
When cis but-2-ene is treated with $B{{r}_{2}}$ in $CC{{l}_{4}}$ medium, the product formed will be
a) (2R, 3S) dibromobutane
b) (2R, 3R) dibromobutane
c) (2S, 3S) dibromobutane
d) mixture of (2R, 3R) and (2S, 3S) dibromobutane
Answer
533.1k+ views
Hint: Reaction of alkene with halogens in $CC{{l}_{4}}$ medium is an anti-addition reaction in which the halide ions will add opposite to the geometry of the reactant. In case of cis but-2-ene, halide ions will add in opposite faces as reactant is cis which means on same side.
Complete answer:
In this reaction, cis but-2-ene will act as nucleophile and attack on $B{{r}_{2}}$which leads to the formation of non- classical carbocation. Since the medium is a non-polar solvent hence other parts of $B{{r}_{2}}$ will act as nucleophiles and attack from the opposite side of the non-classical carbocation and we will get our desired product.
-Attack by alkene on $B{{r}_{2}}$:-
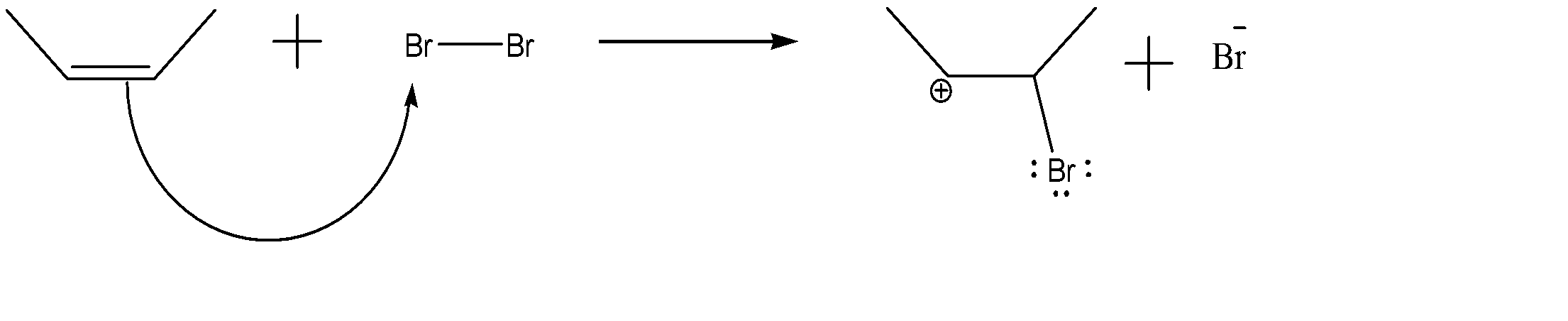
As we can see, alkene acts as a nucleophile and attacks the electrophile ($B{{r}_{2}}$). This step is the rate determining step of the reaction.
-Formation of non-classical carbocation:-
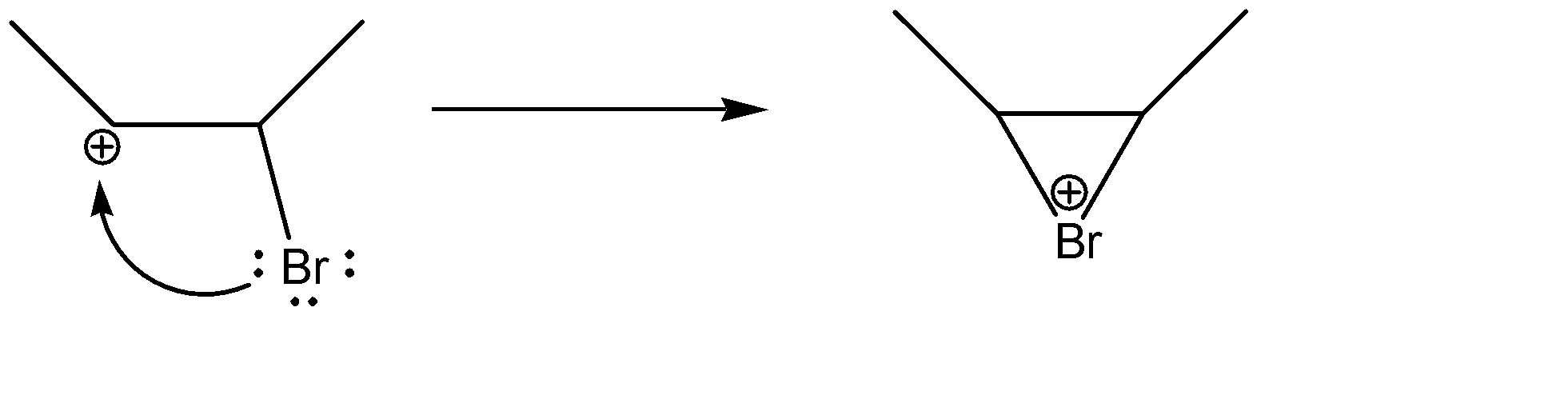
As soon as carbocation forms on carbon, bromine gives its lone pair to it, hence forming the non-classical carbocation (which is not a complete carbocation).
-Attack of nucleophile to form our final product:-
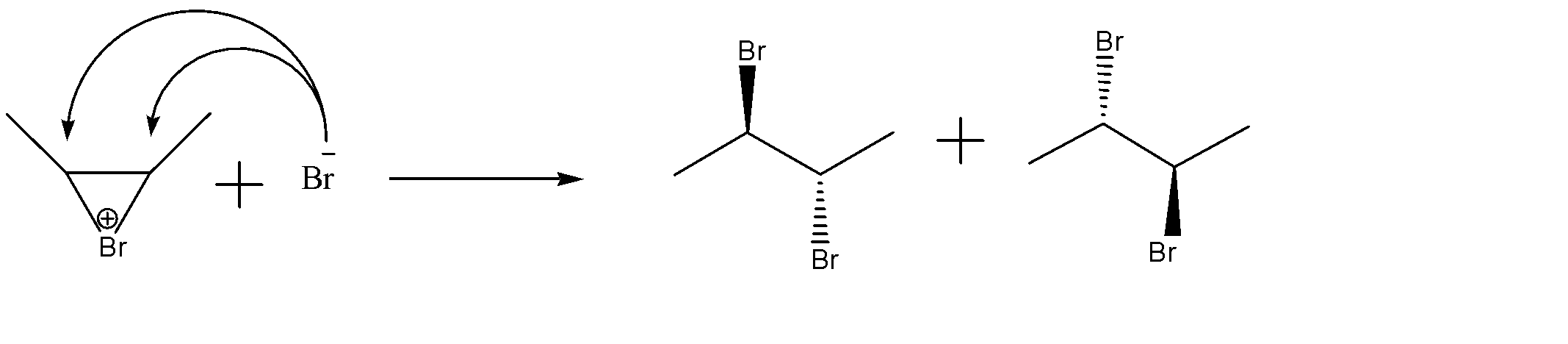
Since no other nucleophile is present other than $B{{r}^{-}}$ ion, it can attack on both the carbon from the opposite side of the other bromine atom. This way the anti reaction takes place.
-The product formed is an enantiomeric pair as they are non-superimposable mirror images of each other. The pair is (2R, 3R) and (2S, 3S) dibromobutane.
Hence the correct answer is: d) mixture of (2R, 3R) and (2S, 3S) dibromobutane.
Note:
In the final solution both enantiomers will be present in equal amounts hence we will obtain a racemic mixture.
-If we are given polar solvent instead of non-polar solvent, than the ions of polar solvent will act as nucleophile and will attack the carbocation before $B{{r}^{-}}$ion could, as in actual reaction it is weakly attached to the non-classical carbocation for a while due to which other ions get to attack easily.
Complete answer:
In this reaction, cis but-2-ene will act as nucleophile and attack on $B{{r}_{2}}$which leads to the formation of non- classical carbocation. Since the medium is a non-polar solvent hence other parts of $B{{r}_{2}}$ will act as nucleophiles and attack from the opposite side of the non-classical carbocation and we will get our desired product.
-Attack by alkene on $B{{r}_{2}}$:-

As we can see, alkene acts as a nucleophile and attacks the electrophile ($B{{r}_{2}}$). This step is the rate determining step of the reaction.
-Formation of non-classical carbocation:-

As soon as carbocation forms on carbon, bromine gives its lone pair to it, hence forming the non-classical carbocation (which is not a complete carbocation).
-Attack of nucleophile to form our final product:-

Since no other nucleophile is present other than $B{{r}^{-}}$ ion, it can attack on both the carbon from the opposite side of the other bromine atom. This way the anti reaction takes place.
-The product formed is an enantiomeric pair as they are non-superimposable mirror images of each other. The pair is (2R, 3R) and (2S, 3S) dibromobutane.
Hence the correct answer is: d) mixture of (2R, 3R) and (2S, 3S) dibromobutane.
Note:
In the final solution both enantiomers will be present in equal amounts hence we will obtain a racemic mixture.
-If we are given polar solvent instead of non-polar solvent, than the ions of polar solvent will act as nucleophile and will attack the carbocation before $B{{r}^{-}}$ion could, as in actual reaction it is weakly attached to the non-classical carbocation for a while due to which other ions get to attack easily.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




