
Define crest and trough.
Answer
554.4k+ views
Hint :In a wave, the maximum value of upward displacement is called its crest. On the other hand trough is just opposite to the crest, in a wave the minimum value of downward displacement is called its trough. We can also say that the highest upward amplitude is called crest while the lowest downward amplitude called trough.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Where the displacement of the medium is at a maximum, that point on the surface of the wave is known as crest. But the trough is just opposite to the crest, in simple words the minimum or lowest point in a cycle is known as trough.
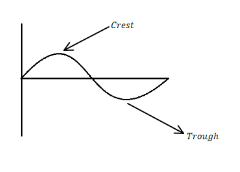
When the crests and troughs of two sine waves of equal amplitude and frequency intersect or collide, while being in phase with each other, the result is called constructive interference and the magnitudes double (above and below the line). When in antiphase – $ {180^o}C $ out of phase – the result is destructive interference: the resulting wave is the undisturbed line having zero amplitude.
Additional Information:
There are two types of waves used in classical physics : mechanical waves and electromagnetic waves. In mechanical waves, stress and strain are the two fields which oscillate about a mechanical equilibrium. In electromagnetic waves, energy gets interchanged between electric and magnetic fields.
Note :
Wave is propagating dynamic disturbance which occurs when change in equilibrium takes place of one or more quantities. Wave is always described in wave function. In physical waves, there should be at least two field quantities involved in wave medium. Waves are periodic when these quantities oscillate frequently about a resting value at some frequency. Travelling waves are said to be those waves when the entire waveform moves in one direction.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Where the displacement of the medium is at a maximum, that point on the surface of the wave is known as crest. But the trough is just opposite to the crest, in simple words the minimum or lowest point in a cycle is known as trough.

When the crests and troughs of two sine waves of equal amplitude and frequency intersect or collide, while being in phase with each other, the result is called constructive interference and the magnitudes double (above and below the line). When in antiphase – $ {180^o}C $ out of phase – the result is destructive interference: the resulting wave is the undisturbed line having zero amplitude.
Additional Information:
There are two types of waves used in classical physics : mechanical waves and electromagnetic waves. In mechanical waves, stress and strain are the two fields which oscillate about a mechanical equilibrium. In electromagnetic waves, energy gets interchanged between electric and magnetic fields.
Note :
Wave is propagating dynamic disturbance which occurs when change in equilibrium takes place of one or more quantities. Wave is always described in wave function. In physical waves, there should be at least two field quantities involved in wave medium. Waves are periodic when these quantities oscillate frequently about a resting value at some frequency. Travelling waves are said to be those waves when the entire waveform moves in one direction.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




