
What is the compound formed between hydrogen and fluorine?
Answer
495k+ views
Hint: Crystalline solids have the capability to exist in different types of solid including molecular solids, ionic solids, metallic solids and covalent solids. Solid compounds in which different molecules combine with each other to form a compound are known as molecular solid.
Complete answer:
Molecular solids are of three different types depending upon the nature of molecules which undergo the combination with another molecule to form a solid.
Non-polar molecular solid is made up of atoms of non-polar element or noble gas atoms like helium argon. Examples are solid helium and solid argon.
Polar molecular solid is made up of atoms of polar elements like chlorine, sulphur etc. these solids are formed by covalent bond formation. Examples are solid $ S{O_2} $ , solid $ N{H_2} $ .
The last category of molecular solids is Hydrogen bonded molecular solids which is made up of a hydrogen atom and another atom by the formation of a hydrogen bond. These solids contain usually a hydrogen atom and more electronegative atom; $ F,O,N. $
Hence when hydrogen atoms combine with fluorine atoms form a hydrogen fluoride $ \left( {HF} \right) $ by the formation of hydrogen bonding.
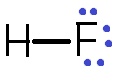
There is some special feature of hydrogen bonded molecular solids includes: -
They exist naturally as a volatile liquid or as a soft solid at room temperature.
They are generally bad conductors of electricity.
Melting and boiling point of these compounds are generally high.
$ \Rightarrow $ $ HF $ is the compound formed between the hydrogen and fluorine atoms.
Note:
Hydrogen fluoride is a fuming gas or liquid preparation which does not possess any characteristic colour and they have a very irritating odor. Hydrogen fluoride is very soluble in water to find a strong acid hydrofluoric acid. This is highly corrosive in nature.
Complete answer:
Molecular solids are of three different types depending upon the nature of molecules which undergo the combination with another molecule to form a solid.
Non-polar molecular solid is made up of atoms of non-polar element or noble gas atoms like helium argon. Examples are solid helium and solid argon.
Polar molecular solid is made up of atoms of polar elements like chlorine, sulphur etc. these solids are formed by covalent bond formation. Examples are solid $ S{O_2} $ , solid $ N{H_2} $ .
The last category of molecular solids is Hydrogen bonded molecular solids which is made up of a hydrogen atom and another atom by the formation of a hydrogen bond. These solids contain usually a hydrogen atom and more electronegative atom; $ F,O,N. $
Hence when hydrogen atoms combine with fluorine atoms form a hydrogen fluoride $ \left( {HF} \right) $ by the formation of hydrogen bonding.
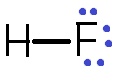
There is some special feature of hydrogen bonded molecular solids includes: -
They exist naturally as a volatile liquid or as a soft solid at room temperature.
They are generally bad conductors of electricity.
Melting and boiling point of these compounds are generally high.
$ \Rightarrow $ $ HF $ is the compound formed between the hydrogen and fluorine atoms.
Note:
Hydrogen fluoride is a fuming gas or liquid preparation which does not possess any characteristic colour and they have a very irritating odor. Hydrogen fluoride is very soluble in water to find a strong acid hydrofluoric acid. This is highly corrosive in nature.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




