
Choose the correct option, if $BL$ and $CM$ are the median of a triangle $ABC$, right angled at $A$, then which one is true
$
{\text{A}}{\text{.4}}\left( {B{L^2} + C{M^2}} \right) = 5B{C^2} \\
{\text{B}}{\text{.4}}\left( {B{L^2} + C{M^2}} \right) = 3B{C^2} \\
{\text{C}}{\text{.2}}\left( {B{L^2} + C{M^2}} \right) = 5B{C^2} \\
{\text{D}}{\text{.2}}\left( {B{L^2} + C{M^2}} \right) = 3B{C^2} \\
$
Answer
594.6k+ views
Hint: Here, at first we have to write what is given to us in the question and the most important hint is to remember the basic properties of a right angles triangle and medians. Usage of Pythagoras theorem is required and we can find the desired answer using this theorem alone.
Complete step by step answer:
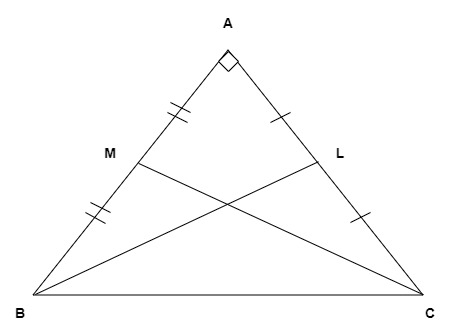
Given- ${\text{BL and CM}}$ are median on ${\text{AC and AB}}$ respectively.
In $\Delta {\text{ABC}}$, by using Pythagoras theorem
${\text{B}}{{\text{C}}^2} = {\text{A}}{{\text{B}}^2}{\text{ + A}}{{\text{C}}^2}$…. (1)
In $\Delta {\text{ABL}}$, by using Pythagoras theorem
$
{\text{B}}{{\text{L}}^2}{\text{ = A}}{{\text{L}}^2}{\text{ + A}}{{\text{B}}^2} \\
{\text{B}}{{\text{L}}^2}{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{{\text{A}}{{\text{C}}^2}}}{4} + {\text{A}}{{\text{B}}^2} \\
$
Since ${\text{BL}}$ is the median on ${\text{AC}}$
Then ${\text{AL = }}\dfrac{{{\text{AC}}}}{2}$
Solving the above equation, we get
$4{\text{B}}{{\text{L}}^2} = {\text{A}}{{\text{C}}^2} + 4{\text{A}}{{\text{B}}^2}$ …. (2)
In $\Delta {\text{AMC}}$, by using Pythagoras theorem
$
{\text{C}}{{\text{M}}^2}{\text{ = A}}{{\text{C}}^2}{\text{ + A}}{{\text{M}}^2} \\
{\text{C}}{{\text{M}}^2}{\text{ = A}}{{\text{C}}^2}{\text{ + }}\dfrac{{{\text{A}}{{\text{B}}^2}}}{4} \\
$
Since ${\text{CM}}$ is median on ${\text{AB}}$
Then ${\text{AM = }}\dfrac{{{\text{AB}}}}{2}$
Solving the equation, we get
${\text{4C}}{{\text{M}}^2}{\text{ = 4A}}{{\text{C}}^2}{\text{ + A}}{{\text{B}}^2}$ …. (3)
Adding equations (2) and (3), we get
${\text{4B}}{{\text{L}}^2}{\text{ + 4C}}{{\text{M}}^2}{\text{ = A}}{{\text{C}}^2}{\text{ + 4A}}{{\text{B}}^2}{\text{ + 4A}}{{\text{C}}^2}{\text{ + A}}{{\text{B}}^2}$
Solving it further
$
{\text{4B}}{{\text{L}}^2}{\text{ + 4C}}{{\text{M}}^2}{\text{ = 5A}}{{\text{C}}^2}{\text{ + 5A}}{{\text{B}}^2} \\
4\left( {{\text{B}}{{\text{L}}^2}{\text{ + C}}{{\text{M}}^2}} \right) = 5\left( {{\text{A}}{{\text{C}}^2}{\text{ + A}}{{\text{B}}^2}} \right) \\
\\
$
$4\left( {{\text{B}}{{\text{L}}^2}{\text{ + C}}{{\text{M}}^2}} \right) = 5{\text{B}}{{\text{C}}^2}$…. (Using (1))
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: As the medians are given in the question we can use the Pythagoras theorem to solve it as well as we add the two equations where we find median values using the theorem and then check the options given and select the right answer.
Pythagoras Theorem applies to a right angled triangle and is as follows:
${\left( {{\text{Hypotenuse}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\text{Base}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{\text{Perpendicular}}} \right)^2}$ .
Complete step by step answer:

Given- ${\text{BL and CM}}$ are median on ${\text{AC and AB}}$ respectively.
In $\Delta {\text{ABC}}$, by using Pythagoras theorem
${\text{B}}{{\text{C}}^2} = {\text{A}}{{\text{B}}^2}{\text{ + A}}{{\text{C}}^2}$…. (1)
In $\Delta {\text{ABL}}$, by using Pythagoras theorem
$
{\text{B}}{{\text{L}}^2}{\text{ = A}}{{\text{L}}^2}{\text{ + A}}{{\text{B}}^2} \\
{\text{B}}{{\text{L}}^2}{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{{\text{A}}{{\text{C}}^2}}}{4} + {\text{A}}{{\text{B}}^2} \\
$
Since ${\text{BL}}$ is the median on ${\text{AC}}$
Then ${\text{AL = }}\dfrac{{{\text{AC}}}}{2}$
Solving the above equation, we get
$4{\text{B}}{{\text{L}}^2} = {\text{A}}{{\text{C}}^2} + 4{\text{A}}{{\text{B}}^2}$ …. (2)
In $\Delta {\text{AMC}}$, by using Pythagoras theorem
$
{\text{C}}{{\text{M}}^2}{\text{ = A}}{{\text{C}}^2}{\text{ + A}}{{\text{M}}^2} \\
{\text{C}}{{\text{M}}^2}{\text{ = A}}{{\text{C}}^2}{\text{ + }}\dfrac{{{\text{A}}{{\text{B}}^2}}}{4} \\
$
Since ${\text{CM}}$ is median on ${\text{AB}}$
Then ${\text{AM = }}\dfrac{{{\text{AB}}}}{2}$
Solving the equation, we get
${\text{4C}}{{\text{M}}^2}{\text{ = 4A}}{{\text{C}}^2}{\text{ + A}}{{\text{B}}^2}$ …. (3)
Adding equations (2) and (3), we get
${\text{4B}}{{\text{L}}^2}{\text{ + 4C}}{{\text{M}}^2}{\text{ = A}}{{\text{C}}^2}{\text{ + 4A}}{{\text{B}}^2}{\text{ + 4A}}{{\text{C}}^2}{\text{ + A}}{{\text{B}}^2}$
Solving it further
$
{\text{4B}}{{\text{L}}^2}{\text{ + 4C}}{{\text{M}}^2}{\text{ = 5A}}{{\text{C}}^2}{\text{ + 5A}}{{\text{B}}^2} \\
4\left( {{\text{B}}{{\text{L}}^2}{\text{ + C}}{{\text{M}}^2}} \right) = 5\left( {{\text{A}}{{\text{C}}^2}{\text{ + A}}{{\text{B}}^2}} \right) \\
\\
$
$4\left( {{\text{B}}{{\text{L}}^2}{\text{ + C}}{{\text{M}}^2}} \right) = 5{\text{B}}{{\text{C}}^2}$…. (Using (1))
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: As the medians are given in the question we can use the Pythagoras theorem to solve it as well as we add the two equations where we find median values using the theorem and then check the options given and select the right answer.
Pythagoras Theorem applies to a right angled triangle and is as follows:
${\left( {{\text{Hypotenuse}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\text{Base}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{\text{Perpendicular}}} \right)^2}$ .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




