
What is competitive inhibition. Give an example.
Answer
590.7k+ views
Hint: It is a reversible process in the majority of the cases. It has its major function in the production of pharmaceuticals. It is even seen in normal biological processes in nature.
Complete answer:
Competitive inhibition is a process when a chemical substance abrupts an ongoing chemical reaction by inhibiting the effect of another by bonding or binding. When an inhibitor binds with the target molecule, it competes with the natural substrate of the reaction. It blocks the binding site of the substrate causing a stop to the normal reaction. However this can be controlled by increasing the amount of substrate which increases the possibility of the substrate to bind instead of the inhibitor.
In the majority of the cases the binding of the inhibitor to the target site is a reversible process.
The inhibitor resembles the substrate to properly bond with the target site. In competitive inhibition both the substrate and inhibitor compete with one another to bind on the active enzyme site. This site is the target site which will allow only one of them to bind onto its surface.
This process is commonly used in the pharmaceutical branch.
Example—
A chemotherapy drug, methotrexate is a competitive inhibitor. It is similar to an enzyme folate. It has a similar structure. Folate binds to enzyme dihydrofolate reductase for the synthesis of DNA and RNA. When methotrexate binds instead it abrupts the reaction making it inactive which does not allow any further growth of the cancerous cells.
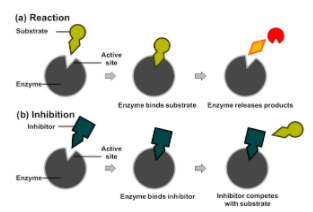
Note: When an inhibitor binds with the target molecule, it competes with the natural substrate of the reaction. It blocks the binding site of the substrate causing a stop to the normal reaction. However this can be controlled by increasing the amount of substrate.
Complete answer:
Competitive inhibition is a process when a chemical substance abrupts an ongoing chemical reaction by inhibiting the effect of another by bonding or binding. When an inhibitor binds with the target molecule, it competes with the natural substrate of the reaction. It blocks the binding site of the substrate causing a stop to the normal reaction. However this can be controlled by increasing the amount of substrate which increases the possibility of the substrate to bind instead of the inhibitor.
In the majority of the cases the binding of the inhibitor to the target site is a reversible process.
The inhibitor resembles the substrate to properly bond with the target site. In competitive inhibition both the substrate and inhibitor compete with one another to bind on the active enzyme site. This site is the target site which will allow only one of them to bind onto its surface.
This process is commonly used in the pharmaceutical branch.
Example—
A chemotherapy drug, methotrexate is a competitive inhibitor. It is similar to an enzyme folate. It has a similar structure. Folate binds to enzyme dihydrofolate reductase for the synthesis of DNA and RNA. When methotrexate binds instead it abrupts the reaction making it inactive which does not allow any further growth of the cancerous cells.

Note: When an inhibitor binds with the target molecule, it competes with the natural substrate of the reaction. It blocks the binding site of the substrate causing a stop to the normal reaction. However this can be controlled by increasing the amount of substrate.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




