
Component of reaction at the hinge in the vertical direction is:
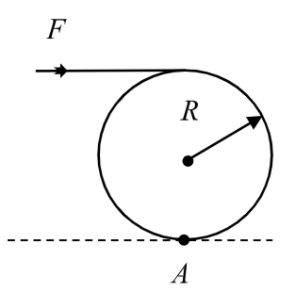

Answer
600.3k+ views
Hint: To solve this question, firstly we will redraw the diagram given and mark all forces acting on the hinge as well as the centre of mass. Then we will consider the rotational motion at a particular moment and see how it is affecting the hinge. Then we will find the component of vertical reaction and the magnitude based on all the forces acting on the hinge.
Complete step-by-step answer:
So, we will re-draw the given diagram and mark all the forces acting on the hinge and the centre of mass.
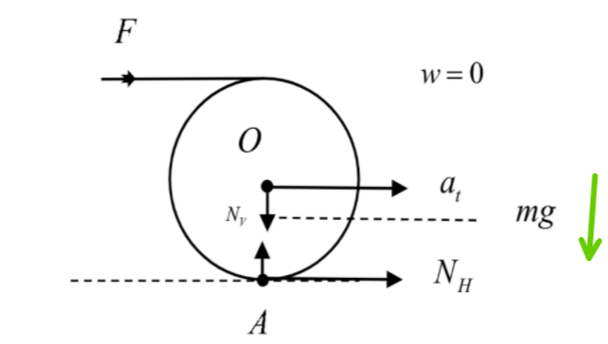
As we drawn in the diagram, if a body is hinged at a point and a force is acting on a body in such a way that the line of force is at some distance from the hinged point, the body will start rotating about the hinged point.
Let the mass of the body be \[m\] and \[{{N}_{V}}\] is the vertical component of the reaction and \[{{N}_{H}}\] be the horizontal component. The weight of the body is acting downwards from the centre of mass as \[mg\].
As the body will be in circular motion a tangential acceleration \[{{a}_{t}}\] and a normal acceleration will be acting on the centre of mass. This acceleration normal to the centre of mass is given by \[{{\omega }^{2}}R\].
But initially the body is at rest so the normal acceleration will be 0.
Now, in the vertical direction, net force acting on the hinge will be \[mg-{{N}_{V}}=0\] as the normal acceleration is zero.
\[\Rightarrow mg= {{N}_{V}}\]
Therefore, the component of vertical reaction on the hinge is obtained as \[{{N}_{V}}=mg\].
Note: We must consider the situation as the body is at rest because when there is rotational motion happening, there will be a component of acceleration present in the vertical direction of the centre of mass. So the magnitude of reaction along vertical direction will not be equal to \[mg\].
Complete step-by-step answer:
So, we will re-draw the given diagram and mark all the forces acting on the hinge and the centre of mass.

As we drawn in the diagram, if a body is hinged at a point and a force is acting on a body in such a way that the line of force is at some distance from the hinged point, the body will start rotating about the hinged point.
Let the mass of the body be \[m\] and \[{{N}_{V}}\] is the vertical component of the reaction and \[{{N}_{H}}\] be the horizontal component. The weight of the body is acting downwards from the centre of mass as \[mg\].
As the body will be in circular motion a tangential acceleration \[{{a}_{t}}\] and a normal acceleration will be acting on the centre of mass. This acceleration normal to the centre of mass is given by \[{{\omega }^{2}}R\].
But initially the body is at rest so the normal acceleration will be 0.
Now, in the vertical direction, net force acting on the hinge will be \[mg-{{N}_{V}}=0\] as the normal acceleration is zero.
\[\Rightarrow mg= {{N}_{V}}\]
Therefore, the component of vertical reaction on the hinge is obtained as \[{{N}_{V}}=mg\].
Note: We must consider the situation as the body is at rest because when there is rotational motion happening, there will be a component of acceleration present in the vertical direction of the centre of mass. So the magnitude of reaction along vertical direction will not be equal to \[mg\].
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

A solution of a substance X is used for white washing class 11 chemistry CBSE




