
Define the food chain. Describe the flow of energy in an ecosystem with the help of a linear diagram.
Answer
595.5k+ views
Hint: The relationship showing the consumption of an organism linearly eating another organism to attain energy for survival. The energy is transferred from one trophic level to another in a sequential manner.
Complete answer:
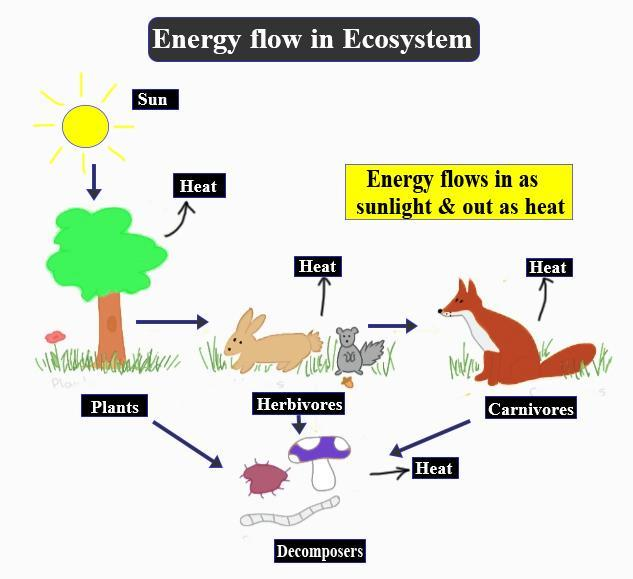
The linear network of links present in the food web which starts from the green plants (producers) and lasts at the predators (consumers) is known as the food chain. It is the sequence of species through which food and energy are passed in an ecosystem. A food chain shows how the organisms are related to each other by the food they eat. Each level of the food chain represents a trophic level.
The energy is transferred from one trophic level to another. The energy is produced from the sun which is absorbed by the producers for the process of photosynthesis. This energy is later converted into the chemical energy which is then stored in the producers. When the herbivores eat these plants it will degrade the energy which is then consumed by the consumers and the energy will further degrade.
There are two types of food chains, they are:
Grazing food chain – this food chain starts with the green plants or producers. The food energy then passes through the herbivores and lastly to the carnivores. Here the energy required in the producers is through the process of photosynthesis.
Detritus food chain – this food chain starts with dead organic matters. The food energy passes into decomposers and detritivores, which are further eaten by smaller organisms like carnivores.
Note: The Arab scientist and philosopher Al-Jahiz were the first to introduce the food chains in the tenth century which was later published in 1927 and was popularized by Charles Elton. The concept of the food web was also introduced by Charles Elton.
Complete answer:
The linear network of links present in the food web which starts from the green plants (producers) and lasts at the predators (consumers) is known as the food chain. It is the sequence of species through which food and energy are passed in an ecosystem. A food chain shows how the organisms are related to each other by the food they eat. Each level of the food chain represents a trophic level.
The energy is transferred from one trophic level to another. The energy is produced from the sun which is absorbed by the producers for the process of photosynthesis. This energy is later converted into the chemical energy which is then stored in the producers. When the herbivores eat these plants it will degrade the energy which is then consumed by the consumers and the energy will further degrade.
There are two types of food chains, they are:
Grazing food chain – this food chain starts with the green plants or producers. The food energy then passes through the herbivores and lastly to the carnivores. Here the energy required in the producers is through the process of photosynthesis.
Detritus food chain – this food chain starts with dead organic matters. The food energy passes into decomposers and detritivores, which are further eaten by smaller organisms like carnivores.

Note: The Arab scientist and philosopher Al-Jahiz were the first to introduce the food chains in the tenth century which was later published in 1927 and was popularized by Charles Elton. The concept of the food web was also introduced by Charles Elton.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




