
Classify the isomers of alcohol in ${{C}_{5}}{{H}_{12}}O$ as primary, secondary, and tertiary alcohols.
Answer
577.8k+ views
Hint: Primary alcohols are those compounds in which the carbon that contains the alcohol group is attached to further one carbon atom. Secondary alcohols are those compounds in which the carbon that contains the alcohol group is attached to further two carbon atoms. Tertiary alcohols are those compounds in which the carbon that contains the alcohol group is attached to further three carbon atoms.
Complete step by step answer:
So the compound has formula ${{C}_{5}}{{H}_{12}}O$, this has five carbon atoms. This compound has 8 isomers in which we can classify them as primary, secondary, and tertiary alcohols.
Pentan-1-ol, this is a straight-chain compound, and the carbon that contains the alcohol group is attached to further one carbon atom so it is primary. The structure is given below:
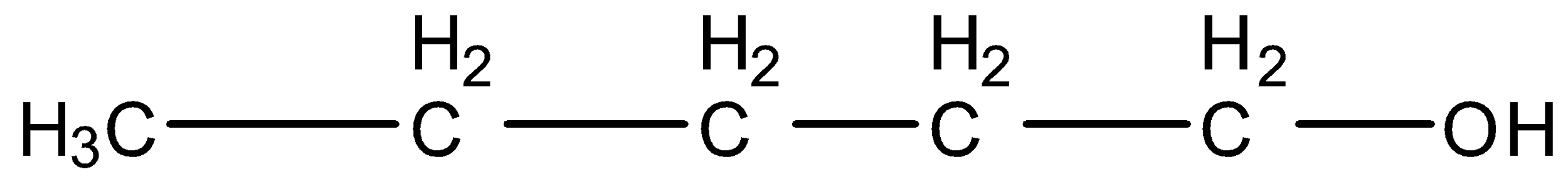
2-Methyl butanol, this is a branched form of ${{C}_{5}}{{H}_{12}}O$ and the carbon that contains the alcohol group is attached to further one carbon atom so it is primary. The structure is given below:
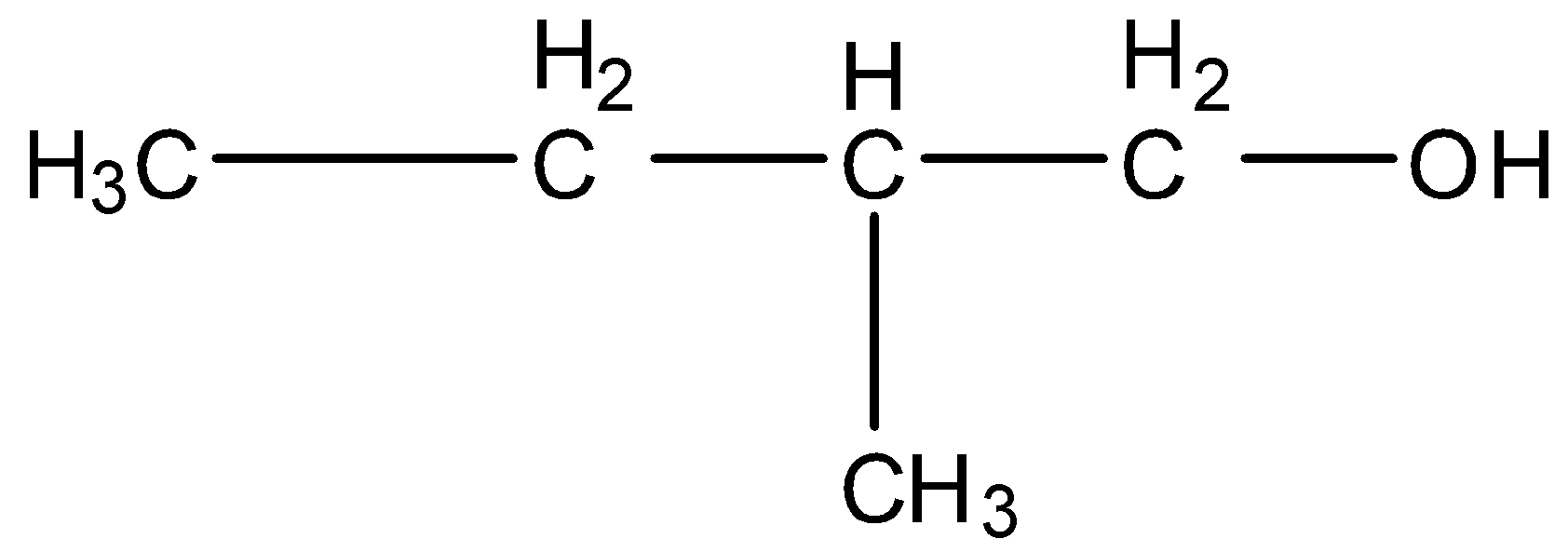
3-Methyl butanol, this is a branched form of ${{C}_{5}}{{H}_{12}}O$ and the carbon that contains the alcohol group is attached to further one carbon atom so it is primary. The structure is given below:
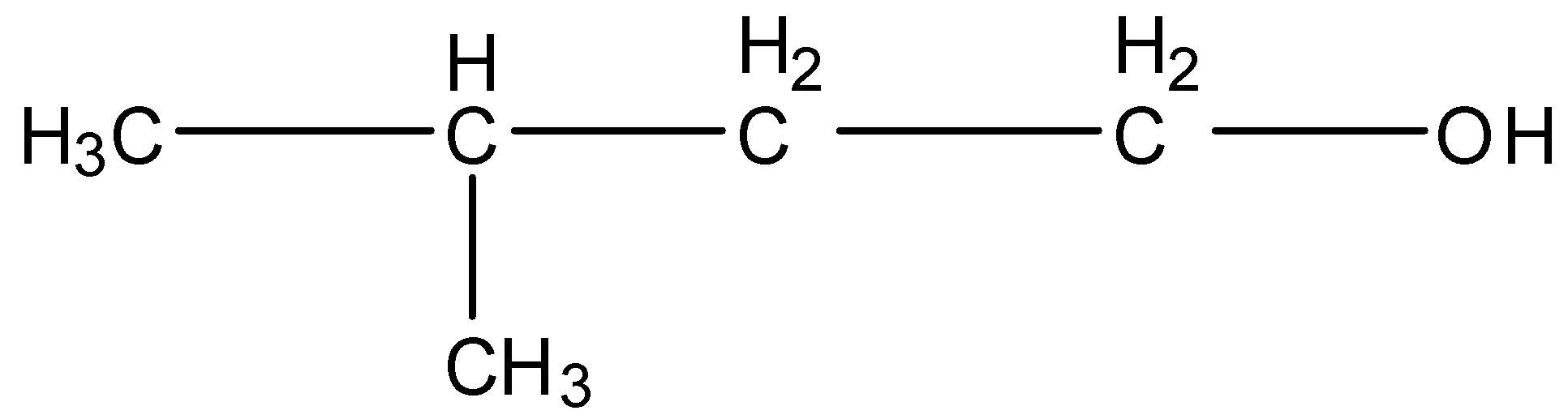
2,2-Dimethyl propanol, this is a branched form of ${{C}_{5}}{{H}_{12}}O$ and the carbon that contains the alcohol group is attached to further one carbon atom so it is primary. The structure is given below:
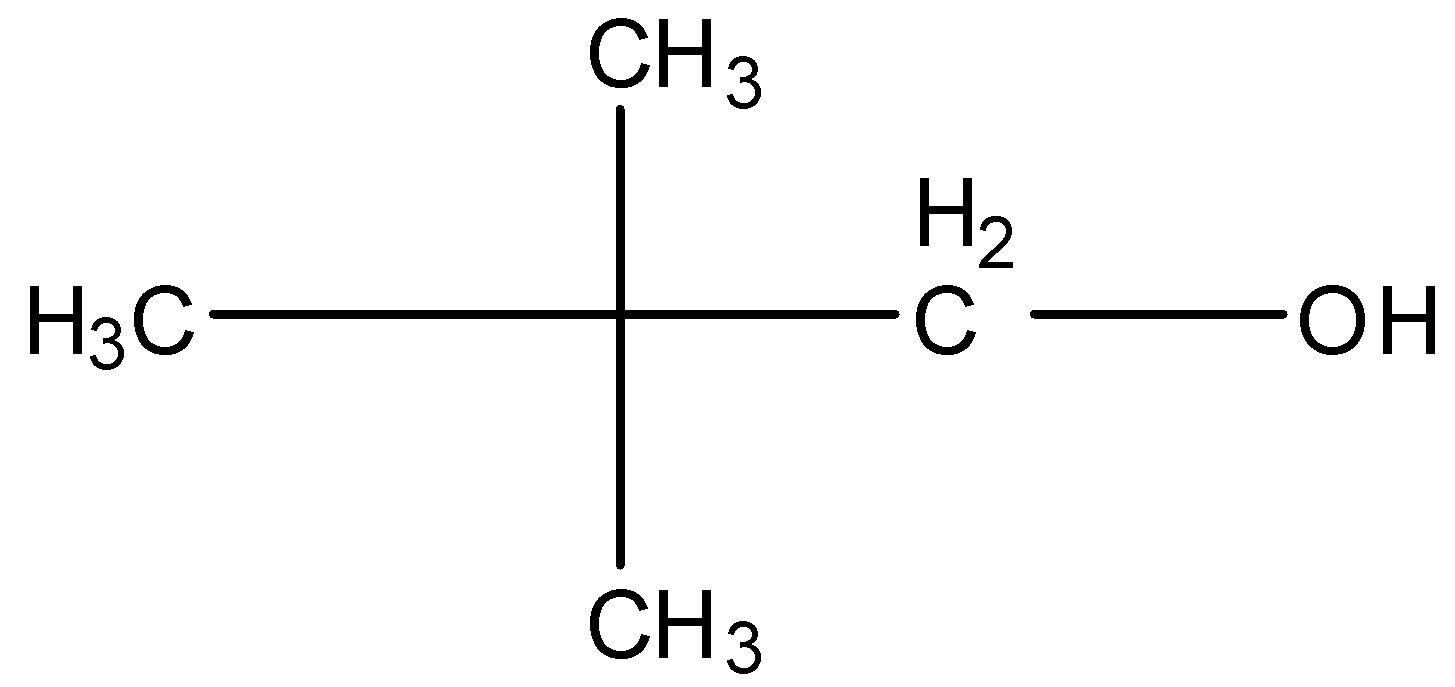
Pentan-2-ol, this is a straight-chain with alcohol at the second position, and the carbon that contains the alcohol group is attached to further two carbon atoms so it is secondary. The structure is given below:
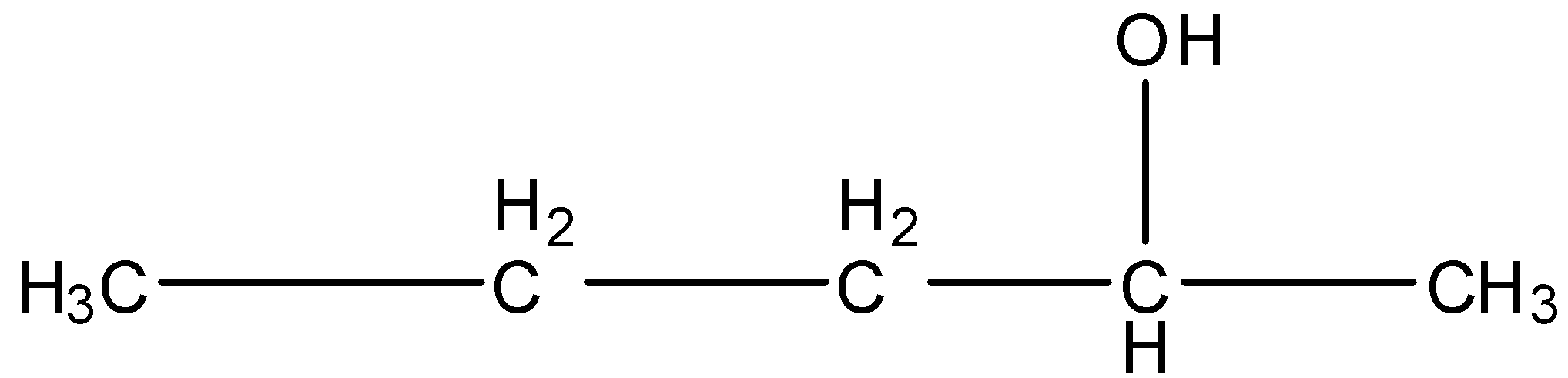
3-Methyl-2-butanol, this is a branched form, and the carbon that contains the alcohol group is attached to further two carbon atoms so it is secondary. The structure is given below:
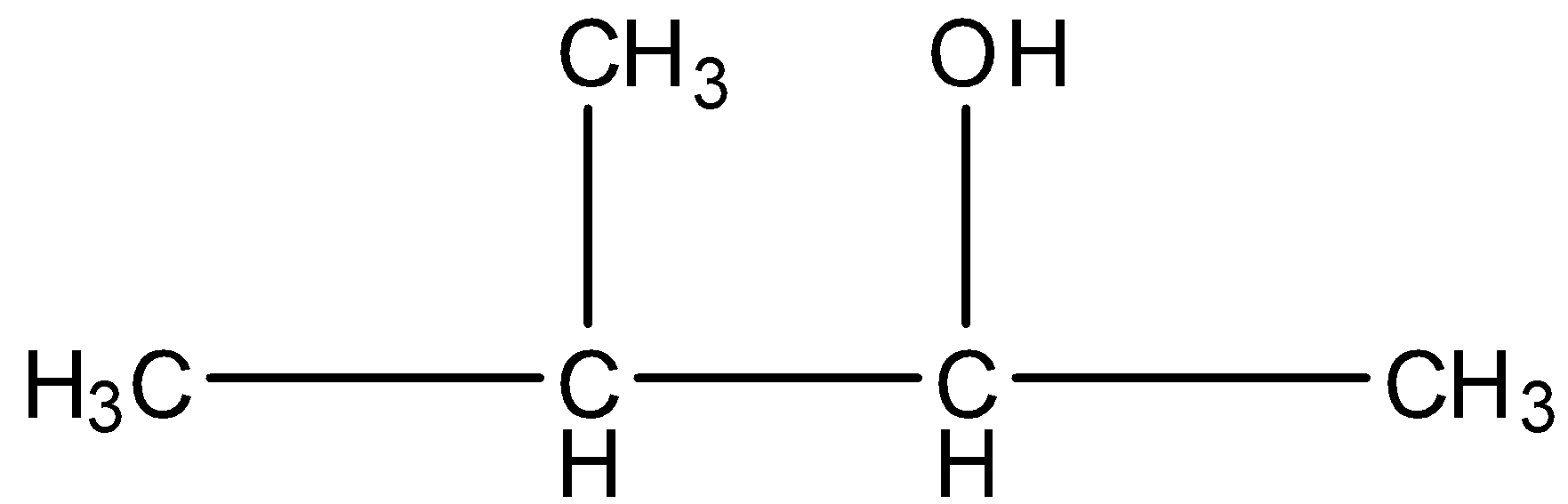
Pentan-3-ol, this is a straight-chain with alcohol at the third position, and the carbon that contains the alcohol group is attached to further two carbon atoms so it is secondary. The structure is given below:
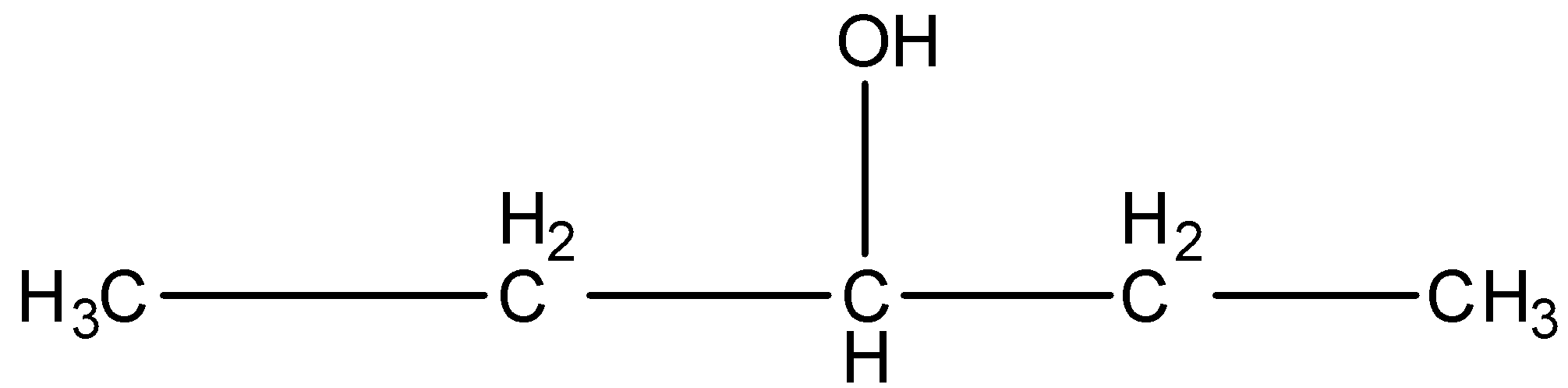
2-Methyl-2-butanol, this is a branched form, and the carbon that contains the alcohol group is attached to further three carbon atoms so it is tertiary. The structure is given below:
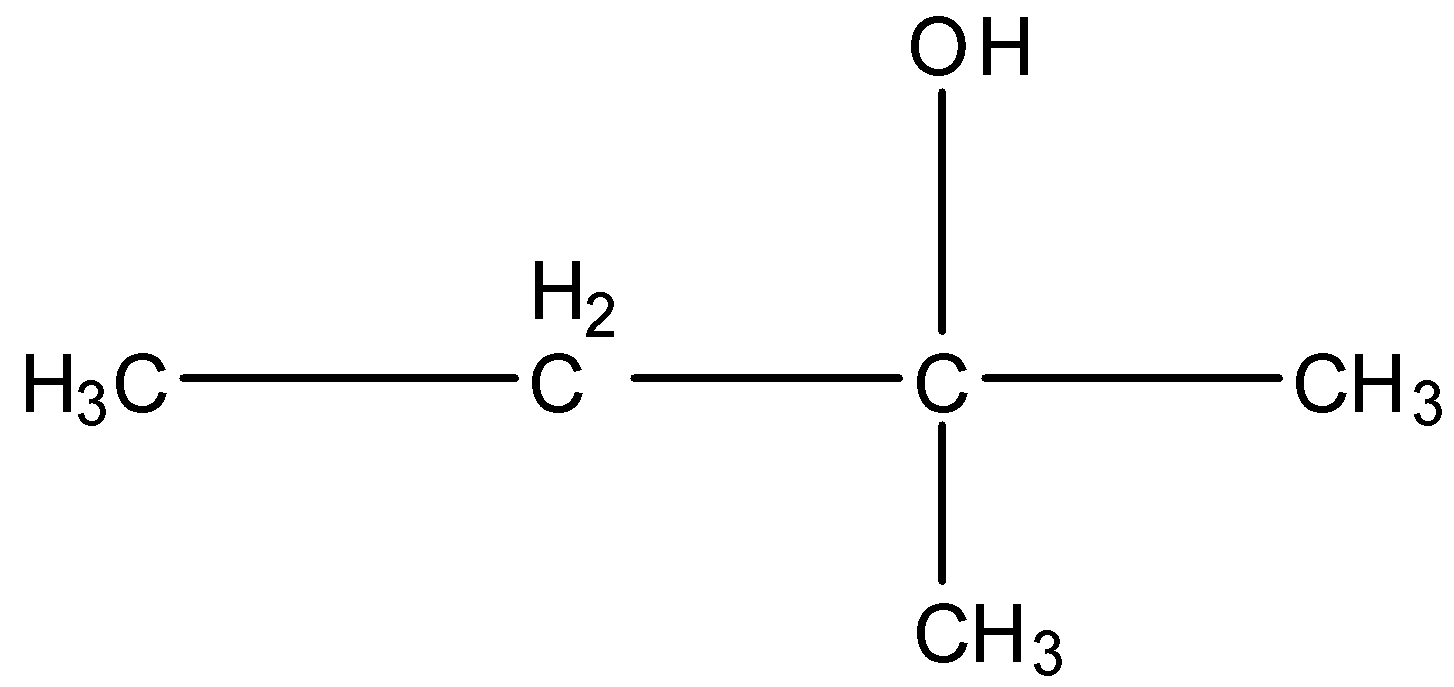
Note: You may think that the alcohol attached to the number of carbon atoms will classify them as primary, secondary, and tertiary, but it is the number of carbon atoms further attached to the carbon atom having an alcohol group.
Complete step by step answer:
So the compound has formula ${{C}_{5}}{{H}_{12}}O$, this has five carbon atoms. This compound has 8 isomers in which we can classify them as primary, secondary, and tertiary alcohols.
Pentan-1-ol, this is a straight-chain compound, and the carbon that contains the alcohol group is attached to further one carbon atom so it is primary. The structure is given below:
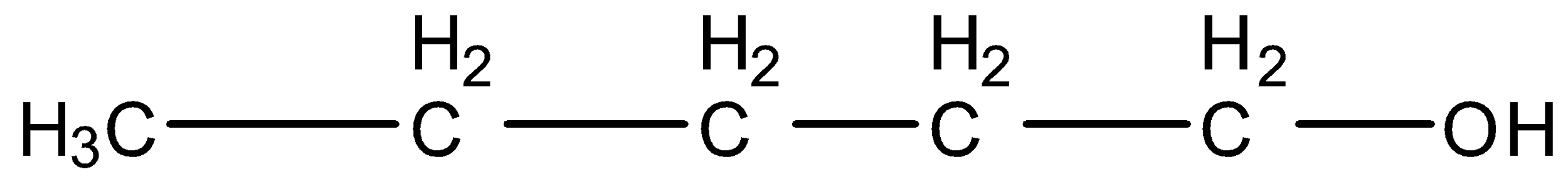
2-Methyl butanol, this is a branched form of ${{C}_{5}}{{H}_{12}}O$ and the carbon that contains the alcohol group is attached to further one carbon atom so it is primary. The structure is given below:

3-Methyl butanol, this is a branched form of ${{C}_{5}}{{H}_{12}}O$ and the carbon that contains the alcohol group is attached to further one carbon atom so it is primary. The structure is given below:

2,2-Dimethyl propanol, this is a branched form of ${{C}_{5}}{{H}_{12}}O$ and the carbon that contains the alcohol group is attached to further one carbon atom so it is primary. The structure is given below:

Pentan-2-ol, this is a straight-chain with alcohol at the second position, and the carbon that contains the alcohol group is attached to further two carbon atoms so it is secondary. The structure is given below:

3-Methyl-2-butanol, this is a branched form, and the carbon that contains the alcohol group is attached to further two carbon atoms so it is secondary. The structure is given below:

Pentan-3-ol, this is a straight-chain with alcohol at the third position, and the carbon that contains the alcohol group is attached to further two carbon atoms so it is secondary. The structure is given below:

2-Methyl-2-butanol, this is a branched form, and the carbon that contains the alcohol group is attached to further three carbon atoms so it is tertiary. The structure is given below:

Note: You may think that the alcohol attached to the number of carbon atoms will classify them as primary, secondary, and tertiary, but it is the number of carbon atoms further attached to the carbon atom having an alcohol group.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE




