
Coiling of B DNA duplex is
(a)Left hand
(b)Right hand
(d)Parallel
(d)All of the above
Answer
578.4k+ views
Hint: DNA helix is divided into 3 types based on the structure of the helix. These are A, B, and Z DNA. The most commonly occurring type is the B form of DNA. The structure of this form was shown in the Watson Crick model of DNA helix.
Complete answer:
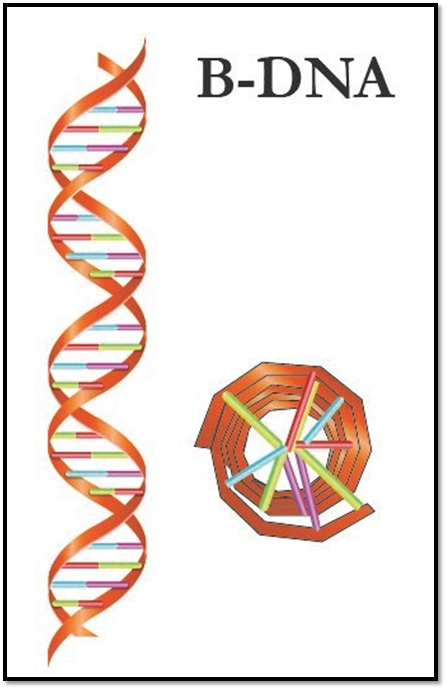
The coiling of the B DNA helix occurs in the right hand. This type of DNA helix has two antiparallel strands. These two run opposite, one from 5'-3' and the other from 3'-5' and coils around the same axis and forms the right-handed helix.
Additional Information:
DNA double helix is the structure formed by double-stranded molecules of nucleic acids. It arises as a consequence of its secondary structure and is a fundamental component in determining the tertiary structure.
In the case of B DNA, the helix is right-handed with 10-15 base pairs per turn. It is the most common double-helical structure in nature. The major groove of B DNA is wider than the minor groove. The backbone of this DNA is made by the sugar-phosphate sugar chain. The nitrogenous base lies perpendicular to it.
The B form of DNA helix was discovered by Watson and Cruck on the X-ray diffraction patterns. Below are some measurements of B DNA:
-0.34nm between each base pair, 3.4 nm per turn, and 10-15 base pair per turn
-1.9nm in diameter.
-3.4A is the vertical rise per base pair
-Rotation per base pair is +36°
Therefore, the correct answer is the right hand.
Note: The other two types of DNA helix are A and Z type. A is also a right-handed helix whereas Z is left-handed. In the case of A, the dehydrated DNA takes an A form and protects the DNA during conditions like desiccation. In the case of Z, the helix winds to the left into a zig-zag pattern. This form was discovered by Andres Wang and Alexander Rich. It is believed that Z DNA plays some kind of role in gene regulation as well.
Complete answer:
The coiling of the B DNA helix occurs in the right hand. This type of DNA helix has two antiparallel strands. These two run opposite, one from 5'-3' and the other from 3'-5' and coils around the same axis and forms the right-handed helix.
Additional Information:
DNA double helix is the structure formed by double-stranded molecules of nucleic acids. It arises as a consequence of its secondary structure and is a fundamental component in determining the tertiary structure.
In the case of B DNA, the helix is right-handed with 10-15 base pairs per turn. It is the most common double-helical structure in nature. The major groove of B DNA is wider than the minor groove. The backbone of this DNA is made by the sugar-phosphate sugar chain. The nitrogenous base lies perpendicular to it.
The B form of DNA helix was discovered by Watson and Cruck on the X-ray diffraction patterns. Below are some measurements of B DNA:
-0.34nm between each base pair, 3.4 nm per turn, and 10-15 base pair per turn
-1.9nm in diameter.
-3.4A is the vertical rise per base pair
-Rotation per base pair is +36°
Therefore, the correct answer is the right hand.
Note: The other two types of DNA helix are A and Z type. A is also a right-handed helix whereas Z is left-handed. In the case of A, the dehydrated DNA takes an A form and protects the DNA during conditions like desiccation. In the case of Z, the helix winds to the left into a zig-zag pattern. This form was discovered by Andres Wang and Alexander Rich. It is believed that Z DNA plays some kind of role in gene regulation as well.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




