
Crossing over takes place in
(a)Mitotic cell
(b)Meiotic cell
(c)Mutating cell
(d)Amitotic cell
Answer
585.9k+ views
Hint: : These are a type of cell division during which a single cell divides twice and produces four daughter cells. These four daughter cells contain half the amount of genetic material and known as our sex cells (gametes).
Complete answer:
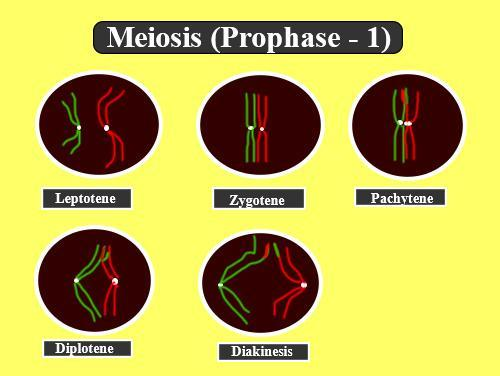
Crossing over, in other terms, is the interchange of segments seen in homologous chromosomes between non-sister chromatids and occurs during the pachytene stage of the prophase I in the cell division process of meiosis and always takes place within linked genes. The recombination of linked genes that crossing over initiate plays an important role in evolution.
Additional Information:
The linked frequency of crossover between two gene loci (markers) is the crossing-over value. For a fixed set of genetic and environmental conditions, recombination during a particular region of a linkage structure (chromosome) tends to be constant and the same is then true for the crossing-over value which is employed within the production of genetic maps.[ There are two popular and overlapping theories that specify the origins of crossing-over, coming from the various theories on the origin of meiosis. The primary theory rests upon the thought that meiosis evolved as another method of DNA repair, and thus crossing-over may be a novel way to replace possibly damaged sections of DNA.
So, the correct answer is ‘Meiotic cell’.
Note:
The crossover was described, in theory, by Thomas Hunt Morgan. He relied on the invention of Frans Alfons Janssens who described the phenomenon in 1909 and called it "chiasma type". Crossover and DNA repair are very similar processes, which utilize many of equivalent protein complexes.
Complete answer:
Crossing over, in other terms, is the interchange of segments seen in homologous chromosomes between non-sister chromatids and occurs during the pachytene stage of the prophase I in the cell division process of meiosis and always takes place within linked genes. The recombination of linked genes that crossing over initiate plays an important role in evolution.
Additional Information:
The linked frequency of crossover between two gene loci (markers) is the crossing-over value. For a fixed set of genetic and environmental conditions, recombination during a particular region of a linkage structure (chromosome) tends to be constant and the same is then true for the crossing-over value which is employed within the production of genetic maps.[ There are two popular and overlapping theories that specify the origins of crossing-over, coming from the various theories on the origin of meiosis. The primary theory rests upon the thought that meiosis evolved as another method of DNA repair, and thus crossing-over may be a novel way to replace possibly damaged sections of DNA.
So, the correct answer is ‘Meiotic cell’.
Note:
The crossover was described, in theory, by Thomas Hunt Morgan. He relied on the invention of Frans Alfons Janssens who described the phenomenon in 1909 and called it "chiasma type". Crossover and DNA repair are very similar processes, which utilize many of equivalent protein complexes.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




