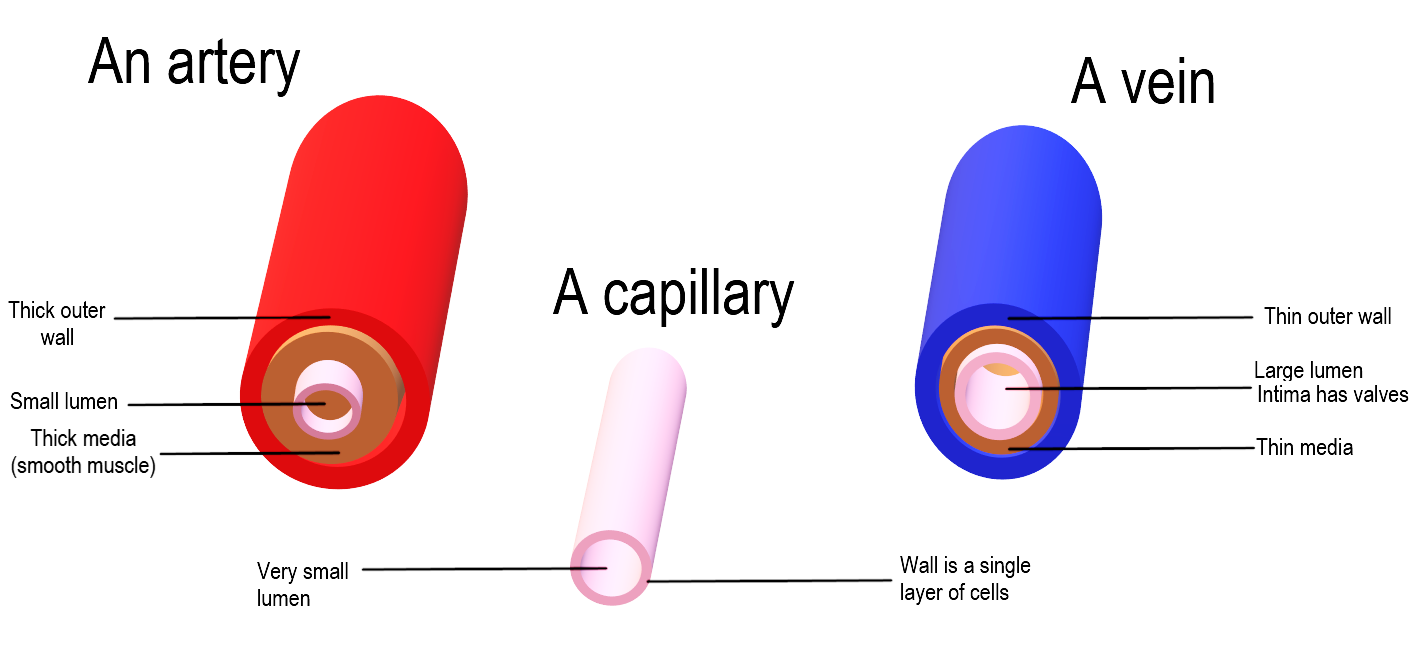
Complete answer: Arteries are the blood vessels made up of three layers that transport blood from the heart to the tissues of the body. The outer layer of arteries is made up of connective tissues and has elastic and collagen fibres that provide support to the blood vessel. The middle layer is made up of smooth muscles, collagen, and a huge amount of elastic fibres. This layer provides strength and elasticity. Elastic fibres allow the wall to stretch. The inner layer of endothelium is made up of very smooth epithelial cells, that help in, reducing friction. Veins are similar to arteries in shape and structure except for the three layers which are thin and elastic. In veins, the muscle and connective tissues are poorly developed. But the collagen fibres of the outer layer are well developed. The middle layer in the veins is very thin with no muscles. Semilunar valves are found in the lumen of some veins to restrict the backflow of blood when it moves towards the heart. The arteries have a narrow lumen, whereas the veins have a wide lumen. The blood flow in spurts, which corresponds to the ventricular contractions of the heart. Whereas in veins the blood flows uniformly.
Note: The arteries always carry deoxygenated blood from different organs to the heart, except for the pulmonary artery which carries oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart. The arteries and veins divide further and further to form capillaries, which exchange blood from the cell. There are no muscles present in the capillaries.
Complete answer: Arteries are the blood vessels made up of three layers that transport blood from the heart to the tissues of the body. The outer layer of arteries is made up of connective tissues and has elastic and collagen fibres that provide support to the blood vessel. The middle layer is made up of smooth muscles, collagen, and a huge amount of elastic fibres. This layer provides strength and elasticity. Elastic fibres allow the wall to stretch. The inner layer of endothelium is made up of very smooth epithelial cells, that help in, reducing friction. Veins are similar to arteries in shape and structure except for the three layers which are thin and elastic. In veins, the muscle and connective tissues are poorly developed. But the collagen fibres of the outer layer are well developed. The middle layer in the veins is very thin with no muscles. Semilunar valves are found in the lumen of some veins to restrict the backflow of blood when it moves towards the heart. The arteries have a narrow lumen, whereas the veins have a wide lumen. The blood flow in spurts, which corresponds to the ventricular contractions of the heart. Whereas in veins the blood flows uniformly.

Note: The arteries always carry deoxygenated blood from different organs to the heart, except for the pulmonary artery which carries oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart. The arteries and veins divide further and further to form capillaries, which exchange blood from the cell. There are no muscles present in the capillaries.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




