
Consider the regular hexagon ABCDEF with center at O (origin).
Find the resultant vector for $ \overrightarrow{AD}+\overrightarrow{EB}+\overrightarrow{FC} $ .
A. $ 2\overrightarrow{AB} $
B. $ 3\overrightarrow{AB} $
C. $ 4\overrightarrow{AB} $
D. None of these.
Answer
566.4k+ views
Hint: A regular hexagon has 6 sides of equal length and 6 equal angles measuring $ 120{}^\circ $ each.
A regular hexagon can be divided into 6 identical equilateral triangles by joining each vertex with the center.
The resultant is the vector sum of two or more vectors. It is the result of adding two or more vectors together.
Vectors are added using the Triangle Law of vector addition:
$ \overrightarrow{PQ}+\overrightarrow{QR}=\overrightarrow{PR} $
Complete step by step answer:
Let's draw the diagram for the given vectors:
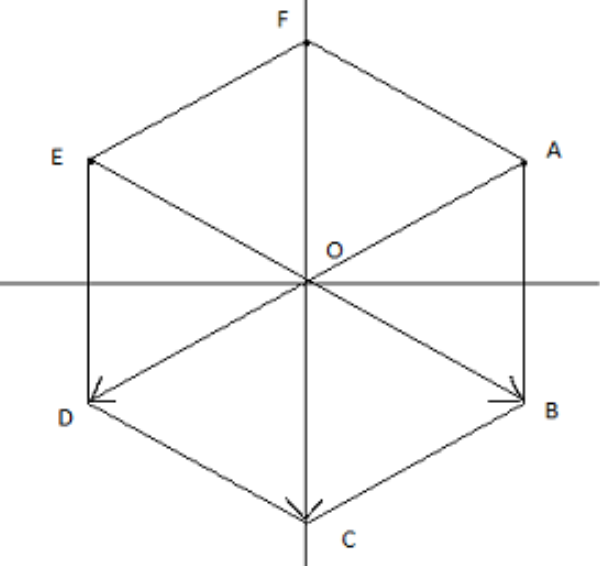
We know that the 6 equilateral triangles around the center are identical.
∴ $ \overrightarrow{AB}=\overrightarrow{OC} $ ... (1)
$ \overrightarrow{AD}=2\overrightarrow{AO} $ ... (2)
$ \overrightarrow{EB}=2\overrightarrow{OB} $ ... (3)
$ \overrightarrow{FC}=2\overrightarrow{OC} $ ... (4)
Now, $ \overrightarrow{AD}+\overrightarrow{EB}+\overrightarrow{FC} $
= $ 2\overrightarrow{AO}+2\overrightarrow{OB}+2\overrightarrow{OC} $ ... [Using (2), (3) and (4).]
= $ 2\left( \overrightarrow{AO}+\overrightarrow{OB} \right)+2\overrightarrow{AB} $ ... [Using (1).]
= $ 2\left( \overrightarrow{AB} \right)+2\overrightarrow{AB} $ ... [Using Triangle law of vector addition.]
= $ 4\overrightarrow{AB} $
The correct answer is C. $ 4\overrightarrow{AB} $ .
Note: The direction of a vector is important: $ \overrightarrow{AB}=-\overrightarrow{BA} $ .
The vector component along the x-axis, of a vector $ \overrightarrow{r} $ which makes an angle $ \theta $ with the positive direction of the x-axis, is $ \overrightarrow{r}\sin \theta $ and the component along the y-axis is $ \overrightarrow{r}\cos \theta $ .
A regular polygon has sides of equal length and equal angles as well. All vertices are at equal distances from the center, and all the sides are also at equal distances from the center.
A regular hexagon can be divided into 6 identical equilateral triangles by joining each vertex with the center.
The resultant is the vector sum of two or more vectors. It is the result of adding two or more vectors together.
Vectors are added using the Triangle Law of vector addition:
$ \overrightarrow{PQ}+\overrightarrow{QR}=\overrightarrow{PR} $
Complete step by step answer:
Let's draw the diagram for the given vectors:

We know that the 6 equilateral triangles around the center are identical.
∴ $ \overrightarrow{AB}=\overrightarrow{OC} $ ... (1)
$ \overrightarrow{AD}=2\overrightarrow{AO} $ ... (2)
$ \overrightarrow{EB}=2\overrightarrow{OB} $ ... (3)
$ \overrightarrow{FC}=2\overrightarrow{OC} $ ... (4)
Now, $ \overrightarrow{AD}+\overrightarrow{EB}+\overrightarrow{FC} $
= $ 2\overrightarrow{AO}+2\overrightarrow{OB}+2\overrightarrow{OC} $ ... [Using (2), (3) and (4).]
= $ 2\left( \overrightarrow{AO}+\overrightarrow{OB} \right)+2\overrightarrow{AB} $ ... [Using (1).]
= $ 2\left( \overrightarrow{AB} \right)+2\overrightarrow{AB} $ ... [Using Triangle law of vector addition.]
= $ 4\overrightarrow{AB} $
The correct answer is C. $ 4\overrightarrow{AB} $ .
Note: The direction of a vector is important: $ \overrightarrow{AB}=-\overrightarrow{BA} $ .
The vector component along the x-axis, of a vector $ \overrightarrow{r} $ which makes an angle $ \theta $ with the positive direction of the x-axis, is $ \overrightarrow{r}\sin \theta $ and the component along the y-axis is $ \overrightarrow{r}\cos \theta $ .
A regular polygon has sides of equal length and equal angles as well. All vertices are at equal distances from the center, and all the sides are also at equal distances from the center.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

The Equation xxx + 2 is Satisfied when x is Equal to Class 10 Maths

Which Country is Called "The Land of Festivals"?

What is Contraception List its four different methods class 10 biology CBSE




