
Define Reflection.
Answer
588k+ views
Hint:You can easily answer the question by recalling what reflection is and how can you define it. Reflection basically occurs when a light ray strikes a wall or a surface through which it can’t get past and thus gets reflected back.
Complete step by step answer:
Reflection is a term very frequently and commonly used in Physics to describe a phenomenon when a travelling incident light ray cannot pass through an object or surface and thus gets reflected back.
The process is also depicted in the diagram given below:
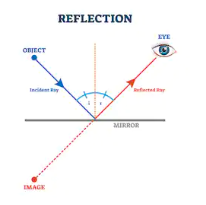
The given image shows you reflection of light from a plane mirror, which is the simplest of all the possible cases of reflection. Reflection of light rays isn’t random and follows some key set of rules. Light is known to behave in a very predictable manner. If a ray of light could be observed approaching and reflecting off of a flat mirror, then the behavior of the light as it reflects would follow a few predictable laws known as the laws of reflection, which are as follows:
The law of reflection defines that upon reflection from a smooth surface, the angle of the reflected ray is always equal to the angle of the incident ray, with respect to the normal to the surface at the point of contact.
The reflected ray, the incident ray and the normal to the surface is always in the same plane and can never be in any other plane than the one defined by the incident ray and normal to the surface at the point of contact.
Note: There are two main types of reflection: Regular reflection and Irregular reflection. Regular reflection is the type of reflection when the light rays strike with a smooth or plane surface and get reflected back. On the other hand, irregular reflection or Diffuse reflection happens when the light rays get reflected back from a rough surface.
Complete step by step answer:
Reflection is a term very frequently and commonly used in Physics to describe a phenomenon when a travelling incident light ray cannot pass through an object or surface and thus gets reflected back.
The process is also depicted in the diagram given below:

The given image shows you reflection of light from a plane mirror, which is the simplest of all the possible cases of reflection. Reflection of light rays isn’t random and follows some key set of rules. Light is known to behave in a very predictable manner. If a ray of light could be observed approaching and reflecting off of a flat mirror, then the behavior of the light as it reflects would follow a few predictable laws known as the laws of reflection, which are as follows:
The law of reflection defines that upon reflection from a smooth surface, the angle of the reflected ray is always equal to the angle of the incident ray, with respect to the normal to the surface at the point of contact.
The reflected ray, the incident ray and the normal to the surface is always in the same plane and can never be in any other plane than the one defined by the incident ray and normal to the surface at the point of contact.
Note: There are two main types of reflection: Regular reflection and Irregular reflection. Regular reflection is the type of reflection when the light rays strike with a smooth or plane surface and get reflected back. On the other hand, irregular reflection or Diffuse reflection happens when the light rays get reflected back from a rough surface.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




