
Consider a circular coil of wire carrying a constant current I, forming a magnetic dipole. The magnetic flux through an infinite plane contains the circular coil and excluding the circular area is given by ${\phi _i}$. The magnetic flux through the area of the circular coil area is given by ${\phi _0}$.
Which of the following options is correct?
$
{\text{A}}{\text{. }}{\phi _i} < {\phi _0} \\
{\text{B}}{\text{. }}{\phi _i} = {\phi _0} \\
{\text{C}}{\text{. }}{\phi _i} > {\phi _0} \\
{\text{D}}{\text{. }}{\phi _i} = - {\phi _0} \\
$
Answer
613.8k+ views
Hint: The magnetic field lines formed around a current carrying loop are circular in shape. So, think about the magnetic flux generated inside and outside the loop and then compare.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Magnetic Flux- It is defined as the number of magnetic field lines that pass through a given closed surface. It is a measure of the magnetic field intensity from a given area.
It is the product of the magnetic field and the projected surface area through the field.
The formula for magnetic flux is:
$\phi = B.A = BA\cos \theta $
Magnetic flux follows superposition, as flux due to different fields is added to calculate the net flux through a given area. Flux is a vector, so sign is concerned with it, to mention its direction. It describes the effects of the magnetic force on something occupying a given area.
Applications of magnetic flux
1.) In electric motors and generators, where faraday’s laws are used to generate the fields.
Used in explaining the non-existence of magnetic monopoles.
Here, ${\phi _i}{\text{ and }}{\phi _0}$ are the fluxes through the inner and outer regions of the loop. In case of a current carrying loop, circular magnetic field lines are generated. Now taking the vector inside and outside the loop, they are exactly the same in magnitudes but opposite in directions.
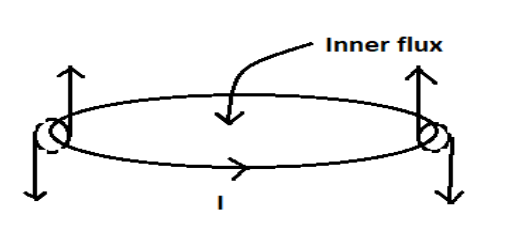
So, the outer and inner fluxes are the same.
\[{\text{ }}{\phi _i} = {\phi _0}\]
But are just opposite in direction
\[{\phi _i} = - {\phi _0}\]
The correct option is (D).
Note: One should be thorough with the concept of magnetic flux and the area considered. Despite the outer region having a larger area, the magnetic fields link only with the small projected area.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Magnetic Flux- It is defined as the number of magnetic field lines that pass through a given closed surface. It is a measure of the magnetic field intensity from a given area.
It is the product of the magnetic field and the projected surface area through the field.
The formula for magnetic flux is:
$\phi = B.A = BA\cos \theta $
Magnetic flux follows superposition, as flux due to different fields is added to calculate the net flux through a given area. Flux is a vector, so sign is concerned with it, to mention its direction. It describes the effects of the magnetic force on something occupying a given area.
Applications of magnetic flux
1.) In electric motors and generators, where faraday’s laws are used to generate the fields.
Used in explaining the non-existence of magnetic monopoles.
Here, ${\phi _i}{\text{ and }}{\phi _0}$ are the fluxes through the inner and outer regions of the loop. In case of a current carrying loop, circular magnetic field lines are generated. Now taking the vector inside and outside the loop, they are exactly the same in magnitudes but opposite in directions.

So, the outer and inner fluxes are the same.
\[{\text{ }}{\phi _i} = {\phi _0}\]
But are just opposite in direction
\[{\phi _i} = - {\phi _0}\]
The correct option is (D).
Note: One should be thorough with the concept of magnetic flux and the area considered. Despite the outer region having a larger area, the magnetic fields link only with the small projected area.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the class 12 chemistry CBSE

Define Vant Hoff factor How is it related to the degree class 12 chemistry CBSE




