
How do you convert a Kekule structure from Lewis diagram form to condensed and line-angle structure?
Answer
528k+ views
Hint: Lewis diagram tells the number of electrons between the atoms and with the help of this number of electrons we can find the number of bonds that are used to draw Kekule form. The condensed form shows the least substituents in the organic chain.
Complete answer:
According to Kekule, benzene's six carbon atoms form a hexagonal ring by forming alternate single and double covalent bonds. Drawing a Lewis diagram, also known as an electron dot diagram for the atom, is the simplest way to figure out how electrons are exchanged in a covalent molecule. In the Kekule structure all the bonds, i.e., the hydrogen bonds are also shown in the structure. The Kekule structure of benzene is given below:
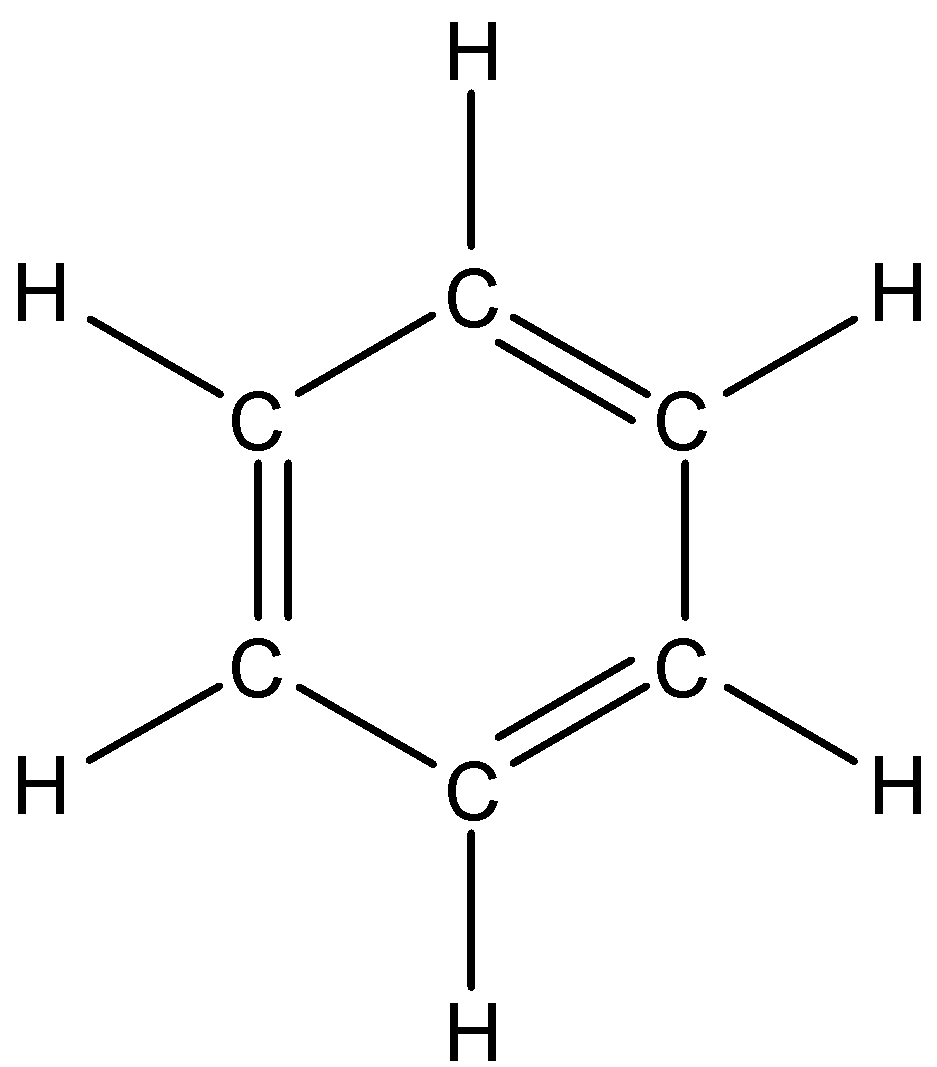
And we know that each bond is made up of two electrons between the atoms. So, this Kekule structure is made from the Lewis structure as given below:
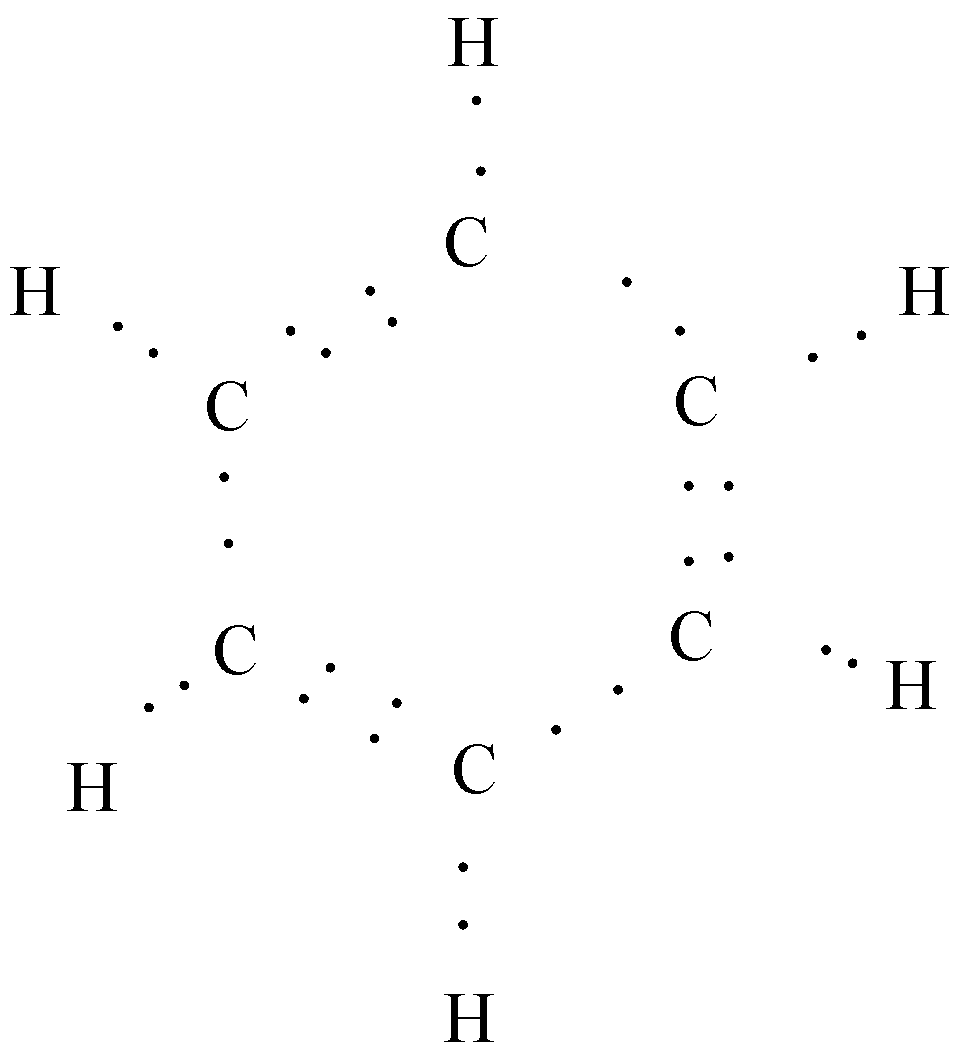
These structures can be converted into a condensed form in which we show the least substituent groups. Usually, only the different substituent groups are shown in the condensed form. so, the condensed form of the benzene will be:
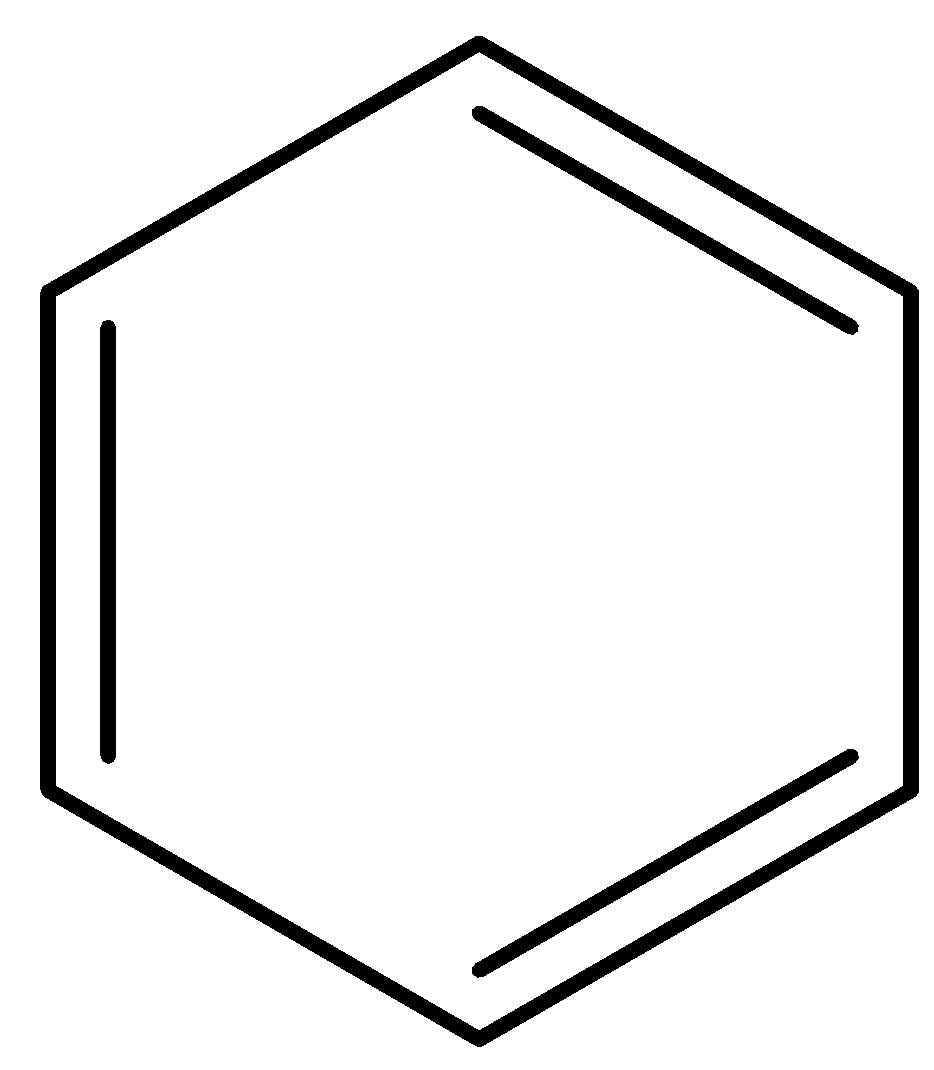
The line structure is derived from a simplified structure of the elements H and C that shows no atoms: bonds between C atoms are seen as lines, each vertice and end of the line structure represents C atoms, and the unfilled valencies are supposed to be filled by H.
Note:
Don’t forget that if the number of electrons between two atoms is two, then there will be only one bond, if there are four electrons then there will be two bonds and if there are six electrons then there will be a triple bond.
Complete answer:
According to Kekule, benzene's six carbon atoms form a hexagonal ring by forming alternate single and double covalent bonds. Drawing a Lewis diagram, also known as an electron dot diagram for the atom, is the simplest way to figure out how electrons are exchanged in a covalent molecule. In the Kekule structure all the bonds, i.e., the hydrogen bonds are also shown in the structure. The Kekule structure of benzene is given below:

And we know that each bond is made up of two electrons between the atoms. So, this Kekule structure is made from the Lewis structure as given below:

These structures can be converted into a condensed form in which we show the least substituent groups. Usually, only the different substituent groups are shown in the condensed form. so, the condensed form of the benzene will be:

The line structure is derived from a simplified structure of the elements H and C that shows no atoms: bonds between C atoms are seen as lines, each vertice and end of the line structure represents C atoms, and the unfilled valencies are supposed to be filled by H.
Note:
Don’t forget that if the number of electrons between two atoms is two, then there will be only one bond, if there are four electrons then there will be two bonds and if there are six electrons then there will be a triple bond.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




