
Deduce expression for the resultant potential difference, impedance and current in L-R alternating circuit. Draw a graph to show the phase difference between the current and voltage.
Answer
600.9k+ views
Hint: In L-R circuit an inductor and a resistance are connected in series with a voltage source. Due to current in the circuit there is potential drop across the resistor and the inductor.
Complete step by step solution:
A pure resistance $R$ and a pure inductive coil of inductance $L$ as shown connected in series along an alternating current source.
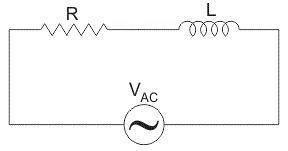
Let $V=$r.m.s. value of the applied voltage,
$I=$r.m.s value of the resultant current in the circuit.
${{V}_{R}}=IR$ is the voltage drop across the resistor which is in phase with the current $I$,
${{V}_{L}}=I{{X}_{L}}$ is the voltage drop across the inductor which is ahead of $I$ by $90{}^\circ $.
The applied voltage from the alternating voltage source is the vector sum of the voltage drop across the resistor and the inductor.
\[\begin{align}
& V=\sqrt{V_{R}^{2}+V_{L}^{2}} \\
& =\sqrt{{{\left( IR \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( I{{X}_{L}} \right)}^{2}}} \\
& =I\sqrt{{{R}^{2}}+X_{L}^{2}}
\end{align}\]
The quantity \[\sqrt{{{R}^{2}}+X_{L}^{2}}\] is known as the impedance of the circuit. Impedance of the circuit is represented as $Z$.
As seen from the impedance triangle ABC,
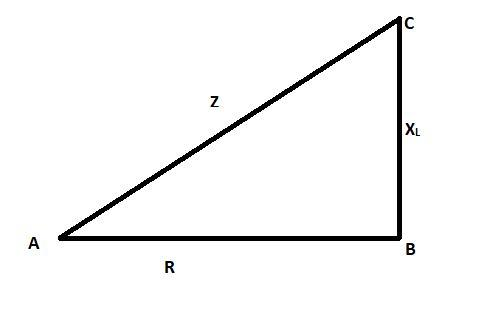
$\begin{align}
& {{Z}^{2}}={{R}^{2}}+X_{L}^{2} \\
& {{\left( \text{Impedance} \right)}^{2}}={{\left( \text{Resistance} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( \text{Inductive Reactance} \right)}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
From the given figure it is clear that the applied voltage V leads the current I by an angle ϕ such that
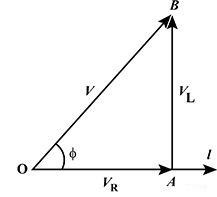
$\tan \phi =\dfrac{{{V}_{L}}}{{{V}_{R}}}=\dfrac{I{{X}_{L}}}{IR}=\dfrac{{{X}_{L}}}{R}=\dfrac{\omega L}{R}$
$\therefore \phi ={{\tan }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{\omega L}{R} \right)$
Note: - Across inductor voltage leads the electric current.
- Across the resistor the voltage is in phase with electric current.
Complete step by step solution:
A pure resistance $R$ and a pure inductive coil of inductance $L$ as shown connected in series along an alternating current source.

Let $V=$r.m.s. value of the applied voltage,
$I=$r.m.s value of the resultant current in the circuit.
${{V}_{R}}=IR$ is the voltage drop across the resistor which is in phase with the current $I$,
${{V}_{L}}=I{{X}_{L}}$ is the voltage drop across the inductor which is ahead of $I$ by $90{}^\circ $.
The applied voltage from the alternating voltage source is the vector sum of the voltage drop across the resistor and the inductor.
\[\begin{align}
& V=\sqrt{V_{R}^{2}+V_{L}^{2}} \\
& =\sqrt{{{\left( IR \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( I{{X}_{L}} \right)}^{2}}} \\
& =I\sqrt{{{R}^{2}}+X_{L}^{2}}
\end{align}\]
The quantity \[\sqrt{{{R}^{2}}+X_{L}^{2}}\] is known as the impedance of the circuit. Impedance of the circuit is represented as $Z$.
As seen from the impedance triangle ABC,

$\begin{align}
& {{Z}^{2}}={{R}^{2}}+X_{L}^{2} \\
& {{\left( \text{Impedance} \right)}^{2}}={{\left( \text{Resistance} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( \text{Inductive Reactance} \right)}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
From the given figure it is clear that the applied voltage V leads the current I by an angle ϕ such that

$\tan \phi =\dfrac{{{V}_{L}}}{{{V}_{R}}}=\dfrac{I{{X}_{L}}}{IR}=\dfrac{{{X}_{L}}}{R}=\dfrac{\omega L}{R}$
$\therefore \phi ={{\tan }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{\omega L}{R} \right)$
Note: - Across inductor voltage leads the electric current.
- Across the resistor the voltage is in phase with electric current.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the class 12 chemistry CBSE

Define Vant Hoff factor How is it related to the degree class 12 chemistry CBSE




