
Define radius and the terms needed to define radius.
Answer
604.5k+ views
Hint: Circle can be drawn by taking a fixed length of rope and keeping one point fixed and the locus of another point gives you a circle. The length of the rope is called a radius. Each point on the circle is at the same distance from the centre. The terms required to define the radius are the centre of the circle and any point one point on the circle.
Complete step-by-step answer:
A circle is a set of points at some distance $r$from some fixed point. The value of $r$ is called the radius of the circle, and the point is called the centre of the circle.
Let the fixed point be $\left( h,k \right)$ .
The centre radius form of a circle is
${{\left( x-h \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y-k \right)}^{2}}={{r}^{2}}.......................(i)$
Where h and k are the x and y coordinate of the centre respectively.
If the centre is located at (0,0) then the equation simplifies to as follows,
${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}={{r}^{2}}$
Pictorially, it can be shown as follows,
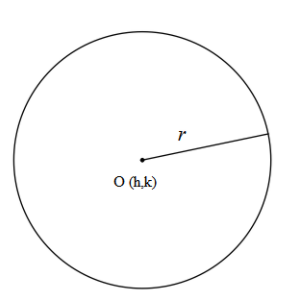
We can simplify the equation (i) to get the expression for radius,
$\begin{align}
& {{r}^{2}}={{\left( x-h \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y-k \right)}^{2}} \\
& {{\left( r \right)}^{2}}={{\left( \sqrt{{{\left( x-h \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y-k \right)}^{2}}} \right)}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
Taking the square root on both sides we get,
$r=\sqrt{{{\left( x-h \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y-k \right)}^{2}}}...........................(ii)$
We can see from the equation (ii), we need two points on the plane to plot a circle, from which one point is fixed named as $\left( h,k \right)$ .
Note: It is easily mistaken that $\left( x,y \right)$ to be the centre of the circle but it's wrong. Instead, the centre of the circle is $\left( h,k \right)$ . While taking the square root, we neglect the negative sign because a radius is a constant number and it does not depend on the direction. Radius is constant in all directions.
Complete step-by-step answer:
A circle is a set of points at some distance $r$from some fixed point. The value of $r$ is called the radius of the circle, and the point is called the centre of the circle.
Let the fixed point be $\left( h,k \right)$ .
The centre radius form of a circle is
${{\left( x-h \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y-k \right)}^{2}}={{r}^{2}}.......................(i)$
Where h and k are the x and y coordinate of the centre respectively.
If the centre is located at (0,0) then the equation simplifies to as follows,
${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}={{r}^{2}}$
Pictorially, it can be shown as follows,

We can simplify the equation (i) to get the expression for radius,
$\begin{align}
& {{r}^{2}}={{\left( x-h \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y-k \right)}^{2}} \\
& {{\left( r \right)}^{2}}={{\left( \sqrt{{{\left( x-h \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y-k \right)}^{2}}} \right)}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
Taking the square root on both sides we get,
$r=\sqrt{{{\left( x-h \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y-k \right)}^{2}}}...........................(ii)$
We can see from the equation (ii), we need two points on the plane to plot a circle, from which one point is fixed named as $\left( h,k \right)$ .
Note: It is easily mistaken that $\left( x,y \right)$ to be the centre of the circle but it's wrong. Instead, the centre of the circle is $\left( h,k \right)$ . While taking the square root, we neglect the negative sign because a radius is a constant number and it does not depend on the direction. Radius is constant in all directions.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Full Form of IASDMIPSIFSIRSPOLICE class 7 social science CBSE

Convert 200 Million dollars in rupees class 7 maths CBSE

Write a letter to the editor of the national daily class 7 english CBSE

Fill in the blanks with appropriate modals a Drivers class 7 english CBSE

What are the controls affecting the climate of Ind class 7 social science CBSE

What were the major teachings of Baba Guru Nanak class 7 social science CBSE





