
Cyclohexane on chlorination gives:
A) Chloro cyclohexane
B) 1,2-dichloro cyclohexane
C) 1,4-dichloro cyclohexane
D) A mixture of all the above
Answer
570.3k+ views
Hint The answer is based on the basic organic chemistry reactions which involves the reactions of halogenations and in the presence of light at room temperature or at higher temperature, the substitution reaction occurs.
Complete step – by – step answer:
In the classes of organic chemistry, we have come across the topics which deal with some of the basic named reactions and also several common reactions like substitution reactions, addition reactions, elimination reactions and so on.
Let us now see what happens when cyclohexane is chlorinated.
- Cyclohexane is the six membered ring with no presence of double bonds between them and they are the cyclic alkanes.
- The alkanes are usually not reactive unless they are subjected to a high temperature or in the presence of light or treatment of very reactive chemicals.
- Usually, alkanes undergo free radical substitution reactions when subjected to UV light that is at higher temperatures.
Therefore, the free radical reactions proceed through a chain mechanism and this reaction that is chlorination of cyclohexane, usually produces one substituted product that is chloro cyclohexane and hydrochloric acid.
The reaction is as shown below,
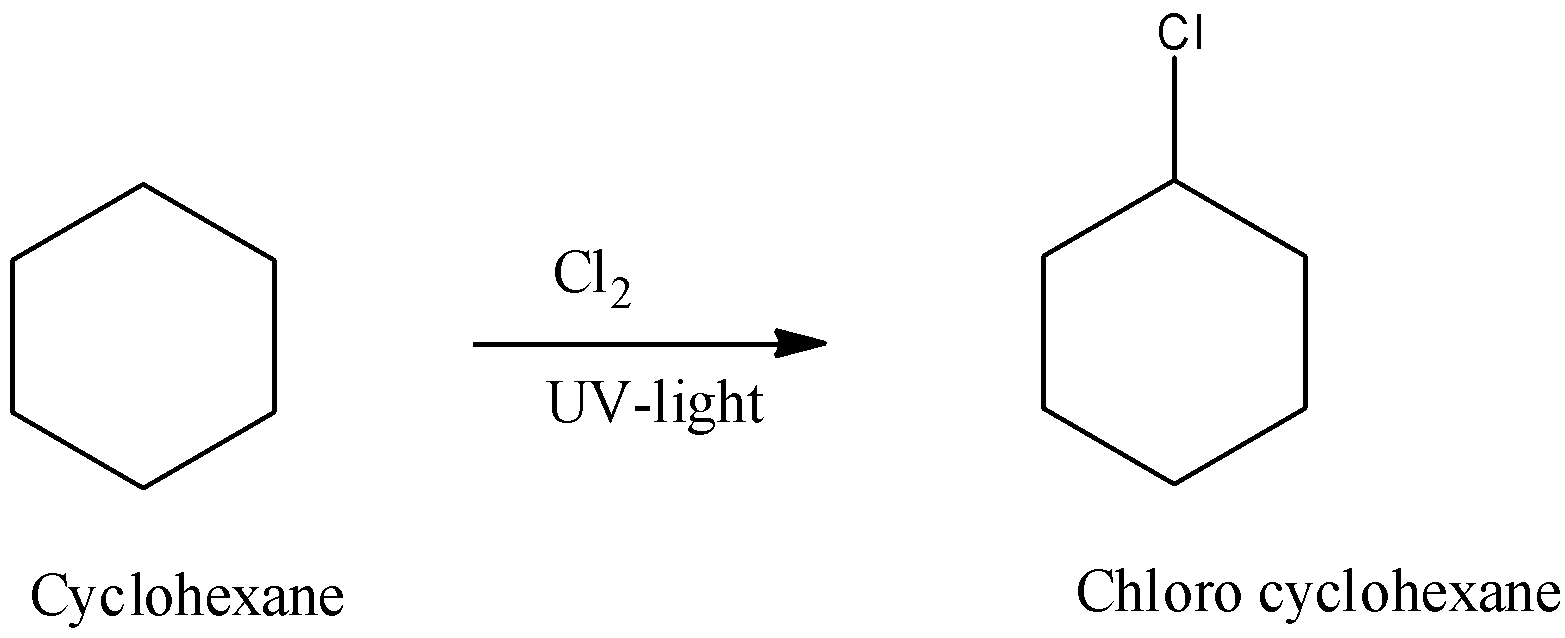
Therefore, in the above reaction, we can see that cyclohexane on irradiation of UV light produces mono substituted products because all the carbon atoms in cyclohexane are exactly the same.
Note: Note that even the alkyl substituted aromatic compounds undergo free radical substitution reactions which is mainly free radical chain reactions in the presence of UV light that is usually at higher temperatures and this process is used for the industrial synthesis of chloroform, dichloromethane and hexachlorobutadiene.
Complete step – by – step answer:
In the classes of organic chemistry, we have come across the topics which deal with some of the basic named reactions and also several common reactions like substitution reactions, addition reactions, elimination reactions and so on.
Let us now see what happens when cyclohexane is chlorinated.
- Cyclohexane is the six membered ring with no presence of double bonds between them and they are the cyclic alkanes.
- The alkanes are usually not reactive unless they are subjected to a high temperature or in the presence of light or treatment of very reactive chemicals.
- Usually, alkanes undergo free radical substitution reactions when subjected to UV light that is at higher temperatures.
Therefore, the free radical reactions proceed through a chain mechanism and this reaction that is chlorination of cyclohexane, usually produces one substituted product that is chloro cyclohexane and hydrochloric acid.
The reaction is as shown below,

Therefore, in the above reaction, we can see that cyclohexane on irradiation of UV light produces mono substituted products because all the carbon atoms in cyclohexane are exactly the same.
Note: Note that even the alkyl substituted aromatic compounds undergo free radical substitution reactions which is mainly free radical chain reactions in the presence of UV light that is usually at higher temperatures and this process is used for the industrial synthesis of chloroform, dichloromethane and hexachlorobutadiene.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




