
Cumene process is the most important commercial method for the manufacture of phenol, cumene is:
A. (1-methyl ethyl) benzene
B. ethylbenzene
C. Vinyl benzene
D. propyl benzene
Answer
596.1k+ views
Hint: Cumene is a 6-membered ring structure on which the alkyl group is attached. In the presence of air or ${{\text{O}}_{2}}$ and a catalyst, cumene is oxidised that is the removal of hydrogen and attachment of the oxygen atom in place of hydrogen takes place.
Complete answer:
As we know that phenol is a 6 membered ring structure with an alcohol group attached to it.
The formula of phenol is ${{\text{C}}_{6}}{{\text{H}}_{5}}\text{OH}$.
Cumene has a chemical formula of ${{\text{C}}_{6}}{{\text{H}}_{5}}\text{CH(C}{{\text{H}}_{3}}{{\text{)}}_{2}}$ and structure is
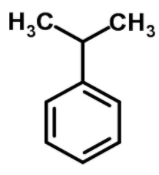
The IUPAC name of the cumene is 1-methyl ethylbenzene.
As we see that a methyl group is attached to the benzene ring so the numbering will be 1 and as the ethyl group is attached the methyl group so it will be named as (1- methyl ethyl) benzene.
When cumene reacts with oxygen in the presence of a catalyst, it forms carboxylic acid also known as cumene hydroperoxide by the oxidation on the carbon that is attached to the benzene.
In oxidation, the hydrogen atom present at the main carbon releases and carboxylic group attaches.
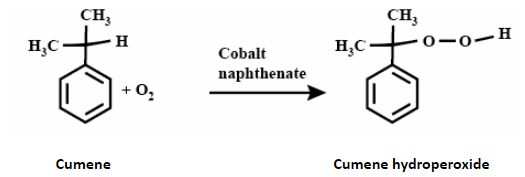
The common catalyst used in the reaction to increase the speed of reaction is Cobalt naphthenate.
Now, cumene hydroperoxide reacts with water in the acidic medium to yield phenol along with acetone.
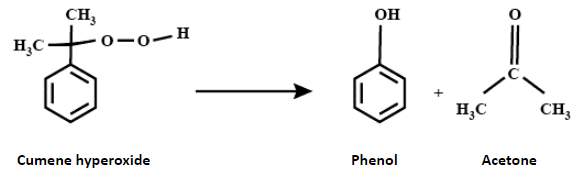
Therefore, option A is the correct answer.
Note: The formation of phenol and acetone from cumene is known as cumene process or Hock's process. The formation of cumene takes place by Friedel - craft alkylation ( it is a process in which the alkylation of the aromatic ring along with an alkyl halide with the help of Lewis acid takes place) of a benzene ring with propylene takes place.
Complete answer:
As we know that phenol is a 6 membered ring structure with an alcohol group attached to it.
The formula of phenol is ${{\text{C}}_{6}}{{\text{H}}_{5}}\text{OH}$.
Cumene has a chemical formula of ${{\text{C}}_{6}}{{\text{H}}_{5}}\text{CH(C}{{\text{H}}_{3}}{{\text{)}}_{2}}$ and structure is

The IUPAC name of the cumene is 1-methyl ethylbenzene.
As we see that a methyl group is attached to the benzene ring so the numbering will be 1 and as the ethyl group is attached the methyl group so it will be named as (1- methyl ethyl) benzene.
When cumene reacts with oxygen in the presence of a catalyst, it forms carboxylic acid also known as cumene hydroperoxide by the oxidation on the carbon that is attached to the benzene.
In oxidation, the hydrogen atom present at the main carbon releases and carboxylic group attaches.

The common catalyst used in the reaction to increase the speed of reaction is Cobalt naphthenate.
Now, cumene hydroperoxide reacts with water in the acidic medium to yield phenol along with acetone.

Therefore, option A is the correct answer.
Note: The formation of phenol and acetone from cumene is known as cumene process or Hock's process. The formation of cumene takes place by Friedel - craft alkylation ( it is a process in which the alkylation of the aromatic ring along with an alkyl halide with the help of Lewis acid takes place) of a benzene ring with propylene takes place.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




