
Define aerobic respiration with example.
Answer
569.4k+ views
Hint: One of the most essential chemical processes is respiration, which is brought up by all living organisms involving plants, animals, and humans to release energy which is required to carry out all life processes. The process of respiration may occur in both conditions such as in the presence and absence of oxygen.
Complete answer:
Aerobic respiration is a biological process that involves the breakdown of food glucose. In this respiration, oxygen serves as an electron acceptor which produces ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) more successfully.
The chemical reaction of the aerobic respiration:
\[\mathop {{{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{12}}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{6}}}}\limits_{{\text{Glucose}}} {\text{ + }}\mathop {{\text{6}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}}\limits_{{\text{Oxygen}}} \to \mathop {{\text{6C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}}\limits_{{\text{CarbonDioxide}}} {\text{ + }}\mathop {{\text{6}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}}\limits_{{\text{Water}}} {\text{ + }}\mathop {{\text{ATP}}}\limits_{{\text{Energy}}} \]
According to the chemical reaction, energy is released due to the splitting of sugar molecules with the help of Oxygen gas. At the end of the reaction, carbon dioxide, water molecules, and energy currency i.e. ATP are released as the end-products.
This aerobic respiration process starts from the cytosol of the cells and occurs in four steps:
1. Glycolysis- It is the main step of aerobic respiration and takes place in the cytosol. During this mechanism, the glucose molecule splits into two ATP, two NADH molecules, and two molecules of pyruvic acid.
2. Oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate- Pyruvate which is synthesized in the glycolysis pathway enters into the mitochondrial matrix and undergoes oxidative decarboxylation catalyzed by pyruvic dehydrogenase. Acetyl CoA and NADH are produced in this process.
3. TCA (Tricarboxylic acid) cycle- This cycle is the third step in the process of aerobic respiration also known as the Citric acid cycle or Kreb cycle. In the TCA cycle oxaloacetate combines with Acetyl CoA and it produces citric acid, and the reaction is catalyzed by citrate synthase enzyme and CoA molecules are produced. This cycle undergoes several reactions and produces 2 molecules of${\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$, 1 molecule of ATP and reduced forms of NADH and FADH.
4. Electron Transport System- This is the last step in the aerobic respiration mechanism taking place in the inner mitochondrial membrane. A large number of ATP molecules are produced by transferring electrons from the NADH to FADH.
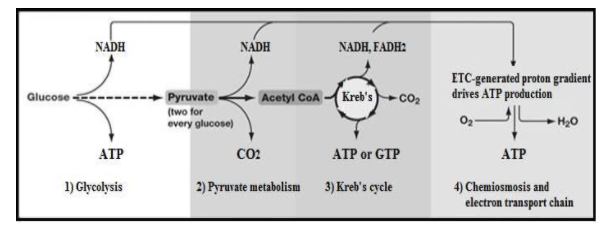
Note: Aerobic respiration occurs in every multicellular organism involving plants, animals, and other living organisms. In respiration, carbohydrates oxidized to exert energy in certain cases proteins, fats, and some organic acids as respiratory substances can also be utilized to produce energy in plants.
Complete answer:
Aerobic respiration is a biological process that involves the breakdown of food glucose. In this respiration, oxygen serves as an electron acceptor which produces ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) more successfully.
The chemical reaction of the aerobic respiration:
\[\mathop {{{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{12}}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{6}}}}\limits_{{\text{Glucose}}} {\text{ + }}\mathop {{\text{6}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}}\limits_{{\text{Oxygen}}} \to \mathop {{\text{6C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}}\limits_{{\text{CarbonDioxide}}} {\text{ + }}\mathop {{\text{6}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}}\limits_{{\text{Water}}} {\text{ + }}\mathop {{\text{ATP}}}\limits_{{\text{Energy}}} \]
According to the chemical reaction, energy is released due to the splitting of sugar molecules with the help of Oxygen gas. At the end of the reaction, carbon dioxide, water molecules, and energy currency i.e. ATP are released as the end-products.
This aerobic respiration process starts from the cytosol of the cells and occurs in four steps:
1. Glycolysis- It is the main step of aerobic respiration and takes place in the cytosol. During this mechanism, the glucose molecule splits into two ATP, two NADH molecules, and two molecules of pyruvic acid.
2. Oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate- Pyruvate which is synthesized in the glycolysis pathway enters into the mitochondrial matrix and undergoes oxidative decarboxylation catalyzed by pyruvic dehydrogenase. Acetyl CoA and NADH are produced in this process.
3. TCA (Tricarboxylic acid) cycle- This cycle is the third step in the process of aerobic respiration also known as the Citric acid cycle or Kreb cycle. In the TCA cycle oxaloacetate combines with Acetyl CoA and it produces citric acid, and the reaction is catalyzed by citrate synthase enzyme and CoA molecules are produced. This cycle undergoes several reactions and produces 2 molecules of${\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$, 1 molecule of ATP and reduced forms of NADH and FADH.
4. Electron Transport System- This is the last step in the aerobic respiration mechanism taking place in the inner mitochondrial membrane. A large number of ATP molecules are produced by transferring electrons from the NADH to FADH.

Note: Aerobic respiration occurs in every multicellular organism involving plants, animals, and other living organisms. In respiration, carbohydrates oxidized to exert energy in certain cases proteins, fats, and some organic acids as respiratory substances can also be utilized to produce energy in plants.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




