
Define:
(a) Saturated hydrocarbon
(b) Unsaturated hydrocarbon
(c) Catenation
Answer
591.9k+ views
Hint: All the organic compounds possessing carbon as well as hydrogen atoms are known as hydrocarbons. These are naturally-occurring compounds and they generally form the basis of natural gas, crude oil, coal, and other energy sources.
Complete step by step answer:
Hydrocarbons are mainly classified as saturated hydrocarbons and unsaturated hydrocarbons.
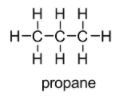
(a) Saturated hydrocarbon: Saturated hydrocarbons are the simplest form of hydrocarbons consisting of only single bonded carbon atoms. They are known as saturated owing to the capacity of each carbon atom to form bonds with as many hydrogen atoms as possible. We can say that carbon atoms are saturated with the hydrogen atoms. Example: alkanes like methane, ethane, propane, etc.
(b) Unsaturated hydrocarbon: Unsaturated hydrocarbons belong to the class of hydrocarbons which possess either double or triple covalent bonds between the adjacent carbon atoms. The term "unsaturated" indicates that more hydrogen atoms can be appended into the hydrocarbon in order to make it saturated. Generally, an unsaturated hydrocarbon includes straight chains (alkenes and alkynes) and also branched chains or aromatic compounds. Examples: propene, propyne, cis-2-butene, cyclopentene etc.

(c) Catenation: Catenation refers to the process in which an element binds to itself via covalent bonds which leads to the formation of either chain or ring molecules. Carbon is the most common example of an element which exhibits catenation. Carbon can lead to the formation of long hydrocarbon chains as well as rings like benzene.

Note: If hydrocarbons enter the lungs, it usually causes pneumonia and even death. Some hydrocarbons can also cause coma, irregular heart rhythms, seizures, or damage to the liver or kidneys.
Complete step by step answer:
Hydrocarbons are mainly classified as saturated hydrocarbons and unsaturated hydrocarbons.
(a) Saturated hydrocarbon: Saturated hydrocarbons are the simplest form of hydrocarbons consisting of only single bonded carbon atoms. They are known as saturated owing to the capacity of each carbon atom to form bonds with as many hydrogen atoms as possible. We can say that carbon atoms are saturated with the hydrogen atoms. Example: alkanes like methane, ethane, propane, etc.

(b) Unsaturated hydrocarbon: Unsaturated hydrocarbons belong to the class of hydrocarbons which possess either double or triple covalent bonds between the adjacent carbon atoms. The term "unsaturated" indicates that more hydrogen atoms can be appended into the hydrocarbon in order to make it saturated. Generally, an unsaturated hydrocarbon includes straight chains (alkenes and alkynes) and also branched chains or aromatic compounds. Examples: propene, propyne, cis-2-butene, cyclopentene etc.

(c) Catenation: Catenation refers to the process in which an element binds to itself via covalent bonds which leads to the formation of either chain or ring molecules. Carbon is the most common example of an element which exhibits catenation. Carbon can lead to the formation of long hydrocarbon chains as well as rings like benzene.

Note: If hydrocarbons enter the lungs, it usually causes pneumonia and even death. Some hydrocarbons can also cause coma, irregular heart rhythms, seizures, or damage to the liver or kidneys.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




