
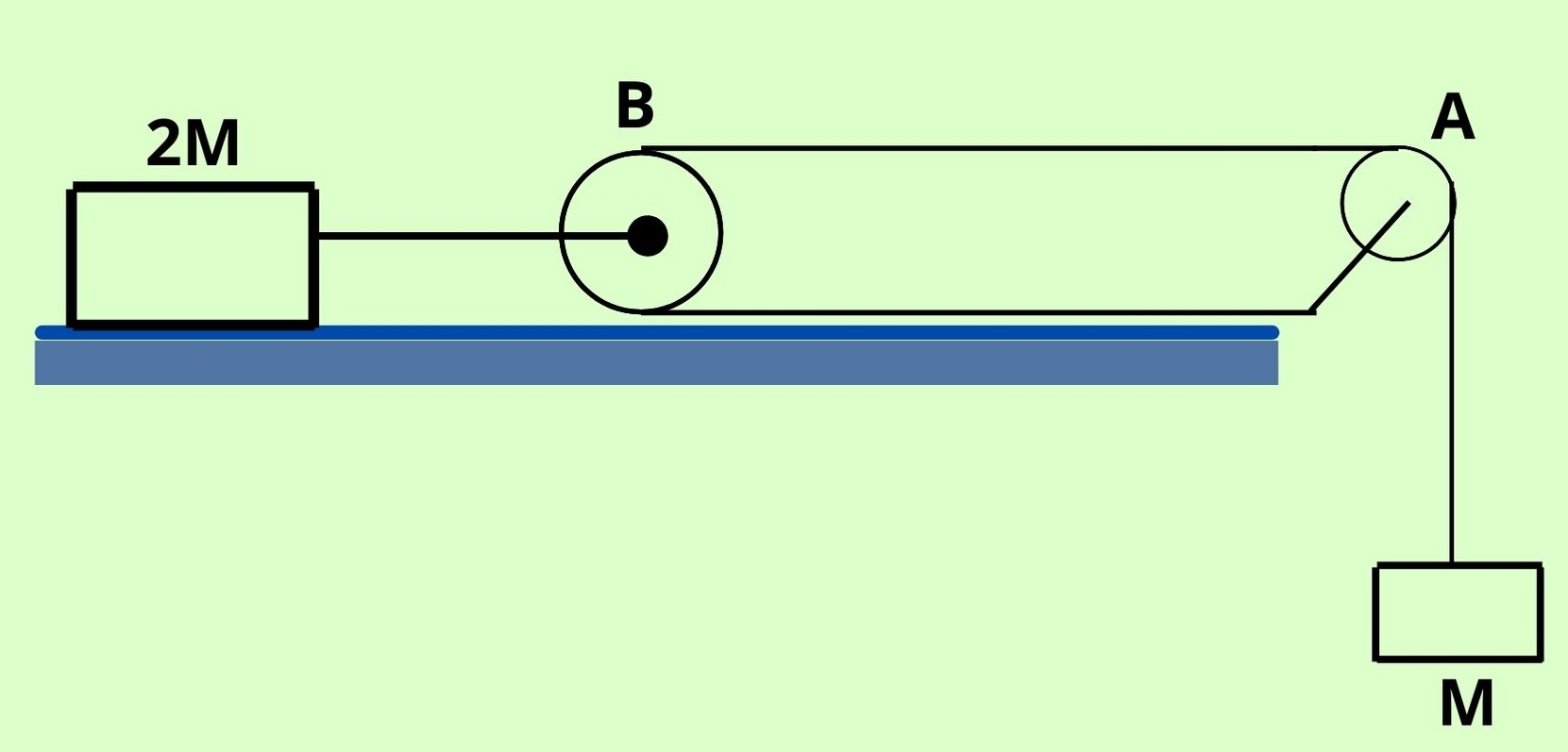
Consider the situation in figure. Both the pulleys and the string are light and all the surfaces are frictionless. Calculate the force exerted by the clamp on the pulley A in the figure.

Answer
535.2k+ views
Hint: The above problem can be solved by using the equilibrium equations of the forces in the given system. The hanged mass exerts the tension in the string. Both the strings between the pulley A and pulley B also remain under the tension in both strings. The block on the table starts moving if the effect of the tension in both strings becomes more than the force of the block.
Complete step by step solution:
Given: The mass of the hanging block is M, mass of the block on the table is 2 M.
The force on the block on the table is given as:
$T + T = Ma$
$2T = Ma$
$T = \dfrac{{Ma}}{2}$
The equilibrium equation for horizontal equilibrium is given as:
$T + Ma - Mg = 0......\left( 1 \right)$
Substitute all the values in the above expression.
$\dfrac{{Ma}}{2} + Ma - Mg = 0$
$\dfrac{{3Ma}}{2} = Mg$
$a = \dfrac{{2g}}{3}$
The resultant force exerted by the clamp on the pulley A is given as:
$F = \sqrt 2 T$
Substituting all the values in the above expression.
$F = \sqrt 2 \left( {Ma} \right)$
$F = \sqrt 2 M\left( {\dfrac{{2g}}{3}} \right)$
On simplification, we get
$F = \dfrac{{2\sqrt 2 Mg}}{3}$
Therefore, the resultant force exerted by the clamp on the pulley A is $\dfrac{{2\sqrt 2 Mg}}{3}$.
Additional Information:
The resultant tension of the both strings at the pulley A is obtained by the horizontal and vertical components of the tension acting on the pulley A.
Note: The tension arises in the string due to the weight of the hanging mass in downward direction. The object remains in the equilibrium conditions if the net forces in horizontal and vertical direction become zero.
Complete step by step solution:
Given: The mass of the hanging block is M, mass of the block on the table is 2 M.
The force on the block on the table is given as:
$T + T = Ma$
$2T = Ma$
$T = \dfrac{{Ma}}{2}$
The equilibrium equation for horizontal equilibrium is given as:
$T + Ma - Mg = 0......\left( 1 \right)$
Substitute all the values in the above expression.
$\dfrac{{Ma}}{2} + Ma - Mg = 0$
$\dfrac{{3Ma}}{2} = Mg$
$a = \dfrac{{2g}}{3}$
The resultant force exerted by the clamp on the pulley A is given as:
$F = \sqrt 2 T$
Substituting all the values in the above expression.
$F = \sqrt 2 \left( {Ma} \right)$
$F = \sqrt 2 M\left( {\dfrac{{2g}}{3}} \right)$
On simplification, we get
$F = \dfrac{{2\sqrt 2 Mg}}{3}$
Therefore, the resultant force exerted by the clamp on the pulley A is $\dfrac{{2\sqrt 2 Mg}}{3}$.
Additional Information:
The resultant tension of the both strings at the pulley A is obtained by the horizontal and vertical components of the tension acting on the pulley A.
Note: The tension arises in the string due to the weight of the hanging mass in downward direction. The object remains in the equilibrium conditions if the net forces in horizontal and vertical direction become zero.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




