
Construct an angle of $90^\circ $ at the initial point of a given ray and justify the construction.
Answer
590.4k+ views
Hint:We will draw two arcs of $60^\circ $ and $120^\circ $ then the bisector will be of angle $90^\circ $.
Complete step-by-step solution
Let us start the problem by step-by-step construction.The following are the steps to construct an angle of $90^\circ $.
Step 1:
Draw a ray OA. Taking O as centre and any radius, draw an arc that cuts OA at B.
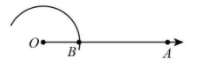
Step 2:
Now, taking B as centre and with the same radius as before, draw an arc intersecting the previously drawn arc at point C.
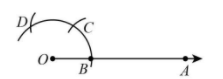
Step 3: With C as centre and the same radius, draw an arc cutting the arc at D.
Step 5:
With C and D as centres and radius more than half of CD, draw two arcs intersecting at P.
Step 6:
Join OP.
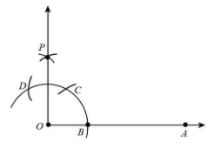
Therefore, the angle of $90^\circ $ at the initial point of the given ray is obtained.
JUSTIFICATION
Here, we will prove that$\angle AOP = 90^\circ $.
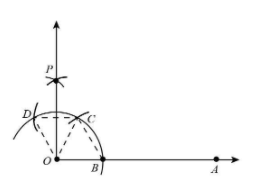
Construction
Join OC and BC
Also, sides OB, BC and OC are equal because these are radii of equal arcs.
$OB = BC = OC$
Therefore, \[\Delta OCB\] is an equilateral triangle in which,
\[\angle BOC = 60^\circ \]
Now, Join OD, OC and CD.
Also, sides OD, OC and DC are equal because these are radii of equal arcs.
\[OD = OC = DC\]
Therefore, \[\Delta DOC\] is an equilateral triangle in which,
\[\angle DOC = 60^\circ \]
Also, Join PD and PC.
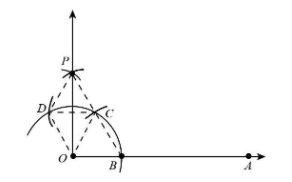
In triangle ODP and triangle OCP,
\[\begin{array}{*{20}{l}}
{OC = OD}\\
{DP = CP}\\
{OP = OP}
\end{array}\]
Therefore, both the triangles $\Delta ODP \cong \Delta OCP$ are congruent through the SSS congruent rule.
Also, by CPCT,
$\angle DOP = \angle COP$
Now, we can say that
$\begin{array}{c}
\angle DOP = \angle COP\\
\angle DOP = \dfrac{1}{2} \times \angle DOC\\
\angle DOP = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 60^\circ = 30^\circ
\end{array}$
Since, we know that,
$\begin{array}{l}
\angle AOP = \angle BOC + \angle COP\\
\angle AOP = 60^\circ + 30^\circ \\
\angle AOP = 90^\circ
\end{array}$
Hence, $\angle AOP = 90^\circ $ is justified.
Note:Circumcircle of a triangle is a circle on which all three vertices of triangle lie. Make sure to draw the circle through the points A, B and P and join line OB and OC.
Complete step-by-step solution
Let us start the problem by step-by-step construction.The following are the steps to construct an angle of $90^\circ $.
Step 1:
Draw a ray OA. Taking O as centre and any radius, draw an arc that cuts OA at B.

Step 2:
Now, taking B as centre and with the same radius as before, draw an arc intersecting the previously drawn arc at point C.

Step 3: With C as centre and the same radius, draw an arc cutting the arc at D.
Step 5:
With C and D as centres and radius more than half of CD, draw two arcs intersecting at P.
Step 6:
Join OP.

Therefore, the angle of $90^\circ $ at the initial point of the given ray is obtained.
JUSTIFICATION
Here, we will prove that$\angle AOP = 90^\circ $.

Construction
Join OC and BC
Also, sides OB, BC and OC are equal because these are radii of equal arcs.
$OB = BC = OC$
Therefore, \[\Delta OCB\] is an equilateral triangle in which,
\[\angle BOC = 60^\circ \]
Now, Join OD, OC and CD.
Also, sides OD, OC and DC are equal because these are radii of equal arcs.
\[OD = OC = DC\]
Therefore, \[\Delta DOC\] is an equilateral triangle in which,
\[\angle DOC = 60^\circ \]
Also, Join PD and PC.

In triangle ODP and triangle OCP,
\[\begin{array}{*{20}{l}}
{OC = OD}\\
{DP = CP}\\
{OP = OP}
\end{array}\]
Therefore, both the triangles $\Delta ODP \cong \Delta OCP$ are congruent through the SSS congruent rule.
Also, by CPCT,
$\angle DOP = \angle COP$
Now, we can say that
$\begin{array}{c}
\angle DOP = \angle COP\\
\angle DOP = \dfrac{1}{2} \times \angle DOC\\
\angle DOP = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 60^\circ = 30^\circ
\end{array}$
Since, we know that,
$\begin{array}{l}
\angle AOP = \angle BOC + \angle COP\\
\angle AOP = 60^\circ + 30^\circ \\
\angle AOP = 90^\circ
\end{array}$
Hence, $\angle AOP = 90^\circ $ is justified.
Note:Circumcircle of a triangle is a circle on which all three vertices of triangle lie. Make sure to draw the circle through the points A, B and P and join line OB and OC.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




