
Construct the incircle and circumcircle of an equilateral \[\Delta DSP\] with side \[7.5\text{ cm}\]. Measure the radii of both the circles and find the ratio of radius of circumcircle to the radius of incircle.
Answer
617.1k+ views
Hint: Incentre is the meeting point of angle bisectors of triangle while circumcenter is meeting point of perpendicular bisector of sides and in equilateral triangle all the centers lie on the same point.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Here we have to construct the incircle and circumcircle of an equilateral \[\Delta DSP\] with side \[7.5\text{ cm}\]. Also we have to find the ratio of circumradius to inradius.
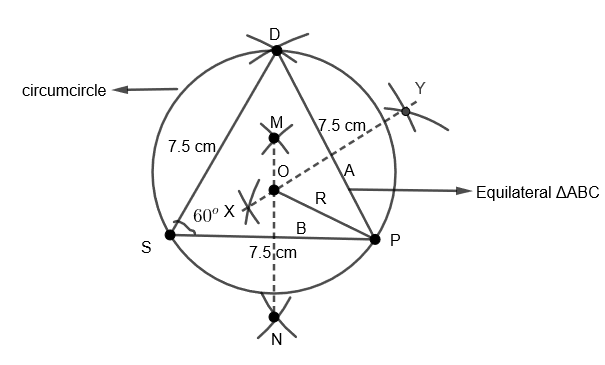
First of all we have to construct the equilateral \[\Delta DSP\] with side \[7.5\text{ cm}\] for which given steps should be followed.
1. Draw the line \[SP=7.5\text{ }cm\].
2. Now, with \[S\] as center and \[7.5\text{ }cm\] as radius, draw an arc above the line \[SP\].
3. With \[P\] as a center and \[7.5\text{ }cm\] as radius, cut an arc on the previous drawn arc and name the point \[D\].
4. Join \[DS\] and \[DP\]. Therefore our equilateral \[\Delta DSP\] is obtained.
Now to draw the circumcenter of \[\Delta DSP\], we need to follow the following steps.
1. As we know the circumcenter is a point of intersection of perpendicular bisectors of sides of a triangle. First, construct the perpendicular bisectors of sides.
2. We first have to mark the mid points of sides \[DP\] and \[SP\] which is at the length \[\dfrac{7.5}{2}=3.75\text{ cm}\] that is \[A\] and \[B\] respectively.
3. Now with \[D\] as a center and radius greater than \[DA\], draw two arcs on both sides of \[DP\].
4. With the same radius and center as \[P\], draw two arcs on both sides of \[DP\] cutting the previous arcs and name them \[X\] and \[Y\]. Join the \[X\] and \[Y\]. Therefore \[XY\] is a perpendicular bisector of \[DP\].
5. Now with \[S\] as center and radius greater than \[SB\], draw two arcs on both sides of \[SP\].
6. With the same radius and center as \[P\], draw two arcs on both sides of \[SP\] cutting the previous arcs and name them \[M\] and \[N\]. Join \[M\] and \[N\]. Therefore \[MN\] is a perpendicular bisector of \[SP\].
7. The point of intersection of \[MN\] and \[XY\] is \[O\], that is the circumcenter.
8. Circumradius of the given circle is \[OP=OD=OS=R\].
9. Therefore, with \[O\]as center and \[OP\]as radius, draw a circumcircle of \[\Delta DSP\].
10. Now measure the circumradius that is the length of \[OP\], which comes out to be \[OP=R=4.33\text{ cm}\].
Now to draw the incircle of \[\Delta DSP\], we need to follow the following steps.
1. Incircle is the point of intersection of angle bisectors of triangles.
2. As we know that, in an equilateral triangle, all the centers coincide. Therefore, with \[O\] as center and \[OA\] as radius, draw the incircle of \[\Delta DSP\] as shown.
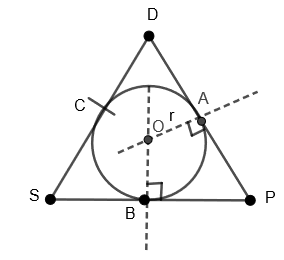
3. Inradius of the given incircle is \[OA=OB=OC=r\].
4. Now measure the inradius that is the length of \[OA\], which comes out to be \[OA=r=2.165\].
Therefore ratio radius of circumcircle to the radius of incircle \[=\dfrac{\text{length of circumradius}}{\text{length of inradius}}=\dfrac{OP}{OA}\]
Therefore we get, \[\dfrac{R}{r}=\dfrac{4.33}{2.165}=\dfrac{2}{1}=2:1\]
Note: Students can also first construct the angle bisectors and get the center with their intersection which is the same as \[O\]. Also, students must remember that incenter and circumcenter coincide only in equilateral triangles.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Here we have to construct the incircle and circumcircle of an equilateral \[\Delta DSP\] with side \[7.5\text{ cm}\]. Also we have to find the ratio of circumradius to inradius.

First of all we have to construct the equilateral \[\Delta DSP\] with side \[7.5\text{ cm}\] for which given steps should be followed.
1. Draw the line \[SP=7.5\text{ }cm\].
2. Now, with \[S\] as center and \[7.5\text{ }cm\] as radius, draw an arc above the line \[SP\].
3. With \[P\] as a center and \[7.5\text{ }cm\] as radius, cut an arc on the previous drawn arc and name the point \[D\].
4. Join \[DS\] and \[DP\]. Therefore our equilateral \[\Delta DSP\] is obtained.
Now to draw the circumcenter of \[\Delta DSP\], we need to follow the following steps.
1. As we know the circumcenter is a point of intersection of perpendicular bisectors of sides of a triangle. First, construct the perpendicular bisectors of sides.
2. We first have to mark the mid points of sides \[DP\] and \[SP\] which is at the length \[\dfrac{7.5}{2}=3.75\text{ cm}\] that is \[A\] and \[B\] respectively.
3. Now with \[D\] as a center and radius greater than \[DA\], draw two arcs on both sides of \[DP\].
4. With the same radius and center as \[P\], draw two arcs on both sides of \[DP\] cutting the previous arcs and name them \[X\] and \[Y\]. Join the \[X\] and \[Y\]. Therefore \[XY\] is a perpendicular bisector of \[DP\].
5. Now with \[S\] as center and radius greater than \[SB\], draw two arcs on both sides of \[SP\].
6. With the same radius and center as \[P\], draw two arcs on both sides of \[SP\] cutting the previous arcs and name them \[M\] and \[N\]. Join \[M\] and \[N\]. Therefore \[MN\] is a perpendicular bisector of \[SP\].
7. The point of intersection of \[MN\] and \[XY\] is \[O\], that is the circumcenter.
8. Circumradius of the given circle is \[OP=OD=OS=R\].
9. Therefore, with \[O\]as center and \[OP\]as radius, draw a circumcircle of \[\Delta DSP\].
10. Now measure the circumradius that is the length of \[OP\], which comes out to be \[OP=R=4.33\text{ cm}\].
Now to draw the incircle of \[\Delta DSP\], we need to follow the following steps.
1. Incircle is the point of intersection of angle bisectors of triangles.
2. As we know that, in an equilateral triangle, all the centers coincide. Therefore, with \[O\] as center and \[OA\] as radius, draw the incircle of \[\Delta DSP\] as shown.

3. Inradius of the given incircle is \[OA=OB=OC=r\].
4. Now measure the inradius that is the length of \[OA\], which comes out to be \[OA=r=2.165\].
Therefore ratio radius of circumcircle to the radius of incircle \[=\dfrac{\text{length of circumradius}}{\text{length of inradius}}=\dfrac{OP}{OA}\]
Therefore we get, \[\dfrac{R}{r}=\dfrac{4.33}{2.165}=\dfrac{2}{1}=2:1\]
Note: Students can also first construct the angle bisectors and get the center with their intersection which is the same as \[O\]. Also, students must remember that incenter and circumcenter coincide only in equilateral triangles.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




