
How to convert benzene to benzophenone?
Answer
513.3k+ views
Hint: We know that the Friedel Crafts Acylation is the one where the reactant is an alkyl-aryl halide and benzene which reacts in the presence of a catalyst to form a benzophenone. The type of reaction is an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
Complete answer:
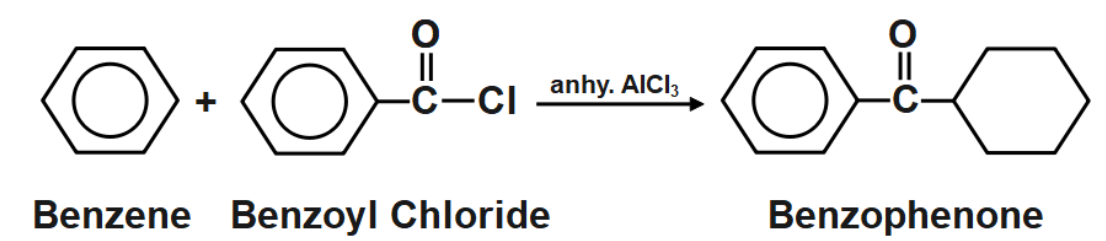
As we know that the Friedel Crafts Acylation method is used to obtain alkanes. But in this method, the reaction proceeds in two steps. In the first step, an acylated product is formed and then on further reduction an alkane is formed. The type of reaction is an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. It allows the syntheses of monoarylated products from the reaction between arenes and acyl chlorides. To process these reactions, Lewis Acid as catalyst is required as the reaction mechanism involves forming complexes of both the substrate and reactant as well.
The Friedel-Crafts acylation of benzene with benzoyl chloride within the presence of a Lewis Acid (e.g., \[AlC{{l}_{3}}\] ) and once benzene react with benzoyl chloride within the presence of \[AlC{{l}_{3}}\] as a catalyst to create benzophenone. This reaction is thought to be because of the Friedel-crafts acylation. The carbonyl gas of acid chloride forms complexes with \[AlC{{l}_{3}}.\] Acylium particles are created that could be a strong electrophile. Acylium particle attacks benzene ring to create arenium particle The arenium particle undergoes loss of proton and removal of \[HCl.\] The resultant product from these three steps are benzophenone.
Note:
Remember that the aluminium chloride is a Lewis acid and majorly used in a variety of reactions especially in substitution reactions. The reaction will take place and benzophenone will be formed but it will be so unstable that it will further react with the catalyst and form triphenylmethanol with phenyl magnesium bromide.
Complete answer:
As we know that the Friedel Crafts Acylation method is used to obtain alkanes. But in this method, the reaction proceeds in two steps. In the first step, an acylated product is formed and then on further reduction an alkane is formed. The type of reaction is an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. It allows the syntheses of monoarylated products from the reaction between arenes and acyl chlorides. To process these reactions, Lewis Acid as catalyst is required as the reaction mechanism involves forming complexes of both the substrate and reactant as well.
The Friedel-Crafts acylation of benzene with benzoyl chloride within the presence of a Lewis Acid (e.g., \[AlC{{l}_{3}}\] ) and once benzene react with benzoyl chloride within the presence of \[AlC{{l}_{3}}\] as a catalyst to create benzophenone. This reaction is thought to be because of the Friedel-crafts acylation. The carbonyl gas of acid chloride forms complexes with \[AlC{{l}_{3}}.\] Acylium particles are created that could be a strong electrophile. Acylium particle attacks benzene ring to create arenium particle The arenium particle undergoes loss of proton and removal of \[HCl.\] The resultant product from these three steps are benzophenone.

Note:
Remember that the aluminium chloride is a Lewis acid and majorly used in a variety of reactions especially in substitution reactions. The reaction will take place and benzophenone will be formed but it will be so unstable that it will further react with the catalyst and form triphenylmethanol with phenyl magnesium bromide.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




