
Chlorobenzene on reaction with acetyl chloride in presence of anhydrous$AlC{{l}_{3}}$ gives major product of:
(A) 2 - chloro acetanilide
(B) 2 - chloro acetophenone
(C) 3 - chloro acetanilide
(D) 4 - chloro acetophenone
Answer
593.1k+ views
Hint: The above reaction is Friedel Craft acylation reaction. Acetyl Chloride generates the acylium ion which acts as the electrophile. After this you have to follow the rules of electrophilic aromatic substitution. The chlorine atom acts as the directing atom.
Complete step by step answer:
Electrophilic aromatic substitution also called E.A.S is an organic reaction in which an atom gets attached to the present aromatic system and replaces the hydrogen atom present.
Some of the most important and known Electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions are:
- Aromatic nitration
- Aromatic halogenation
- Aromatic sulfonation
- Friedel-Crafts acylation
- Friedel-Crafts alkylation
We will now draw the structure of chlorobenzene and then write its reaction with acetyl chloride.
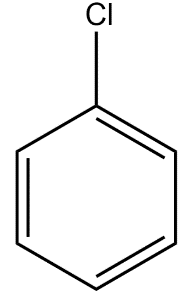
We will now generate the electrophile from the reacting acetyl chloride molecule in the presence of anhydrous aluminium chloride.
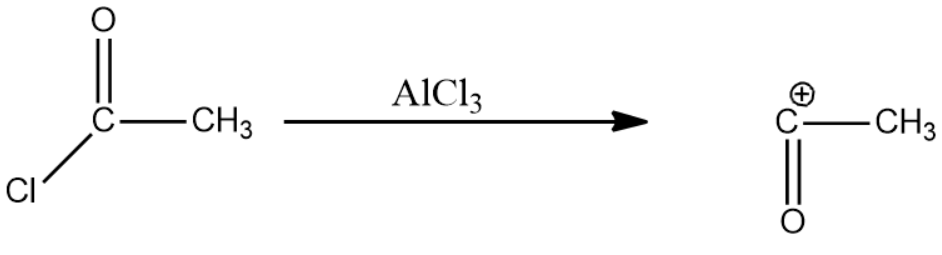
The electrophile generated is the acylium ion. Acylium ion now attaches to the aromatic ring in accordance with the reaction mechanism defined by Friedel-Crafts acylation reaction.
The reaction goes as follows:
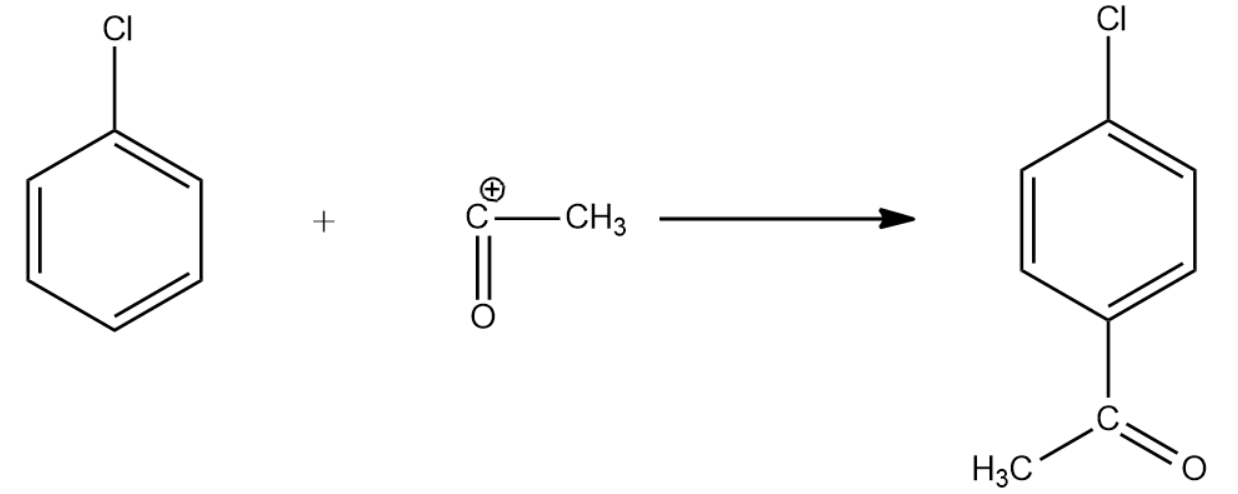
The IUPAC name for the above product is 4-chloroacetophenone.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: In the above reaction we use anhydrous aluminium chloride to generate an electrophile. Aluminium chloride is a Lewis acid and needs electrons to fill its vacant orbital. This is the reason why the chlorine atom of acetyl chloride attaches to aluminium atoms thereby generating the acylium ion which acts as the incoming electrophile to chlorobenzene.
Complete step by step answer:
Electrophilic aromatic substitution also called E.A.S is an organic reaction in which an atom gets attached to the present aromatic system and replaces the hydrogen atom present.
Some of the most important and known Electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions are:
- Aromatic nitration
- Aromatic halogenation
- Aromatic sulfonation
- Friedel-Crafts acylation
- Friedel-Crafts alkylation
We will now draw the structure of chlorobenzene and then write its reaction with acetyl chloride.

We will now generate the electrophile from the reacting acetyl chloride molecule in the presence of anhydrous aluminium chloride.

The electrophile generated is the acylium ion. Acylium ion now attaches to the aromatic ring in accordance with the reaction mechanism defined by Friedel-Crafts acylation reaction.
The reaction goes as follows:

The IUPAC name for the above product is 4-chloroacetophenone.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: In the above reaction we use anhydrous aluminium chloride to generate an electrophile. Aluminium chloride is a Lewis acid and needs electrons to fill its vacant orbital. This is the reason why the chlorine atom of acetyl chloride attaches to aluminium atoms thereby generating the acylium ion which acts as the incoming electrophile to chlorobenzene.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




