
Convert the following:
\[1 - bromopropane\] to \[2 - bromopropane\]
Answer
504.9k+ views
Hint: The conversion does not require any change in the number of carbon atoms, but only the position of bromine substituent changes. Any substituent cannot show a shift in position by a single step reaction, it needs to be removed and then placed at the desired position.
Complete answer:
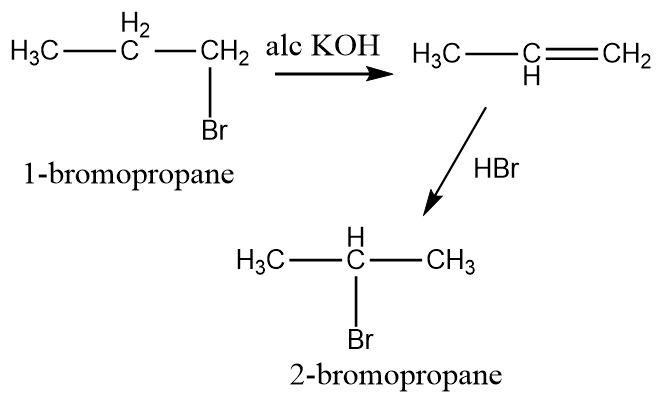
\[1 - bromopropane\] contains a parent chain of three carbon atoms with a bromine substituent attached to the terminal carbon. \[2 - bromopropane\] contains a parent chain of three carbon atoms with a bromine substituent attached to the middle carbon atom.
An elimination reaction can be carried out in the present of strong alkali. The elimination reaction results in dehydrohalogenation i.e. the bromine substituent is removed along with a hydrogen atom attached to the adjacent carbon atom. The product formed is an alkene. Alcoholic potassium hydroxide can be used to perform elimination.
Once the alkene is formed it can undergo an electrophilic addition reaction. To attach a bromine substituent, hydrogen bromide is used in which the positively charged hydrogen atoms act as electrophiles and the electron rich double bond of alkene acts as nucleophile. The carbocation formed as a result of electrophilic addition then forms a bond with the bromide ion.
The addition reaction takes place according to the Markovnikov’s rule in which the bromide anion always gets attached to a position which forms a more stable carbocation.
Since secondary carbocations are more stable than primary carbocations, The bromine substituent selectively occupies the middle position.
Hence, the conversion of \[1 - bromopropane\] to \[2 - bromopropane\] can be carried out by performing elimination followed by Markovnikov’s addition.
Note:
The elimination reaction mainly follows Saytzeff's rule according to which a more substituted alkene is always formed but in this case there was only a single hydrogen available attached to the adjacent carbon atom and therefore this rule was not applicable.
Complete answer:
\[1 - bromopropane\] contains a parent chain of three carbon atoms with a bromine substituent attached to the terminal carbon. \[2 - bromopropane\] contains a parent chain of three carbon atoms with a bromine substituent attached to the middle carbon atom.
An elimination reaction can be carried out in the present of strong alkali. The elimination reaction results in dehydrohalogenation i.e. the bromine substituent is removed along with a hydrogen atom attached to the adjacent carbon atom. The product formed is an alkene. Alcoholic potassium hydroxide can be used to perform elimination.
Once the alkene is formed it can undergo an electrophilic addition reaction. To attach a bromine substituent, hydrogen bromide is used in which the positively charged hydrogen atoms act as electrophiles and the electron rich double bond of alkene acts as nucleophile. The carbocation formed as a result of electrophilic addition then forms a bond with the bromide ion.
The addition reaction takes place according to the Markovnikov’s rule in which the bromide anion always gets attached to a position which forms a more stable carbocation.
Since secondary carbocations are more stable than primary carbocations, The bromine substituent selectively occupies the middle position.
Hence, the conversion of \[1 - bromopropane\] to \[2 - bromopropane\] can be carried out by performing elimination followed by Markovnikov’s addition.

Note:
The elimination reaction mainly follows Saytzeff's rule according to which a more substituted alkene is always formed but in this case there was only a single hydrogen available attached to the adjacent carbon atom and therefore this rule was not applicable.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




