
Conjugate base of $N{H_3}$ is:
A.$N{H_4}^ + $
B.$N{H_2}^ + $
C.$N{H_2}^ - $
D.${N_2}$
Answer
589.5k+ views
Hint: We can define Bronsted-Lowry acid as proton donor and comprises a hydrogen atom. It may be a neutral molecule or may contain a net positive or negative charge.
We can define a conjugate base as the product formed by a loss of proton from an acid. The conjugate base of the acid A will be ${{\text{A}}^{\text{ - }}}{\text{.}}$
Complete step by step answer:
Based on the Bronsted-Lowry Theory, a substance, which releases a proton, is an acid and a base is a substance, which accepts a proton.
Let us consider an example of hydrochloric acid reacting with ammonia to form ammonium ions and chloride ions.
We can write the chemical reaction as,
$HCl\left( {aq} \right) + N{H_3}\left( {aq} \right)\xrightarrow{{}}N{H_4}^ + \left( {aq} \right) + C{l^ - }\left( {aq} \right)$
In the above equation, we can see that hydrochloric acid has donated a proton to ammonia, and ammonia has accepted a proton. Therefore, we can say hydrochloric acid is Bronsted-Lowry acid (proton donor), and ammonia as Bronsted-Lowry base (proton acceptor). Here, ammonium ion is a conjugate acid of ammonia and chloride ions are conjugate bases of hydrochloric acid.
We can define a conjugate base as the product formed by loss of proton from an acid. The conjugate base of the acid A will be ${A^ - }.$
A conjugate acid is the product formed by gain of a proton by a base. The conjugate acid of the base B will be $H{B^ + }{\text{.}}$
Now let us identify the conjugate base of $N{H_3}$.
Ammonia $\left( {N{H_3}} \right)$ loses a proton and acts as an acid. We can write the chemical equation as,
\[N{H_3}\xrightarrow{{ - {H^ + }}}N{H_2}^ - \]
Ammonia loses a proton and forms its conjugate base $N{H_2}^ - $.
Ammonia is the acid and $N{H_2}^ - $ is the conjugate base of $N{H_3}$.
We can give the structure of ammonia as,
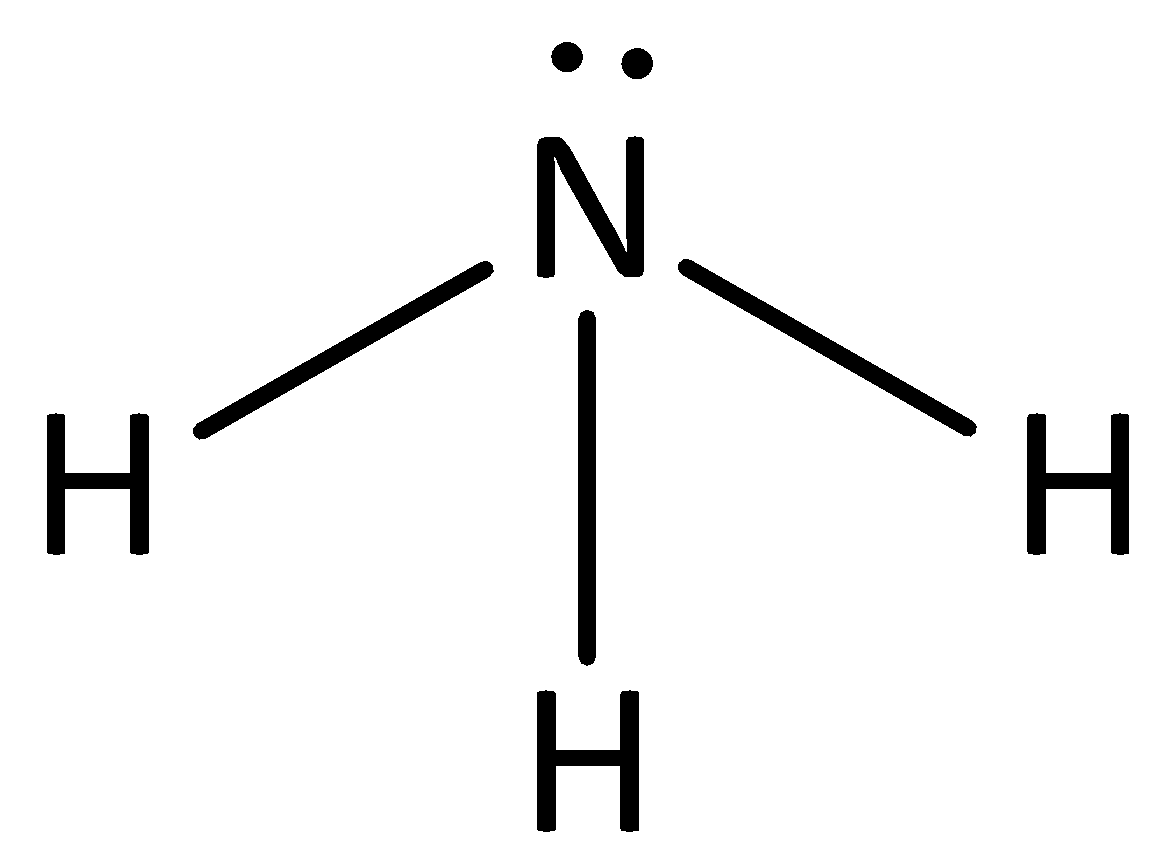
The conjugate base of ammonia will have the structure as,
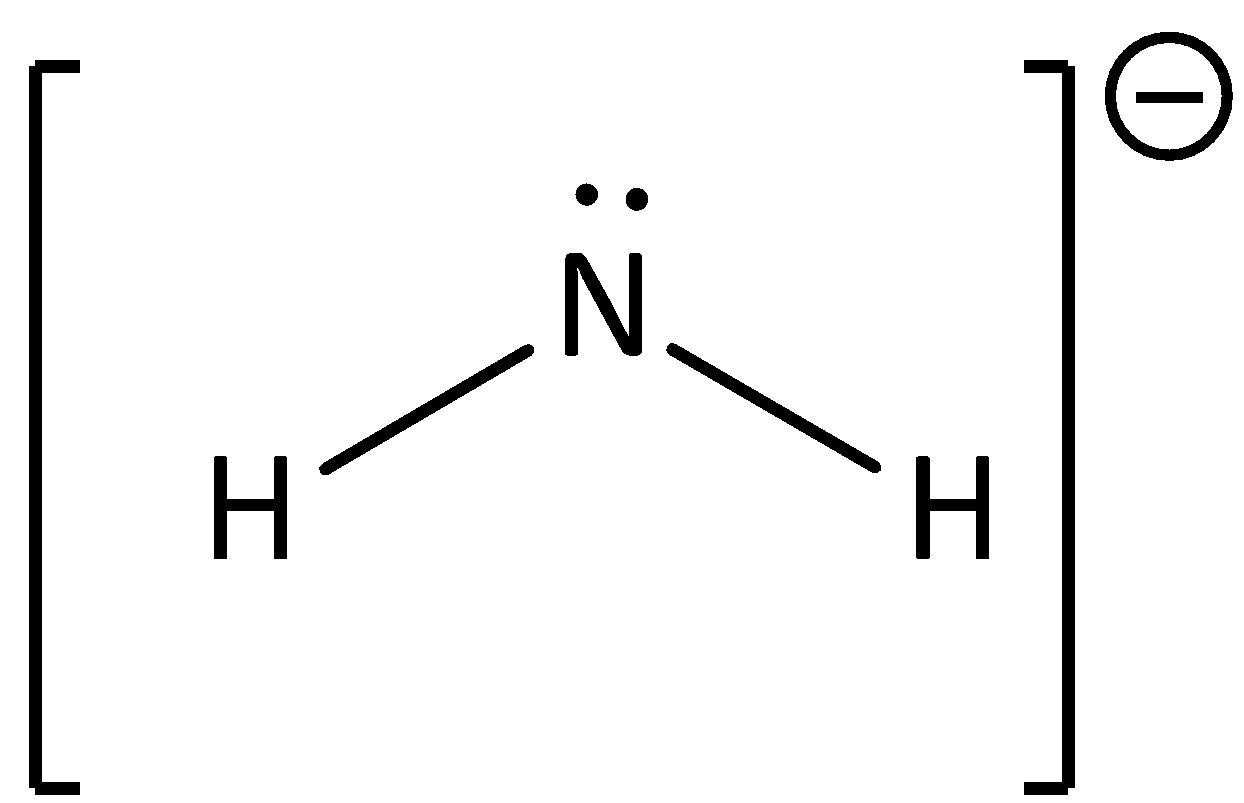
$\therefore $Option (C) is correct.
Note:
We know that acid loses a proton and forms a conjugate base. Base accepts a proton and forms conjugate acid.
Example 1: Let us consider the reaction given below,
\[N{H_3}\left( g \right) + HI\left( g \right)\xrightarrow{{}}{I^ - }\left( {aq} \right) + N{H_4}^ + \left( {aq} \right)\]
Hydrogen iodide loses its proton to form iodide. Ammonia gains a proton to form ammonium ion.
The acid in the reaction is $HI$
The conjugate base of the acid is ${I^ - }$
The base in the reaction is $N{H_3}$
The conjugate acid of the base is $N{H_4}^ + $
Example 2: Let us consider the reaction given below,
$HCOOH\left( l \right) + {H_2}O\left( l \right)\xrightarrow{{}}HCO{O^ - }\left( {aq} \right) + {H_3}{O^ + }\left( {aq} \right)$
Formic acid loses a proton to form formate ion. Water gains a proton and forms hydronium ion.
The acid in the reaction is $HCOOH$
The conjugate base of the acid is $HCO{O^ - }$
The base in the reaction is ${H_2}O$
The conjugate acid of the base is ${H_3}{O^ + }$
Example 3: Let us consider the reaction given below,
$HS{O_4}{^ - _{\left( {aq} \right)}} + {H_2}{O_{(l)}}\xrightarrow{{}}{H_2}S{O_4}_{\left( {aq} \right)} + O{H^ - }_{\left( {aq} \right)}$
$HS{O_4}^ - $ gains a proton and forms sulphuric acid. Water loses a proton to form hydronium ion.
The acid in the reaction is ${H_2}O$
The conjugate base of the acid is $O{H^ - }$
The base in the reaction is $HS{O_4}^ - $
The conjugate acid of the base is ${H_2}S{O_4}$
We can define a conjugate base as the product formed by a loss of proton from an acid. The conjugate base of the acid A will be ${{\text{A}}^{\text{ - }}}{\text{.}}$
Complete step by step answer:
Based on the Bronsted-Lowry Theory, a substance, which releases a proton, is an acid and a base is a substance, which accepts a proton.
Let us consider an example of hydrochloric acid reacting with ammonia to form ammonium ions and chloride ions.
We can write the chemical reaction as,
$HCl\left( {aq} \right) + N{H_3}\left( {aq} \right)\xrightarrow{{}}N{H_4}^ + \left( {aq} \right) + C{l^ - }\left( {aq} \right)$
In the above equation, we can see that hydrochloric acid has donated a proton to ammonia, and ammonia has accepted a proton. Therefore, we can say hydrochloric acid is Bronsted-Lowry acid (proton donor), and ammonia as Bronsted-Lowry base (proton acceptor). Here, ammonium ion is a conjugate acid of ammonia and chloride ions are conjugate bases of hydrochloric acid.
We can define a conjugate base as the product formed by loss of proton from an acid. The conjugate base of the acid A will be ${A^ - }.$
A conjugate acid is the product formed by gain of a proton by a base. The conjugate acid of the base B will be $H{B^ + }{\text{.}}$
Now let us identify the conjugate base of $N{H_3}$.
Ammonia $\left( {N{H_3}} \right)$ loses a proton and acts as an acid. We can write the chemical equation as,
\[N{H_3}\xrightarrow{{ - {H^ + }}}N{H_2}^ - \]
Ammonia loses a proton and forms its conjugate base $N{H_2}^ - $.
Ammonia is the acid and $N{H_2}^ - $ is the conjugate base of $N{H_3}$.
We can give the structure of ammonia as,

The conjugate base of ammonia will have the structure as,

$\therefore $Option (C) is correct.
Note:
We know that acid loses a proton and forms a conjugate base. Base accepts a proton and forms conjugate acid.
Example 1: Let us consider the reaction given below,
\[N{H_3}\left( g \right) + HI\left( g \right)\xrightarrow{{}}{I^ - }\left( {aq} \right) + N{H_4}^ + \left( {aq} \right)\]
Hydrogen iodide loses its proton to form iodide. Ammonia gains a proton to form ammonium ion.
The acid in the reaction is $HI$
The conjugate base of the acid is ${I^ - }$
The base in the reaction is $N{H_3}$
The conjugate acid of the base is $N{H_4}^ + $
Example 2: Let us consider the reaction given below,
$HCOOH\left( l \right) + {H_2}O\left( l \right)\xrightarrow{{}}HCO{O^ - }\left( {aq} \right) + {H_3}{O^ + }\left( {aq} \right)$
Formic acid loses a proton to form formate ion. Water gains a proton and forms hydronium ion.
The acid in the reaction is $HCOOH$
The conjugate base of the acid is $HCO{O^ - }$
The base in the reaction is ${H_2}O$
The conjugate acid of the base is ${H_3}{O^ + }$
Example 3: Let us consider the reaction given below,
$HS{O_4}{^ - _{\left( {aq} \right)}} + {H_2}{O_{(l)}}\xrightarrow{{}}{H_2}S{O_4}_{\left( {aq} \right)} + O{H^ - }_{\left( {aq} \right)}$
$HS{O_4}^ - $ gains a proton and forms sulphuric acid. Water loses a proton to form hydronium ion.
The acid in the reaction is ${H_2}O$
The conjugate base of the acid is $O{H^ - }$
The base in the reaction is $HS{O_4}^ - $
The conjugate acid of the base is ${H_2}S{O_4}$
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




