
Define Refracted ray.
Answer
497.1k+ views
Hint: We start by defining the process, that is refraction and how and why refraction occurs. Then we move onto defining the asked part with the help of a diagram for easier and simple understanding.
Complete answer:
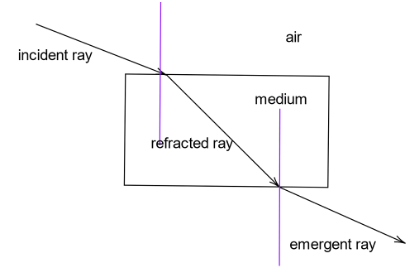
Refraction:When a ray of light travels from one medium to another, there will be a change in the speed of light. The process responsible for this is called refraction.
Incident ray:The ray falling on the surface separating two media is called incident ray. The angle it makes with the normal (the purple line) is called the incident angle.
Refracted ray: When the incident ray travels through the interface separating two media, it undergoes a change in velocity and direction according to the value of density of the medium as a result of interaction with the medium is called refracted ray. Just like the incident angle, it is the angle the refracted ray makes with the normal (the purple line in the figure).Refraction occurs when an incident ray comes in contact with a different medium and the result of refraction is the change in speed and direction of the light ray.
Note: The direction change after refraction is governed by the density of the medium. If the medium is denser, the ray moves towards the normal and if the ray is rarer the ray moves away from the normal. Refraction is also governed by Snell’s law, the formula of Snell’s law is, \[{n_1}\sin {\theta _1} = {n_2}\sin {\theta _2}\] where \[{n_1}\] and \[{n_2}\] are the refractive indices of the medium.
Complete answer:

Refraction:When a ray of light travels from one medium to another, there will be a change in the speed of light. The process responsible for this is called refraction.
Incident ray:The ray falling on the surface separating two media is called incident ray. The angle it makes with the normal (the purple line) is called the incident angle.
Refracted ray: When the incident ray travels through the interface separating two media, it undergoes a change in velocity and direction according to the value of density of the medium as a result of interaction with the medium is called refracted ray. Just like the incident angle, it is the angle the refracted ray makes with the normal (the purple line in the figure).Refraction occurs when an incident ray comes in contact with a different medium and the result of refraction is the change in speed and direction of the light ray.
Note: The direction change after refraction is governed by the density of the medium. If the medium is denser, the ray moves towards the normal and if the ray is rarer the ray moves away from the normal. Refraction is also governed by Snell’s law, the formula of Snell’s law is, \[{n_1}\sin {\theta _1} = {n_2}\sin {\theta _2}\] where \[{n_1}\] and \[{n_2}\] are the refractive indices of the medium.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




