
Define Electrochemical cells. What happens if external potential applied becomes greater than ${E_{cell}}$ of Electrochemical cell?
Answer
502.5k+ views
Hint: Electrochemistry is a branch of Physical chemistry. The word Electrochemistry contains 2 parts- Electro means electricity and chemistry means chemical reactions. Electrochemical cells are devices that convert chemical energy into Electrical energy or convert Electrical energy into chemical energy.
Complete answer:
The Electrochemical cell may be of 2 types-
(1)Electrolytic Cell-Converts Electrical to Chemical energy
(2) Galvanic Cell-Converts Chemical to Electrical energy
Both the cells have a common point that Reduction i.e. gain of electrons occurs at the Cathode while Oxidation i.e. loss of electrons occurs at Anode.
Let us talk about them one by one-
(1)Electrolytic Cell-
The 3 parts are-Cathode (Negatively charged), Anode (Positively charged) and the Electrolyte.
The diagram of Electrolytic cell is as under-
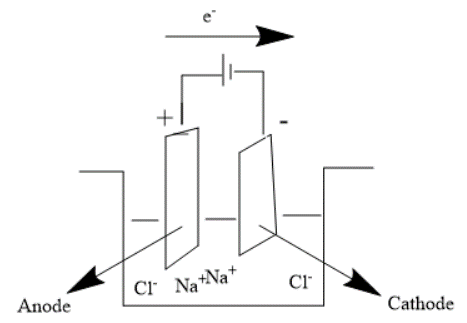
In this case we consider an example where we have an Electrolytic cell with Molten $NaCl$. We have 2 inert electrodes dipped into it and now we pass electric current. The ions are produced. Since Cathode is negatively charged $N{a^ + }$ ions are attracted to it while since Anode is positively charged it attracts $C{l^ - }$ ions towards it.
The reaction is as follows-
Cathode- $N{a^ + } + {e^ - } \to Na$
Anode- $C{l^ - } \to \dfrac{1}{2}C{l_2} + {e^ - }$
Overall reaction- $N{a^ + } + C{l^ - } \to Na + \dfrac{1}{2}C{l_2}$
Electron transfer occurs from Anode to Cathode.
(2)Galvanic cell or voltaic Cell-
One of the popular examples of this cell is Daniel Cell. We consider the following diagram-
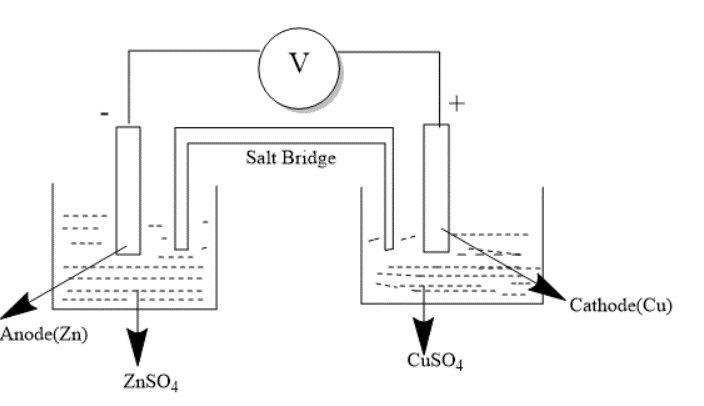
In this case Cathode is positively charged while Anode is negatively charged. Zinc electrode is dipped in Zinc sulphate solution while Copper electrode in Copper sulphate solution. The flow of Electrons occurs from zinc to copper through conducting wires. The flow of Current is opposite to the flow of current.
The cell is represented as- $Zn|Z{n^{ + 2}}||C{u^{ + 2}}|Cu$
The reaction is as follows-
Anode- $Zn \to Z{n^{ + 2}} + 2{e^ - }$
Cathode- $C{u^{ + 2}} + 2{e^ - } \to Cu$
Overall reaction- $Zn + C{u^{ + 2}} \to Z{n^{ + 2}} + Cu$
Here anode change is shown on the left where Zinc loses 2 electrons and the cathode reaction on the right where copper ion gains 2 electrons.
There is a salt bridge in between the containers made up of $KCl/KN{O_3}/{K_2}S{O_4}$ that completes the circuit that allows flow of current and prevents intermixing of ions of solution.
If External EMF (Electromotive force) is less than EMF of cell forward reaction occurs but if External EMF is greater than the EMF of cell backward reaction occurs. When External EMF becomes equal to EMF of the cell, no reaction occurs.
Note:
It is interesting that reactions occurring in galvanic cells are all Spontaneous i.e. do not require input of energy while reactions occurring in Electrolytic cells are all Non-Spontaneous i.e. they require an input of Energy. Commonly all the batteries we see are made up of galvanic cells while electrolytic cells find applications in electroplating.
Complete answer:
The Electrochemical cell may be of 2 types-
(1)Electrolytic Cell-Converts Electrical to Chemical energy
(2) Galvanic Cell-Converts Chemical to Electrical energy
Both the cells have a common point that Reduction i.e. gain of electrons occurs at the Cathode while Oxidation i.e. loss of electrons occurs at Anode.
Let us talk about them one by one-
(1)Electrolytic Cell-
The 3 parts are-Cathode (Negatively charged), Anode (Positively charged) and the Electrolyte.
The diagram of Electrolytic cell is as under-

In this case we consider an example where we have an Electrolytic cell with Molten $NaCl$. We have 2 inert electrodes dipped into it and now we pass electric current. The ions are produced. Since Cathode is negatively charged $N{a^ + }$ ions are attracted to it while since Anode is positively charged it attracts $C{l^ - }$ ions towards it.
The reaction is as follows-
Cathode- $N{a^ + } + {e^ - } \to Na$
Anode- $C{l^ - } \to \dfrac{1}{2}C{l_2} + {e^ - }$
Overall reaction- $N{a^ + } + C{l^ - } \to Na + \dfrac{1}{2}C{l_2}$
Electron transfer occurs from Anode to Cathode.
(2)Galvanic cell or voltaic Cell-
One of the popular examples of this cell is Daniel Cell. We consider the following diagram-

In this case Cathode is positively charged while Anode is negatively charged. Zinc electrode is dipped in Zinc sulphate solution while Copper electrode in Copper sulphate solution. The flow of Electrons occurs from zinc to copper through conducting wires. The flow of Current is opposite to the flow of current.
The cell is represented as- $Zn|Z{n^{ + 2}}||C{u^{ + 2}}|Cu$
The reaction is as follows-
Anode- $Zn \to Z{n^{ + 2}} + 2{e^ - }$
Cathode- $C{u^{ + 2}} + 2{e^ - } \to Cu$
Overall reaction- $Zn + C{u^{ + 2}} \to Z{n^{ + 2}} + Cu$
Here anode change is shown on the left where Zinc loses 2 electrons and the cathode reaction on the right where copper ion gains 2 electrons.
There is a salt bridge in between the containers made up of $KCl/KN{O_3}/{K_2}S{O_4}$ that completes the circuit that allows flow of current and prevents intermixing of ions of solution.
If External EMF (Electromotive force) is less than EMF of cell forward reaction occurs but if External EMF is greater than the EMF of cell backward reaction occurs. When External EMF becomes equal to EMF of the cell, no reaction occurs.
Note:
It is interesting that reactions occurring in galvanic cells are all Spontaneous i.e. do not require input of energy while reactions occurring in Electrolytic cells are all Non-Spontaneous i.e. they require an input of Energy. Commonly all the batteries we see are made up of galvanic cells while electrolytic cells find applications in electroplating.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




