
Who coined the term virus?
A. Dmitri Ivanowsky
B. Pasteur
C. M.W. Beijerinck
D. Meyer
Answer
510.3k+ views
Hint: He was a French microbiologist and chemist who is well known for his works and discoveries in the fields of vaccination, pasteurization, and fermentation. He has also provided detailed information about the causes and prevention of microbial diseases.
Complete answer:
The term ‘virus’ had been coined by Louis Pasteur when he was studying the disease Rabies and he categorized the disease as an infectious disease. He was a French microbiologist and chemist and was famous for his works in the field of viral diseases. A virus is a nucleoprotein entity capable of multiplication by taking over the cellular machinery of the host cell without involving growth and division. The multiplication involves the synthesis of parts followed by their assembly. Smallpox and Polio are some well-known prehistoric diseases caused by viruses. Depending upon the host, viruses are called a bacteriophage, coliphage, cyanophage, mycophage, etc. A bacteriophage has been shown below-
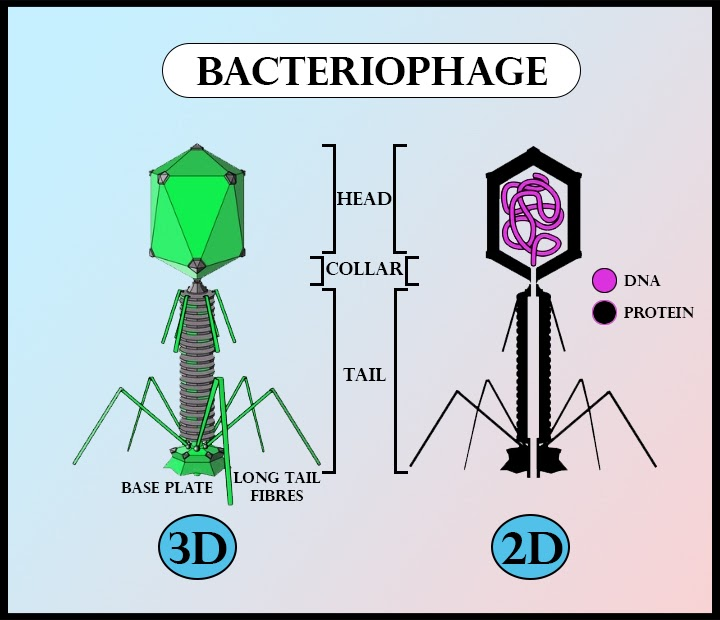
Structurally, a virus consists of an envelope, capsid, nucleoid, and occasionally an enzyme. The protoplasm is absent in viruses and there is no energy storing and utilizing machinery available. Motility and irritability are also absent. The metabolic machinery of the host cell is utilized for the synthesis and assembly of the viral components. The viral particles are inert outside the host cells and in a cell-free environment, they are called virions.
So, the correct answer is ‘Pasteur’.
Note:
Dmitri Ivanowsky was the discoverer of viruses and the founder of virology and discovered a virus when he was investigating for the cause of Tobacco Mosaic disease, which is an infection that causes tobacco leaves to discolor. Beijerinck called viruses as living infectious fluids or contagium vivum fluidum. Adolf Meyer was not related to viruses and was simply a psychiatrist.
Complete answer:
The term ‘virus’ had been coined by Louis Pasteur when he was studying the disease Rabies and he categorized the disease as an infectious disease. He was a French microbiologist and chemist and was famous for his works in the field of viral diseases. A virus is a nucleoprotein entity capable of multiplication by taking over the cellular machinery of the host cell without involving growth and division. The multiplication involves the synthesis of parts followed by their assembly. Smallpox and Polio are some well-known prehistoric diseases caused by viruses. Depending upon the host, viruses are called a bacteriophage, coliphage, cyanophage, mycophage, etc. A bacteriophage has been shown below-

Structurally, a virus consists of an envelope, capsid, nucleoid, and occasionally an enzyme. The protoplasm is absent in viruses and there is no energy storing and utilizing machinery available. Motility and irritability are also absent. The metabolic machinery of the host cell is utilized for the synthesis and assembly of the viral components. The viral particles are inert outside the host cells and in a cell-free environment, they are called virions.
So, the correct answer is ‘Pasteur’.
Note:
Dmitri Ivanowsky was the discoverer of viruses and the founder of virology and discovered a virus when he was investigating for the cause of Tobacco Mosaic disease, which is an infection that causes tobacco leaves to discolor. Beijerinck called viruses as living infectious fluids or contagium vivum fluidum. Adolf Meyer was not related to viruses and was simply a psychiatrist.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




