
Construct an angle of $45^\circ $ from a horizontal line and justify the construction.
Answer
589.5k+ views
Hint: Here, in the construction we will first draw angle of 90 degrees then find its angle bisector to get angle of 45 degrees.
Complete Step-by-step Solution
Step 1 Draw a ray OA.
Step 2 Taking O as centre and any radius, draw an arc cutting OA at B.
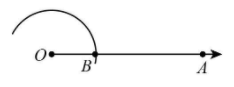
Step 3 Taking B as centre and with the same radius as before, draw an arc intersecting the previously drawn arc at point C.
Step 4 With C as centre and the same radius, draw an arc cutting the arc at D.
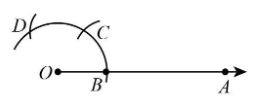
Step 5 With C and D as centres and radius more than half of CD, draw two arc intersecting at P.
Step 6 Join OP.
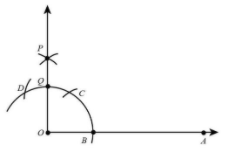
Step 7.Now, we draw a bisector of angle AOP. Let OP intersect the original arc at point Q.
Step 8. Taking B and Q as centres, and radius greater than half of BQ, draw two arcs intersecting at R.
Step 9. Join OR.
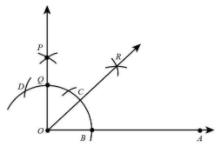
Thus, the angle $45^\circ $ from the horizontal line is constructed that is$\angle AOR = 45^\circ $
JUSTIFICATION
>Join OC and OB.
>Also, sides OB, BC and OC are equal because these are radii of equal arcs.
\[OB = BC = OC\]
>Therefore, $\Delta OCB$ is an equilateral triangle in which,
$\angle BOC = 60^\circ $
>Join OD, OC and CD
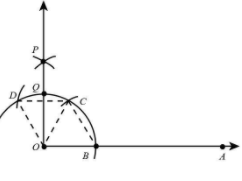
Also, sides OD, OC and DC are equal because these are radii of equal arcs.
\[OD = OC = DC\]
Therefore, $\Delta DOC$ is an equilateral triangle.
$\angle DOC = 60^\circ $
Join PD and PC
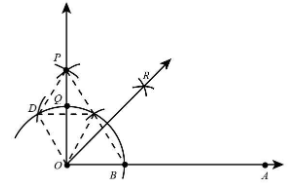
In triangle ODP and triangle OCP,
\[\begin{array}{*{20}{l}}
{OD = OC}\\
\begin{array}{l}
DP = CP{\rm{ }}\\
OP = OP
\end{array}
\end{array}\]
Therefore, both the triangles $\Delta ODP \cong \Delta OCP$ are congruent through SSS Congruency.
Also, by CPCT,
$\angle DOP = \angle COP$
So, we can say that,
$\begin{array}{c}
\angle DOP = \angle COP\\
\angle DOP = \frac{1}{2}\angle DOC\\
\angle DOP = \frac{1}{2} \times 60^\circ \\
\angle DOP = 30^\circ
\end{array}$
Now,
$\begin{array}{c}
\angle AOP = \angle BOC + \angle COP\\
\angle AOP = 60^\circ + 30^\circ \\
= 90^\circ
\end{array}$
Join QR and BR.
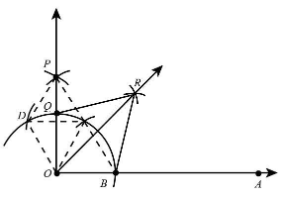
In triangle OQR and triangle OBR,
\[\begin{array}{*{20}{l}}
{OQ = OB}\\
{QR = BR}\\
{OR = OR}
\end{array}\]
Therefore, $\Delta OQR \cong \Delta OBR$ is congruent through SSS Congruency.
Also, by CPCT,
$\angle QOR = \angle BOR$
Now, we can say that,
$\begin{array}{l}
\angle QOR = \angle BOR\\
\angle QOR = \frac{1}{2}\angle AOP\\
\angle QOR = \frac{1}{2} \times 90^\circ \\
\angle QOR = 45^\circ
\end{array}$
Thus, the angle $\angle AOR = 45^\circ $ is justified.
Note:In this problem, make sure to use the corresponding parts of the congruent triangle theorem that is the CPCT theorem to prove that angle QOR and BOR are equal. While drawing the arc, make sure that the arc is intersecting at point R.
Complete Step-by-step Solution
Step 1 Draw a ray OA.
Step 2 Taking O as centre and any radius, draw an arc cutting OA at B.

Step 3 Taking B as centre and with the same radius as before, draw an arc intersecting the previously drawn arc at point C.
Step 4 With C as centre and the same radius, draw an arc cutting the arc at D.

Step 5 With C and D as centres and radius more than half of CD, draw two arc intersecting at P.
Step 6 Join OP.

Step 7.Now, we draw a bisector of angle AOP. Let OP intersect the original arc at point Q.
Step 8. Taking B and Q as centres, and radius greater than half of BQ, draw two arcs intersecting at R.
Step 9. Join OR.

Thus, the angle $45^\circ $ from the horizontal line is constructed that is$\angle AOR = 45^\circ $
JUSTIFICATION
>Join OC and OB.
>Also, sides OB, BC and OC are equal because these are radii of equal arcs.
\[OB = BC = OC\]
>Therefore, $\Delta OCB$ is an equilateral triangle in which,
$\angle BOC = 60^\circ $
>Join OD, OC and CD

Also, sides OD, OC and DC are equal because these are radii of equal arcs.
\[OD = OC = DC\]
Therefore, $\Delta DOC$ is an equilateral triangle.
$\angle DOC = 60^\circ $
Join PD and PC

In triangle ODP and triangle OCP,
\[\begin{array}{*{20}{l}}
{OD = OC}\\
\begin{array}{l}
DP = CP{\rm{ }}\\
OP = OP
\end{array}
\end{array}\]
Therefore, both the triangles $\Delta ODP \cong \Delta OCP$ are congruent through SSS Congruency.
Also, by CPCT,
$\angle DOP = \angle COP$
So, we can say that,
$\begin{array}{c}
\angle DOP = \angle COP\\
\angle DOP = \frac{1}{2}\angle DOC\\
\angle DOP = \frac{1}{2} \times 60^\circ \\
\angle DOP = 30^\circ
\end{array}$
Now,
$\begin{array}{c}
\angle AOP = \angle BOC + \angle COP\\
\angle AOP = 60^\circ + 30^\circ \\
= 90^\circ
\end{array}$
Join QR and BR.

In triangle OQR and triangle OBR,
\[\begin{array}{*{20}{l}}
{OQ = OB}\\
{QR = BR}\\
{OR = OR}
\end{array}\]
Therefore, $\Delta OQR \cong \Delta OBR$ is congruent through SSS Congruency.
Also, by CPCT,
$\angle QOR = \angle BOR$
Now, we can say that,
$\begin{array}{l}
\angle QOR = \angle BOR\\
\angle QOR = \frac{1}{2}\angle AOP\\
\angle QOR = \frac{1}{2} \times 90^\circ \\
\angle QOR = 45^\circ
\end{array}$
Thus, the angle $\angle AOR = 45^\circ $ is justified.
Note:In this problem, make sure to use the corresponding parts of the congruent triangle theorem that is the CPCT theorem to prove that angle QOR and BOR are equal. While drawing the arc, make sure that the arc is intersecting at point R.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

10 examples of friction in our daily life




