
What compound is the terminal electron acceptor in aerobic respiration?
Answer
577.5k+ views
Hint: To produce energy, the electrons from the inner mitochondrial membrane of the cell should pass through ETC. In ETC each electron donor passes electrons to electron acceptors until all electrons reach the most electronegative terminal molecule. Aerobic respiration happens in presence of oxygen.
Complete step by step answer: Aerobic respiration is a process that happens in the presence of oxygen and provides energy to the cells in the form of ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) from glucose. The process comprises various steps including glycolysis, formation of Acetyl coenzyme A, citric acid cycle, and electron transport chain, ETC. The end products of aerobic respiration are energy molecules of ATP, water, and carbon dioxide.
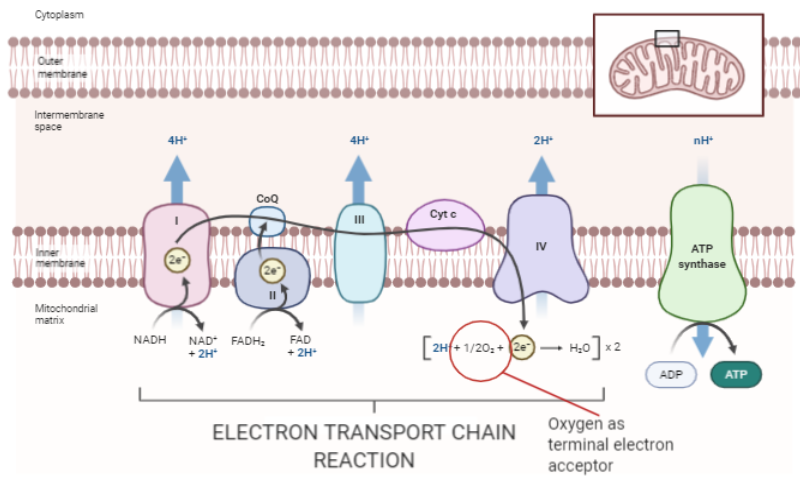
Glycolysis is the first step of aerobic respiration. It happens in the cytoplasm of the cell. Glucose molecules are split into two ATP and two NADH molecules. The second step involves the formation of Acetyl Coenzyme A. 2-carbon acetyl groups are produced from the oxidation of pyruvate. The 2-carbon acetyl group produced will bind to coenzyme A, giving rise to acetyl coenzyme A. The next step is the citric acid cycle or the Krebs cycle. Oxaloacetate combines with acetyl coenzyme A to produce citric acid. The citric acid further produces 1 molecule of ATP, 2 molecules of carbon dioxide, and, NADH and FDA.
The last step involves ETC. It is made up of a series of electron donors and electron acceptors. The electron donors pass the electrons from NADH and FADH to reduce them to water which is an end product of aerobic respiration. Electrons are passed on to more negative acceptors. This process continues until the electrons reach the most electronegative acceptor Oxygen. This is the terminal acceptor. This process results in the formation of a large number of ATP molecules.
So, Oxygen is the compound that is the terminal electron acceptor in aerobic respiration.
Note: A single molecule of glucose in aerobic respiration produces a large amount of energy. It produces a total of 34 ATP molecules. Most bacteria derive energy through aerobic respiration and use oxygen as the terminal electron acceptor.
Complete step by step answer: Aerobic respiration is a process that happens in the presence of oxygen and provides energy to the cells in the form of ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) from glucose. The process comprises various steps including glycolysis, formation of Acetyl coenzyme A, citric acid cycle, and electron transport chain, ETC. The end products of aerobic respiration are energy molecules of ATP, water, and carbon dioxide.

Glycolysis is the first step of aerobic respiration. It happens in the cytoplasm of the cell. Glucose molecules are split into two ATP and two NADH molecules. The second step involves the formation of Acetyl Coenzyme A. 2-carbon acetyl groups are produced from the oxidation of pyruvate. The 2-carbon acetyl group produced will bind to coenzyme A, giving rise to acetyl coenzyme A. The next step is the citric acid cycle or the Krebs cycle. Oxaloacetate combines with acetyl coenzyme A to produce citric acid. The citric acid further produces 1 molecule of ATP, 2 molecules of carbon dioxide, and, NADH and FDA.
The last step involves ETC. It is made up of a series of electron donors and electron acceptors. The electron donors pass the electrons from NADH and FADH to reduce them to water which is an end product of aerobic respiration. Electrons are passed on to more negative acceptors. This process continues until the electrons reach the most electronegative acceptor Oxygen. This is the terminal acceptor. This process results in the formation of a large number of ATP molecules.
So, Oxygen is the compound that is the terminal electron acceptor in aerobic respiration.
Note: A single molecule of glucose in aerobic respiration produces a large amount of energy. It produces a total of 34 ATP molecules. Most bacteria derive energy through aerobic respiration and use oxygen as the terminal electron acceptor.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




