
What is the correct Lewis dot structure for $ {S^{2 - }} $ ion?
Answer
487.5k+ views
Hint: Electron Dot structures also known as the Lewis electron Dot structures, are diagrams that depict the bonding between different atoms and also show their valence electrons and lone pairs, if any exists. It mostly has two types of dots $ \times \& \circ $ that represent electrons from two different atoms.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The inorganic anion of sulphur atoms is known as sulphide. It has the chemical formula $ {S^{2 - }} $ . The sulphide can have one or more $ {S^{2 - }} $ anions. Large families of inorganic and organic compounds like lead sulphides, hydrogen sulphide, etc. are also known as ‘sulphides’ itself. They are the conjugate acids of sulphides. Sulphide solutions are generally corrosive in nature.
Sulphur is the parent element of the sulphide ion, and belongs to the group 16 of the periodic table. The electronic configuration of sulphur is: $ [Ne]3{s^2}3{p^4} $ . The charge on the sulphide ion is -2 meaning it accepts two electrons in its valence orbital, to attain the 8 outer electron configuration and be stable. The lewis dot structure of sulphide can be given as:
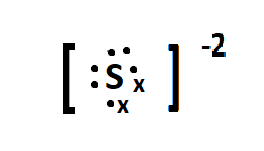
Here the $ \bullet $ represents the valence electrons present in the valence shell of the sulphur atom and x represents the electrons gained from outside.
Note:
Sulphide is precipitated out when transition metal reacts with sulphide sources like Hydrogen Sulphide, Sodium Sulphide, etc. The solubility of such inorganic sulphides in water is very less and are also related to minerals with the same composition. Many metals and ores containing sulphide are their primary content. Examples are argentite, cinnabar, galena, molybdenite, pyrite, chalcopyrite, etc.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The inorganic anion of sulphur atoms is known as sulphide. It has the chemical formula $ {S^{2 - }} $ . The sulphide can have one or more $ {S^{2 - }} $ anions. Large families of inorganic and organic compounds like lead sulphides, hydrogen sulphide, etc. are also known as ‘sulphides’ itself. They are the conjugate acids of sulphides. Sulphide solutions are generally corrosive in nature.
Sulphur is the parent element of the sulphide ion, and belongs to the group 16 of the periodic table. The electronic configuration of sulphur is: $ [Ne]3{s^2}3{p^4} $ . The charge on the sulphide ion is -2 meaning it accepts two electrons in its valence orbital, to attain the 8 outer electron configuration and be stable. The lewis dot structure of sulphide can be given as:
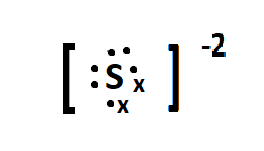
Here the $ \bullet $ represents the valence electrons present in the valence shell of the sulphur atom and x represents the electrons gained from outside.
Note:
Sulphide is precipitated out when transition metal reacts with sulphide sources like Hydrogen Sulphide, Sodium Sulphide, etc. The solubility of such inorganic sulphides in water is very less and are also related to minerals with the same composition. Many metals and ores containing sulphide are their primary content. Examples are argentite, cinnabar, galena, molybdenite, pyrite, chalcopyrite, etc.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

A solution of a substance X is used for white washing class 11 chemistry CBSE




